Abstract
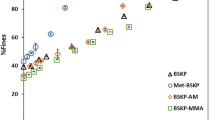
A simple, fully aqueous grafting-through polymerization approach was employed to apply various polymeric surface modifications to bleached softwood kraft pulp (BSKP). Poly(acrylamide), poly(acrylic acid), poly(oligo(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate), poly(methyl methacrylate), and poly(dimethyl itaconate) were chemically attached to the BSKP fiber surface, as confirmed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. The modified and unmodified BSKP samples were fibrillated and evaluated using optical fiber length analysis and scanning electron microscopy analysis. Furthermore, the effect of the polymeric surface modifications before and after fibrillation on the filtration water retention value (WRVfiltration) was studied. While the polymeric surface modifications had little effect on the percentage of fines and width distribution of nanosized fibrils, they significantly reduced the WRVfiltration after fibrillation. The polymeric surface modifications were also found to affect the morphology after drying and grinding.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Electronic supplementary data is available online at the journal’s webpage (https://www.springer.com/journal/10570).
References
Abdul Khalil HPS, Davoudpour Y, Nazrul Islam M, Mustapha A, Sudesh K, Dungani R, Jawaid M (2014) Production and modification of nanofibrillated cellulose using various mechanical processes: a review. Carbohydr Polym 99:649–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.08.069
Ali N, Zhang Q, Liu Z, Li F, Lu M, Fang X (2020) Emerging technologies for the pretreatment of lignocellulosic materials for bio-based products. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104:455–473. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-10158-w
Amini E, Hafez I, Tajvidi M, Bousfield DW (2020) Cellulose and lignocellulose nanofibril suspensions and films: a comparison. Carbohydr Polym 250:117011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117011
Ang S, Haritos V, Batchelor W (2019) Effect of refining and homogenization on nanocellulose fiber development, sheet strength and energy consumption. Cellulose 26:4767–4786. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02400-5
Asada C, Sasaki Y, Nakamura Y (2020) Production of eco-refinery pulp from moso bamboo using steam treatment followed by milling treatment. Waste Biomass Valoriz 11:6139–6146. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-019-00847-y
Bhutto AW, Qureshi K, Harijan K, Abro R, Abbas T, Bazmi AA, Karim S, Yu G (2017) Insight into progress in pre-treatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Energy 122:724–745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.01.005
Bian H, Luo J, Wang R, Zhou X, Ni S, Shi R, Fang G, Dai H (2019) Recyclable and reusable maleic acid for efficient production of cellulose nanofibrils with stable performance. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7:20022–20031. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b05766
Carrillo CA, Laine J, Rojas OJ (2014) Microemulsion systems for fiber deconstruction into cellulose nanofibrils. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:22622–22627. https://doi.org/10.1021/am5067332
Fein K, Bousfield DW, Gramlich WM (2020a) The influence of versatile thiol-norbornene modifications to cellulose nanofibers on rheology and film properties. Carbohydr Polym 230:115672. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115672
Fein K, Bousfield DW, Gramlich WM (2020b) Thiol-norbornene reactions to improve natural rubber dispersion in cellulose nanofiber coatings. Carbohydr Polym 250:117001. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117001
Fein K, Bousfield DW, Gramlich WM (2021) Processing effects on structure, strength, and barrier properties of refiner-produced cellulose nanofibril layers. ACS Appl Polym Mater 3:3666–3678. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsapm.1c00620
Gu F, Wang W, Cai Z, Xue F, Jin Y, Zhu JY (2018) Water retention value for characterizing fibrillation degree of cellulosic fibers at micro and nanometer scales. Cellulose 25:2861–2871. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1765-8
Haldar D, Purkait MK (2021) A review on the environment-friendly emerging techniques for pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass: mechanistic insight and advancements. Chemosphere 264:128523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128523
Hassan SS, Williams GA, Jaiswal AK (2018) Emerging technologies for the pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour Technol 262:310–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.04.099
Hongrattanavichit I, Aht-Ong D (2020) Nanofibrillation and characterization of sugarcane bagasse agro-waste using water-based steam explosion and high-pressure homogenization. J Clean Prod 277:123471. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123471
Hu C, Zhao Y, Li K, Zhu JY, Gleisner R (2015) Optimizing cellulose fibrillation for the production of cellulose nanofibrils by a disk grinder. Holzforschung 69:993–1000. https://doi.org/10.1515/hf-2014-0219
Ishak NAM, Khalil I, Abdullah FZ, Julkapli NM (2020) A correlation on ultrasonication with nanocrystalline cellulose characteristics. Carbohydr Polym 246:116553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116553
Isogai A (2022) TEMPO-catalyzed oxidation of polysaccharides. Polym J 54:387–402. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41428-021-00580-1
Isogai A, Bergström L (2018) Preparation of cellulose nanofibers using green and sustainable chemistry. Curr Opin Green Sustain Chem 12:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cogsc.2018.04.008
Isogai A, Zhou Y (2019) Diverse nanocelluloses prepared from TEMPO-oxidized wood cellulose fibers: nanonetworks, nanofibers, and nanocrystals. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 23:101–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cossms.2019.01.001
Isogai A, Saito T, Fukuzumi H (2011) TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers. Nanoscale 3:71–85. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0NR00583E
Kelly PV, Cheng P, Gardner DJ, Gramlich WM (2021) Aqueous polymer modification of cellulose nanofibrils by grafting-through a reactive methacrylate group. Macromol Rapid Commun 42:2000531. https://doi.org/10.1002/marc.202000531
Kumar AK, Sharma S (2017) Recent updates on different methods of pretreatment of lignocellulosic feedstocks: a review. Bioresour Bioprocess 4:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40643-017-0137-9
Kumar V, Elfving A, Koivula H, Bousfield D, Toivakka M (2016) Roll-to-roll processed cellulose nanofiber coatings. Ind Eng Chem Res 55:3603–3613. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b00417
Lahtinen P, Liukkonen S, Pere J, Sneck A, Kangas H (2014) A comparative study of fibrillated fibers from different mechanical and chemical pulps. Bioresources 9:2115–2127
Lee H, Mani S (2017) Mechanical pretreatment of cellulose pulp to produce cellulose nanofibrils using a dry grinding method. Ind Crops Prod 104:179–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.04.044
Mondal S (2018) Review on nanocellulose polymer nanocomposites. Polym Plast Technol Eng 57:1377–1391. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602559.2017.1381253
Norrrahim MNF, Ariffin H, Yasim-Anuar TAT, Ghaemi F, Hassan MA, Ibrahim NA, Ngee JLH, Yunus WMZW (2018) Superheated steam pretreatment of cellulose affects its electrospinnability for microfibrillated cellulose production. Cellulose 25:3853–3859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1859-3
Rahman MM, Khan MA (2007) Surface treatment of coir (cocos nucifera) fibers and its influence on the fibers’ physico-mechanical properties. Compos Sci Technol 67:2369–2376. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2007.01.009
Roy R, Rahman MS, Raynie DE (2020) Recent advances of greener pretreatment technologies of lignocellulose. Curr Res Green Sustain Chem 3:100035. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crgsc.2020.100035
Sandas SE, Salminen PJ, Eklund DE (1989) Measuring the water retention of coating colors. Tappi J 72:207–210
Sarkanen KV (1962) The chemistry of delignification in pulp bleaching. Pure Appl Chem 5:219–231. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac196205010219
Sarker TR, Pattnaik F, Nanda S, Dalai AK, Meda V, Naik S (2021) Hydrothermal pretreatment technologies for lignocellulosic biomass: a review of steam explosion and subcritical water hydrolysis. Chemosphere 284:131372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131372
Sharma N, Bhardwaj NK, Singh RBP (2020) Environmental issues of pulp bleaching and prospects of peracetic acid pulp bleaching: a review. J Clean Prod 256:120338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120338
Solomon KR (1996) Chlorine in the bleaching of pulp and paper. Pure Appl Chem 68:1721–1730. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac199668091721
Tripathi SK, Bhardwaj NK, Roy Ghatak HR (2020) Developments in ozone-based bleaching of pulps. Ozone Sci Eng 42:194–210. https://doi.org/10.1080/01919512.2019.1647407
Uetani K, Yano H (2011) Nanofibrillation of wood pulp using a high-speed blender. Biomacromolecules 12:348–353. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm101103p
Woiciechowski AL, Dalmas Neto CJ, de Souza P, Vandenberghe L et al (2020) Lignocellulosic biomass: acid and alkaline pretreatments and their effects on biomass recalcitrance—conventional processing and recent advances. Bioresour Technol 304:122848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.122848
Yi T, Zhao H, Mo Q et al (2020) From cellulose to cellulose nanofibrils—a comprehensive review of the preparation and modification of cellulose nanofibrils. Materials 13:5062. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13225062
Zhang K, Pei Z, Wang D (2016) Organic solvent pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass for biofuels and biochemicals: a review. Bioresour Technol 199:21–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.08.102
Zheng J, Rehmann L (2014) Extrusion pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass: a review. Int J Mol Sci 15:18967–18984. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms151018967
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Emma Perry (University of Maine) for her help on the SEM training.
Funding
This work was supported in part by funding from UT-Battelle LLC with the U.S. Department of Energy under contract DE-AC05-00OR22725 (subcontract # 4000174848).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.C. wrote the main manuscript text, performed experiments, analyzed data, and created figures. K.T. and E.S. performed experiments and analyzed data. W.G. secured funding and managed the project. All authors edited and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors reviewed and approved final submission.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Christau, S., Alyamac-Seydibeyoglu, E., Thayer, K. et al. Effects of an aqueous surface modification via a grafting-through polymerization approach on the fibrillation and drying of bleached softwood kraft pulp. Cellulose 30, 901–914 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04938-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04938-3