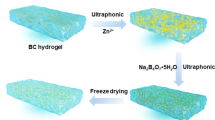
Abstract
Although the high-value utilization of the extensive agroforestry cellulose has attracted more and more attention, the manufacture of cellulose-based flexible sensors with flame retardance is still a promising but challenging work. In this work, we report a silver nanoparticles and phytic acid coated bacterial cellulose (Ag/PA@BC) composite aerogel with high piezoresistive sensitivity and flame retardance, which conquers the intrinsic inflammability of biomass aerogels. Biological phytic acid is used as both flame retardant and complexing agent for the green synthesis of Ag. The resulted Ag/PA@BC aerogel sensor shows high sensitivity (6.92 kPa−1), ultralow detection limit (28 Pa), short response time (200 ms), and good reproducibility. Furthermore, the aerogel sensor exhibits excellent flame retardant performance which can self-extinguish after ignition. The green synthesized biomass aerogel sensor with desirable sensitivity and excellent flame retardance presents great potential in health care, portable equipment and human–machine interaction, etc.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali M, Sharif S, Anjum S, Imran M, Ikram M, Naz M, Ali S (2020) Preparation of Co and Ni doped ZnO nanoparticles served as encouraging nano-catalytic application. Mater Res Express 6:1250d1255
Aqeel M, Ikram M, Asghar A, Haider A, Ul-Hamid A, Naz M, Imran M, Ali S (2020) Synthesis of capped Cr-doped ZnS nanoparticles with improved bactericidal and catalytic properties to treat polluted water. Appl Nanosci 10:2045–2055
Cao J, Sun X, Zhang X, Lu C (2016) Homogeneous synthesis of Ag nanoparticles-doped water-soluble cellulose acetate for versatile applications. Int J Biol Macromol 92:167–173
Cao J, Lu C, Zhuang J, Liu M, Zhang X, Yu Y, Tao Q (2017) Multiple hydrogen bonding enables the self-healing of sensors for human-machine interactions. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 56:8795–8800
Cao J, Zhou Z, Song Q, Chen K, Su G, Zhou T, Zheng Z, Lu C, Zhang X (2020a) Ultrarobust Ti3C2Tx MXene-based soft actuators via bamboo-inspired mesoscale assembly of hybrid nanostructures. ACS Nano 14:7055–7065
Cao X, Zhang J, Chen S, Varley RJ, Pan K (2020b) 1D/2D nanomaterials synergistic, compressible, and response rapidly 3D graphene aerogel for piezoresistive sensor. Adv Funct Mater 30:2003618
Chen Z, Yan T, Pan Z (2020) Review of flexible strain sensors based on cellulose composites for multi-faceted applications. Cellulose 28:615–645
Chen Z, Wang Y, Yang Y, Yang X, Zhang X (2021) Multifunctional sensing platform based on green-synthesized silver nanostructure and microcrack architecture. Chem Eng J 403:126388
Fang Y, Sun W, Li J, Liu H, Liu X (2021) Eco-friendly flame retardant and dripping-resistant of polyester/cotton blend fabrics through layer-by-layer assembly fully bio-based chitosan/phytic acid coating. Int J Biol Macromol 175:140–146
French AD (2014) Idealized powder diffraction patterns for cellulose polymorphs. Cellulose 21:885–896
Guo Q, Cao J, Han Y, Tang Y, Zhang X, Lu C (2017) Biological phytic acid as a multifunctional curing agent for elastomers: towards skin-touchable and flame retardant electronic sensors. Green Chem 19:3418–3427
Han S, Alvi NUH, Granlof L, Granberg H, Berggren M, Fabiano S, Crispin X (2019) A multiparameter pressure-temperature-humidity sensor based on mixed ionic-electronic cellulose aerogels. Adv Sci (weinh) 6:1802128
Hosseini H, Kokabi M, Mousavi SM (2018) Conductive bacterial cellulose/multiwall carbon nanotubes nanocomposite aerogel as a potentially flexible lightweight strain sensor. Carbohydr Polym 201:228–235
Hou W, Sheng N, Zhang X, Luan Z, Qi P, Lin M, Tan Y, Xia Y, Li Y, Sui K (2019) Design of injectable agar/NaCl/polyacrylamide ionic hydrogels for high performance strain sensors. Carbohydr Polym 211:322–328
Huang J, Li D, Zhao M, Lv P, Lucia L, Wei Q (2019) Highly stretchable and bio-based sensors for sensitive strain detection of angular displacements. Cellulose 26:3401–3413
Huo D, Chen B, Meng G, Huang Z, Li M, Lei Y (2020) Ag-nanoparticles@bacterial nanocellulose as a 3D flexible and robust surface-enhanced raman scattering substrate. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:50713–50720
Ikram M, Hassan J, Imran M, Haider J, Ul-Hamid A, Shahzadi I, Ikram M, Raza A, Qumar U, Ali S (2020a) 2D chemically exfoliated hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) nanosheets doped with Ni: synthesis, properties and catalytic application for the treatment of industrial wastewater. Appl Nanosci 10:3525–3528
Ikram M, Raza A, Imran M, Ul-Hamid A, Shahbaz A, Ali S (2020b) Hydrothermal synthesis of silver decorated reduced graphene oxide (rGO) nanoflakes with effective photocatalytic activity for wastewater treatment. Nanoscale Res Lett 15:95
Ikram M, Mahmood A, Haider A, Naz S, Ul-Hamid A, Nabgan W, Shahzadi I, Haider J, Ahmad I, Ali S (2021) Dye degradation, antibacterial and in-silico analysis of Mg/cellulose-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Int J Biol Macromol 185:153–164
Li P, Wang B, Liu YY, Xu YJ, Jiang ZM, Dong CH, Zhang L, Liu Y, Zhu P (2020) Fully bio-based coating from chitosan and phytate for fire-safety and antibacterial cotton fabrics. Carbohydr Polym 237:116173
Li X, Liu J, Li D, Huang S, Huang K, Zhang X (2021) Bioinspired multi-stimuli responsive actuators with synergistic color-and morphing-change abilities. Adv Sci (weinh) 8:e2101295
Li X, Liu J, Guo Q, Zhang X, Tian M (2022) Polymerizable deep eutectic solvent-based skin-like elastomers with dynamic schemochrome and self-healing ability. Small 18:e2201012
Liu X, Lu C, Wu X, Zhang X (2017) Self-healing strain sensors based on nanostructured supramolecular conductive elastomers. J Mater Chem A 5:9824–9832
Liu X, Su G, Guo Q, Lu C, Zhou T, Zhou C, Zhang X (2018) Hierarchically structured self-healing sensors with tunable positive/negative piezoresistivity. Adv Funct Mater 28:1706658
Liu J, Guo Q, Zhang X, Gai J, Zhang C (2021) Multistage responsive materials for real-time, reversible, and sustainable light-writing. Adv Funct Mater 31:2106673
Peng N, Huang D, Gong C, Wang Y, Zhou J, Chang C (2020) Controlled arrangement of nanocellulose in polymeric matrix: from reinforcement to functionality. ACS Nano 14:16169–16179
Qin Z, Lv Y, Fang X, Zhao B, Niu F, Min L, Pan K (2022) Ultralight polypyrrole crosslinked nanofiber aerogel for highly sensitive piezoresistive sensor. Chem Eng J 427:131650
Rashid M, Ikram M, Haider A, Naz S, Haider J, Ul-Hamid A, Shahzadi A, Aqeel M (2020) Photocatalytic, dye degradation, and bactericidal behavior of Cu-doped ZnO nanorods and their molecular docking analysis. Dalton Trans 49:8314–8330
Shaheen S, Iqbal A, Ikram M, Imran M, Naz S, Ul-Hamid A, Shahzadi A, Nabgan W, Haider J, Haider A (2022) Graphene oxide-ZnO nanorods for efficient dye degradation, antibacterial and in-silico analysis. Appl Nanosci 12:165–177
Trung TQ, Lee NE (2016) Flexible and stretchable physical sensor integrated platforms for wearable human-activity monitoringand personal healthcare. Adv Mater 28:4338–4372
Wan C, Liu S, Chen Y, Zhang F (2020) Facile, one-pot, formaldehyde-free synthesis of reactive NP flame retardant for a biomolecule of cotton. Int J Biol Macromol 163:1659–1668
Wang M, Shao C, Zhou S, Yang J, Xu F (2018) Super-compressible, fatigue resistant and anisotropic carbon aerogels for piezoresistive sensors. Cellulose 25:7329–7340
Wang L, Zhang M, Yang B, Tan J, Ding X (2020) Highly compressible, thermally stable, light-weight, and robust aramid nanofibers/Ti3AlC2 MXene composite aerogel for sensitive pressure sensor. ACS Nano 14:10633–10647
Wang S, Meng W, Lv H, Wang Z, Pu J (2021a) Thermal insulating, light-weight and conductive cellulose/aramid nanofibers composite aerogel for pressure sensing. Carbohydr Polym 270:11841
Wang Y, Huang X, Zhang X (2021b) Ultrarobust, tough and highly stretchable self-healing materials based on cartilage-inspired noncovalent assembly nanostructure. Nat Commun 12:1291
Wei S, Qiu X, An J, Chen Z, Zhang X (2021) Highly sensitive, flexible, green synthesized graphene/biomass aerogels for pressure sensing application. Compos Sci Technol 207:108730
Wu X, Han Y, Zhang X, Zhou Z, Lu C (2016) Large-area compliant, low-cost, and versatile pressure-sensing platform based on microcrack-designed carbon black@polyurethane sponge for human-machine interfacing. Adv Funct Mater 26:6246–6256
Xie Y, Yue L, Zheng Y, Zhao L, Liang C, He W, Liu Z, Sun Y, Yang Y (2019) The antibacterial stability of poly(dopamine) in-situ reduction and chelation nano-Ag based on bacterial cellulose network template. Appl Surf Sci 491:383–394
Yang X, Liu J, Fan D, Cao J, Huang X, Zheng Z, Zhang X (2020) Scalable manufacturing of real-time self-healing strain sensors based on brominated natural rubber. Chem Eng J 389:124448
Zhang X, Cao J, Yang Y, Wu X, Zheng Z, Zhang X (2019a) Flame-retardant, highly sensitive strain sensors enabled by renewable phytic acid-doped biotemplate synthesis and spirally structure design. Chem Eng J 374:730–737
Zhang S, Zhang S, Song L (2014) Super-high activity of Bi3+ doped Ag3PO4 and enhanced photocatalytic mechanism. Appl Catal B Environ 152–153:129–139
Zhang Y, Tian W, Liu L, Cheng W, Wang W, Liew KM, Wang B, Hu Y (2019b) Eco-friendly flame retardant and electromagnetic interference shielding cotton fabrics with multi-layered coatings. Chem Eng J 372:1077–1090
Zhang Z, Ma Z, Leng Q, Wang Y (2019c) Eco-friendly flame retardant coating deposited on cotton fabrics from bio-based chitosan, phytic acid and divalent metal ions. Int J Biol Macromol 140:303–310
Zhang L, Liao Y, Wang YC, Zhang S, Yang W, Pan X, Wang ZL (2020) Cellulose II aerogel-based triboelectric nanogenerator. Adv Funct Mater 30:2001763
Zhang X, Lin H, Shang H, Xu J, Zhu J, Huang W (2021) Recent advances in functional fiber electronics. SusMat 1:105–126
Zhi H, Zhang X, Wang F, Wan P, Feng L (2021) Flexible Ti3C2Tx MXene/PANI/bacterial cellulose aerogel for e-skins and gas sensing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13:45987–45994
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51873123 and 52173112), the Sichuan Provincial Natural Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (2021JDJQ0017), and the Startup Project Supported by Yibin University (2020QH12) for financial support. The authors also thank Dr. Guiping Yuan from the Analytical and Testing Centre of Sichuan University for providing the TEM measurement.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Zhou, P. & Zhang, X. Green synthesis of Ag-doped cellulose aerogel for highly sensitive, flame retardant strain sensors. Cellulose 29, 8719–8731 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04802-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04802-4