Abstract
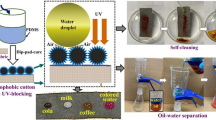
In this work, robust superhydrophobic cotton fabrics with ultraviolet (UV) shielding, self-cleaning, photocatalysis, and oil/water separation were successfully prepared based on micro/nano hierarchical ZnO/HNTs (halloysite nanotubes) hybrid particles and silicone elastomer polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS). ZnO/HNTs hybrid particles were prepared by in-situ growth of ZnO nanoparticles on the surface of halloysite nanotubes (HNTs). ZnO/HNTs hybrid particles and PDMS were used to successively coat cotton fabrics by dip-coating approach. The coated cotton fabrics displayed excellent superhydrophobicity with a water contact angle (WCA) of 162.5 ± 1.0° owing to the roughness provided by micro/nano hierarchical ZnO/HNTs hybrid particles and low surface energy achieved by PDMS. After being exposed to the UV lamp for 5 h, about 90.8% of the methylene blue was degraded, indicating that the coated cotton fabrics had excellent photocatalytic activity. The as-prepared cotton fabrics also displayed outstanding self-cleaning and antifouling properties. In addition, due to both superhydrophobic and superoleophilic characteristics, the as-prepared cotton fabrics could be used to separate several oil/water mixtures and showed good recoverability. The superhydrophobic cotton fabrics also exhibited excellent UV shielding performance with a large ultraviolet protection factor (UPF) of 1643.28 due to strong ultraviolet-absorption, light scattering and frequent light reflection of ZnO nanoparticles from ZnO/HNTs composites coated on cotton fabrics. Importantly, the as-prepared cotton fabrics retained superhydrophobic performance after 2000 cycles rubbing, 90 h UV illumination, and immersing in acidic and alkali solutions with different pH values ranging from 1 to 14 for 1 h. These characteristics made multifunctional cotton fabrics a satisfactory candidate in various promising fields.
Graphical abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banerjee S, Dionysios DD, Pillai SC (2015) Self-cleaning applications of TiO2 by photo-induced hydrophilicity and photocatalysis. Appl Catal B-Environ 176:396–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.03.058
Cao CY, Ge MZ, Huang JY, Li SH, Deng S, Zhang SN, Chen Z, Zhang KQ, Al-Deyab SS, Lai YK (2016) Robust fluorine-free superhydrophobic PDMS-ormosil@fabrics for highly effective self-cleaning and efficient oil-water separation. J Mater Chem A 4:12179–12187. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta04420d
Cheng ZL, Sun W (2015) Preparation of N-doped ZnO-loaded halloysite nanotubes catalysts with high solar-light photocatalytic activity. Water Sci Technol 72:1817–1823. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2015.403
Gang W, Guo ZG, Liu WM (2017) Biomimetic polymeric superhydrophobic surfaces and nanostructures: from fabrication to applications. Nanoscale 9:3338–3366. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nr00096k
Gao SW, Dong XL, Huang JY, Li SH, Chen Z, Lai YK (2017) Rational construction of highly transparent superhydrophobic coatings based on a non-particle, fluorine-free and water-rich system for versatile oil-water separation. Chem Eng J 333:621–629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.10.006
Ge MZ, Cao CY, Liang FH, Liu R, Zhang Y, Zhang W, Zhu TX, Yi B, Tang YX, Lai YK (2020) “PDMS-in-water” emulsion enables mechanochemically robust superhydrophobic surfaces with self-healing nature. Nanoscale Horizons 5(1):65–73. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NH00519F
Guo HS, Yang J, Xu T, Zhao WQ, Zhang JM, Zhu YN, Wen CY, Li QS, Sui JX, Zhang L (2019) A robust cotton textile-based material for high flux oil-water separation. ACS App Mater Inter 11(14):13704–13713. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b01108
Jiang B, Zhang HJ, Sun YL, Zhang LH, Xu LD, Hao L, Yang HW (2017) Covalent layer-by-layer grafting (LBLG) functionalized superhydrophobic stainless steel mesh for oil/ water separation. Appl Surf Sci 406:150–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.02.102
Jin M, Feng X, Feng L, Sun T, Zhai J, Li T, Jiang L (2005) Superhydrophobic aligned polystyrene nanotube films with high adhesive force. Adv Mater 17:1977–1981. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200401726
Jin GW, Kim JY, Min BG (2018) Superhydrophobic and antibacterial properties of cotton fabrics treated with PVDF and nano-ZnO through phase inversion process. Fiber Polym 19:1835–1842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-018-8313-x
Kim M, Kim K, Lee NY, Shin K, Kim YS (2007) A simple fabrication route to a highly transparent superhydrophobic surface with a poly(dimethylsiloxane) coated flexible mold. Chem Commun 22:2237–2239. https://doi.org/10.1039/b618123f
Kim JH, Mirzaei A, Hyoun W (2018) Novel superamphiphobic surfaces based on micro-nano hierarchical fluorinated Ag/SiO2 structures. App Surf Sci 445:262–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.03.148
Li BC, Zhang JP, Gao ZQ, Wei QY (2016) Semitransparent superoleophobic coatings with low sliding angles for hot liquids based on silica nanotubes. J Mater Chem A 4:953–960. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA08733C
Li SH, Huang JY, Ge MZ, Cao CY, Deng S, Zhang SN, Chen GQ, Zhang KQ, Al-Deyab SS, Lai YK (2015) Self-cleaning cotton: robust flower-like TiO2@cotton fabrics with special wettability for effective self-cleaning and versatile oil/water separation. Adv Mater Interfaces. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201570068
Lin M, Parida K, Cheng X (2017) Flexible superamphiphobic film for water energy harvesting. Adv Mater Technol-Us 2:1600186. https://doi.org/10.1002/admt.201600186
Lin DM, Zeng XR, Li HQ, Lai XJ (2018) Facile fabrication of superhydrophobic and flame-retardant coatings on cotton fabrics via layer-by-layer assembly. Cellulose 25:3135–3149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1748-9
Liu XR, Wang KL, Zhang W, Zhang JP, Li JZ (2019) Robust, self-cleaning, anti-fouling, superamphiphobic soy protein isolate composite films using spray-coating technique with fluorinated HNTs/SiO2. Compos Part B-Eng 174:107002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107002
Ma W, Higaki YJ, Takahara A (2017) Superamphiphobic coatings from combination of a biomimetic catechol-bearing fluoropolymer and halloysite nanotubes. Adv Mater Interfaces 4:1700907. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201700907
Ma W, Wu H, Higaki YJ, Takahara A (2018) Halloysite nanotubes: green nanomaterial for functional organic-inorganic nanohybrids. Chem Rec 18:986–999. https://doi.org/10.1002/tcr.201700093
Martin JW, Mabury SA, Solomon KR (2003a) Bioconcentration and tissue distribution of perfluorinated acids in rainbow trout (oncorhynchus mykiss). Environ Toxicol Chem 22:196–204. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620220126
Martin JW, Mabury SA, Solomon KR, Muir DCG (2003b) Dietary accumulation of perfluorinated acids in juvenile rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Environ Toxicol Chem 22:189–195. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620220125
Momen G, Farzaneh M (2012) A ZnO-based nanocomposite coating with ultra-water repellent properties. Appl Surf Sci 258:5723–5728. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.02.074
Qu MN, Ma XR, Hou LG, Yuan MJ, He J, Xue MH, Liu XG, He JM (2018) Fabrication of durable superamphiphobic materials on various substrates with wear-resistance and self-cleaning performance from kaolin. Appl Surf Sci 456:737–750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.06.194
Qu XF, Cai JB, Tian JH, Luo BH, Liu MX (2020) Superamphiphobic surfaces with self-cleaning and antifouling properties by functionalized chitin nanocrystals. Acs Sustain Chem Eng 8(17):6690–6699. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c00340
Rezaei S, Manoucheri I, Moradian R, Pourabbas B (2014) One-step chemical vapor deposition and modification of silica nanoparticles at the lowest possible temperature and superhydrophobic surface fabrication. Chem Eng J 252:11–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.04.100
Shishodiaa A, Aroraa HS, Babua A, Mandalb P, Grewala HS (2019) Multidimensional durability of superhydrophobic self-cleaning surface derived from rice-husk ash. Prog Org Coat 136:105221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2019.105221
Tu YY, Zou HL, Lin SD, Hu JW (2017) Understanding the mechanism for building woven fabrics with wettability ranging from superhydrophobic to superamphiphobic via an aqueous process. React Funct Polym 119:75–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2017.08.004
Wang WJ, Liu RP, Chi HJ, Zhang T, Xu ZG, Zhao Y (2019) Durable superamphiphobic and photocatalytic fabrics: tackling the loss of super-non-wettability due to surface organic contamination. ACS Appl Mater Inter 11:35327–35332. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b12141
Wen BN, Peng S, Yang XJ, Long MY, Deng WS, Chen GY, Chen JQ, Deng WL (2017) A cycle-etching approach toward the fabrication of superamphiphobic stainless steel surfaces with excellent anticorrosion properties. Adv Eng Mater 19:1600879. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201600879
Wu L, Zhang JP, Li BC (2013) Mimic nature, beyond nature: facile synthesis of durable superhydrophobic textiles using organosilanes. J Mater Chem B 1:4756–4763. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tb20934b
Xu LH, Liu YD, Yuan XL, Wan J, Wang LM, Pan H, Shen Y (2020) One-pot preparation of robust, ultraviolet-proof superhydrophobic cotton fabrics for self-cleaning and oil/water separation. Cellulose 27:9005–9026. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03369-2
Yang MP, Liu WQ, Jiang C, Liu CH, He S, Xie YK, Wang ZF (2018) Facile preparation of robust superhydrophobic cotton textile for self-cleaning and oil-water separation. Ind Eng Chem Res 58:187–194. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b04433
Yang MP, Jiang C, Liu WQ, Liang LY, Pi K (2019a) A less harmful system of preparing robust fabrics for integrated self-cleaning, oil-water separation and water purification. Environ Pollut 255:113277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2019.113277
Yang MP, Liu WQ, Jiang C, Xie KY, Shi HY, Zhang FY (2019b) Facile fabrication of robust fluorine-free superhydrophobic cellulosic fabric for self-cleaning, photocatalysis and UV shielding. Cellulose 26:8153–8164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02640-5
Yang MP, Liu WQ, Jiang C, Xie YK, Shi HY, Zhang FY, Wang ZF (2019c) Facile construction of robust superhydrophobic cotton textiles for effective UV protection, self-cleaning and oil-water separation. Colloids Surfaces A 570:172–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.03.024
Zhang JP, Li BC, Wu L, Wang AQ (2013) Facile preparation of durable and robust superhydrophobic textiles by dip coating in nanocomposite solution of organosilanes. Chem Commun 49:11509–11511. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cc43238f
Zhang DQ, Williams BL, Shrestha SB, Nasir Z, Becher EM, Lofink BJ, Santos VH, Patel H, Peng XH, Sun LY (2017a) Flame retardant and hydrophobic coatings on cotton fabrics via sol-gel and self-assembly techniques. J Colloid Interf Sci 505:892–899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2017.06.087
Zhang JP, Gao ZQ, Li LX, Li BC, Sun HX (2017b) Waterborne nonfluorinated superhydrophobic coatings with exceptional mechanical durability based on natural nanorods. Adv Mater Interfaces 4:1700723. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201700723
Zhang XT, Liu SQ, Salim A, Seeger S (2019) Hierarchical structured multifunctional self-cleaning material with durable superhydrophobicity and photocatalytic functionalities. Small 15(34):1901822. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201901822
Zheng LZ, Su XJ, Lai XJ, Chen WJ, Li HQ, Zeng XR (2019) Conductive superhydrophobic cotton fabrics via layer-by-layer assembly of carbon nanotubes for oil-water separation and human motion detection. Mater Lett 253:230–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.06.078
Zhou QQ, Chen GQ, Xing TL (2018) Facile construction of robust superhydrophobic tea polyphenol/Fe@cotton fabric for self-cleaning and efficient oil–water separation. Cellulose 25:1513–1525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1654-1
Zuo H, Chen L, Kong M, Qiu LP, Wu P, Yang YH, Chen KP (2018) Toxic effects of fluoride on organisms. Life Sci 198:18–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2018.02.001
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (21ZR426200) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (51703123).
Funding
This work was financially supported by Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (21ZR426200) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (51703123).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, W., Xu, L., Pan, H. et al. Robust ZnO/HNTs-based superhydrophobic cotton fabrics with UV shielding, self-cleaning, photocatalysis, and oil/water separation. Cellulose 29, 4021–4037 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04462-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-022-04462-4