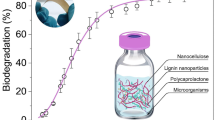
Abstract
Several billion tons of plastic waste were discarded in landfills, specifically in marine environments. Remediation of plastic waste is vital for ensuring a clean marine environment. Photocatalyst such as titanium oxide (TiO2) is a promising and environmental friendly approach for plastic waste degradation, compared to other waste management methods. In this study, switchable degradation of a cellulose acetate (CA) was carried out through composite preparation with a seawater-activated TiO2 (SA-TiO2) photocatalyst. The successful preparation of CA/SA-TiO2 composite was confirmed using Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetric analysis, and field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) results. The degradation of CA through SA-TiO2 in marine environments was confirmed by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, size exclusion chromatography, and FE-SEM results. The seawater-activated degradation makes switchable and degradable polymer-photocatalyst composites an efficient and eco-friendly solution for plastic waste remediation in marine environments.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali SS, Qazi IA, Arshad M, Khan Z, Voice TC, Mehmood CT (2016) Photocatalytic degradation of low density polyethylene (LDPE) films using titania nanotubes. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 5:44–53
Allen NS (1994) Photofading and light-stability of dyed and pigmented polymers. Polym Degrad Stab 44(3):357–374
Araújo D, Castro MCR, Figueiredo A, Vilarinho M, Machado A (2020) Green synthesis of cellulose acetate from corncob: physicochemical properties and assessment of environmental impacts. J Clean Prod 260:120865
Chung J, Chung JW, Kwak SY (2015) Adsorption-assisted photocatalytic activity of nitrogen and sulfur codoped TiO2 under visible light irradiation. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17(26):17279–17287
Da Ros S, Aliev AE, del Gaudio I, King R, Pokorska A, Kearney M, Curran K (2021) Characterising plasticised cellulose acetate-based historic artefacts by NMR spectroscopy: a new approach for quantifying the degree of substitution and diethyl phthalate contents. Polym Degrad Stab 183:109420
Gavilà L, Esposito D (2017) Cellulose acetate as a convenient intermediate for the preparation of 5-acetoxymethylfurfural from biomass. Green Chem 19(11):2496–2500
Gewert B, Plassmann MM, MacLeod M (2015) Pathways for degradation of plastic polymers floating in the marine environment. Environ Sci Process Impacts 17(9):1513–1521
Geyer R, Jambeck JR, Law KL (2017) Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci Adv 3(7):e1700782
Gomez-Hermoso-de-Mendoza J, Gutierrez J, Tercjak A (2020) Transparent and flexible cellulose triacetate–TiO2 nanoparticles with conductive and UV-shielding properties. J Phys Chem C 124(7):4242–4251
Jambeck JR, Geyer R, Wilcox C, Siegler TR, Perryman M, Andrady A, Narayan R, Law KL (2015) Plastic waste inputs from land into the ocean. Science 347(6223):768–771
Jiang X, Manawan M, Feng T, Qian R, Zhao T, Zhou G, Kong F, Wang Q, Dai S, Pan JH (2018) Anatase and rutile in evonik aeroxide P25: heterojunctioned or individual nanoparticles? Catal Today 300:12–17
Joly F-X, Coulis M (2018) Comparison of cellulose vs. plastic cigarette filter decomposition under distinct disposal environments. Waste Manag 72:349–353
Kaur H, Bulasara VK, Gupta RK (2018) Influence of pH and temperature of dip-coating solution on the properties of cellulose acetate-ceramic composite membrane for ultrafiltration. Carbohydr Polym 195:613–621
Kim DS, Kwak SY (2007) The hydrothermal synthesis of mesoporous TiO2 with high crystallinity, thermal stability, large surface area, and enhanced photocatalytic activity. Appl Catal A-Gen 323:110–118
Kono H, Hashimoto H, Shimizu Y (2015) NMR characterization of cellulose acetate: chemical shift assignments, substituent effects, and chemical shift additivity. Carbohydr Polym 118:91–100
Liu L, Gong D, Bratasz L, Zhu Z, Wang C (2019) Degradation markers and plasticizer loss of cellulose acetate films during ageing. Polym Degrad Stab 168:108952
Müller WEG, Tolba E, Schröder HC, Wang S, Glaßer G, Muñoz-Espí R, Link T, Wang X (2015) A new polyphosphate calcium material with morphogenetic activity. Mater Lett 148:163–166
Puls J, Wilson SA, Hölter D (2010) Degradation of cellulose acetate-based materials: a review. J Polym Environ 19(1):152–165
Sharma S, Basu S, Shetti NP, Nadagouda MN, Aminabhavi TM (2021) Microplastics in the environment: occurrence, perils, and eradication. Chem Eng J 408:127317
Tobaldi DM, Pullar RC, Seabra MP, Labrincha JA (2014) Fully quantitative X-ray characterisation of evonik aeroxide TiO2 P25®. Mater Lett 122:345–347
Volhard M-F, Christ JJ, Blank LM, Jüstel T (2020) Seawater activated TiO2 photocatalyst for degradation of organic compounds. Sustain Chem Pharm 16:100251
Yadav N, Adolfsson KH, Hakkarainen M (2021) Carbon dot-triggered photocatalytic degradation of cellulose acetate. Biomacromolecules 22(5):2211–2223
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (2020R1A2C1005394).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. In this experiment, we did not collect any samples of human and animals.
Ethical standards
This study was conducted following Compliance with Ethical Standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J.H., Kwak, SY. Switchable degradation of cellulose acetate composite by seawater-activated TiO2 photocatalyst. Cellulose 29, 1501–1508 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04381-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04381-w