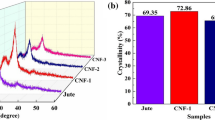
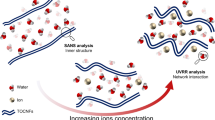
Abstract
Driven by the demand for various cationic biopolymers in recent years, the quaternization of cellulose nanofibers was carefully investigated to have tight control over their final characteristics. The addition of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to the reaction mixture is crucial as it catalyzes the conversion of alcohol groups of cellulose into more reactive alcoholate groups. On the other hand, excessive concentration proves to inhibit the reactivity of hydroxyl groups. The addition of glycidyltrimethylammonium chloride (GTMAC) increases the yield of the trimethylammonium chloride content (TMAC) reaction, while in excess it affects the rheological properties of the quaternizated cellulose nanofibers. The effects of NaOH and GTMAC on the TMAC content and rheological properties have been investigated in detail and mathematically evaluated. Furthermore, a comparison of the viscoelastic behavior and shear thinning character of commercial cationic micro- and nanofibrillated cellulose is presented. The research allows to extend the possibility of using cellulose in many applications of cationic biopolymers.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agoda-Tandjawa G, Durand S, Berot S et al (2010) Rheological characterization of microfibrillated cellulose suspensions after freezing. Carbohydr Polym 80:677–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.11.045
Ahmadi F, Oveisi Z, Samani M, Amoozgar Z (2015) Chitosan based hydrogels: characteristics and pharmaceutical applications. Res Pharm Sci 10:1–16
Ahmed EM (2015) Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: a review. J Adv Res 6:105–121
Budtova T, Navard P (2016) Cellulose in NaOH–water based solvents: a review. Cellulose 23:5–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0779-8
Caló E, Khutoryanskiy VV (2015) Biomedical applications of hydrogels: a review of patents and commercial products. Eur Polym J65:252–67
Chaker A, Boufi S (2015) Cationic nanofibrillar cellulose with high antibacterial properties. Carbohydr Polym 131:224–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.06.003
Cinar Ciftci G, Larsson PA, Riazanova AV et al (2020) Tailoring of rheological properties and structural polydispersity effects in microfibrillated cellulose suspensions. Cellulose 27:9227–9241. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03438-6
Colson J, Bauer W, Mayr M et al (2016) Morphology and rheology of cellulose nanofibrils derived from mixtures of pulp fibres and papermaking fines. Cellulose 23:2439–2448. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-0987-x
Courtenay JC, Ramalhete SM, Skuze WJ et al (2018) Unravelling cationic cellulose nanofibril hydrogel structure: NMR spectroscopy and small angle neutron scattering analyses. Soft Matter 14:255–263. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7sm02113e
Dimic-Misic K, Puisto A, Paltakari J et al (2013) The influence of shear on the dewatering of high consistency nanofibrillated cellulose furnishes. Cellulose 20:1853–1864. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-9964-9
Ebhodaghe SO (2020) Hydrogel – based biopolymers for regenerative medicine applications: a critical review. Int J Polym Mater Polym Biomater 3:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/00914037.2020.1809409
Farshbaf M, Davaran S, Zarebkohan A et al (2017) Significant role of cationic polymers in drug delivery systems. Artif Cells, Nanomedicine, Biotechnol 46:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2017.1395344
Freitas C, Müller RH (1998) Effect of light and temperature on zeta potential and physical stability in solid lipid nanoparticle (SLN®) dispersions. Int J Pharm 168:221–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-5173(98)00092-1
French AD (2017) Glucose, not cellobiose, is the repeating unit of cellulose and why that is important. Cellul 2017 2411 24:4605–4609. https://doi.org/10.1007/S10570-017-1450-3
Gasperini L, Mano JF, Reis RL (2014) Natural polymers for the microencapsulation of cells. J R Soc Interface 11(100):20140817
George A, Sanjay MR, Srisuk R et al (2020) A comprehensive review on chemical properties and applications of biopolymers and their composites. Int J Biol Macromol 154:329–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.120
Ghorbani S, Eyni H, Bazaz SR et al (2018) Hydrogels based on cellulose and its derivatives: applications, synthesis, and characteristics. Polym Sci - Ser A 60:707–722
Hasani M, Cranston ED, Westman G, Gray DG (2008) Cationic surface functionalization of cellulose nanocrystals. Soft Matter 4:2238–2244. https://doi.org/10.1039/b806789a
Ho TTT, Zimmermann T, Hauert R, Caseri W (2011) Preparation and characterization of cationic nanofibrillated cellulose from etherification and high-shear disintegration processes. Cellulose 18:1391–1406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-011-9591-2
Hubbe MA, Tayeb P, Joyce M et al (2017) Rheology of nanocellulose-rich aqueous suspensions: a review. BioResources 12:9556–9661. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.12.4.Hubbe
Iotti M, Gregersen ØW, Moe S, Lenes M (2011) Rheological studies of microfibrillar cellulose water dispersions. J Polym Environ 19:137–145. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-010-0248-2
Isogai A, Saito T, Fukuzumi H (2011) TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers. Nanoscale 3:71–85. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0nr00583e
Jacob J, Haponiuk JT, Thomas S, Gopi S (2018) Biopolymer based nanomaterials in drug delivery systems: a review. Mater Today Chem 9:43–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2018.05.002
John MJ, Thomas S (2008) Biofibres and biocomposites. Carbohydr Polym 71:343–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2007.05.040
Kaneko D, Thi Le NQ, Shimoda T, Kaneko T (2010) Preparation methods of alginate micro-hydrogel particles and evaluation of their electrophoresis behavior for possible electronic paper ink application. Polym J 42:829–833. https://doi.org/10.1038/pj.2010.78
Kopač T, Krajnc M, Ručigaj A (2021) A mathematical model for pH-responsive ionically crosslinked TEMPO nanocellulose hydrogel design in drug delivery systems. Int J Biol Macromol 168:695–707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.11.126
Kopač T, Ručigaj A, Krajnc M (2020) The mutual effect of the crosslinker and biopolymer concentration on the desired hydrogel properties. Int J Biol Macromol 159:557–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.088
Lee D, Oh Y, Yoo JK et al (2020) Rheological study of cellulose nanofiber disintegrated by a controlled high-intensity ultrasonication for a delicate nano-fibrillation. Cellulose 27:9257–9269. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03410-4
Li J, Mooney DJ (2016) Designing hydrogels for controlled drug delivery. Nat Rev Mater 1:16071. https://doi.org/10.1038/natrevmats.2016.71
Lungu A, Cernencu AI, Dinescu S et al (2021) Nanocellulose-enriched hydrocolloid-based hydrogels designed using a Ca2+ free strategy based on citric acid. Mater Des 197:109200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.109200
Mittal A, Katahira R, Himmel ME, Johnson DK (2011) Effects of alkaline or liquid-ammonia treatment on crystalline cellulose: changes in crystalline structure and effects on enzymatic digestibility. Biotechnol Biofuels 4:41. https://doi.org/10.1186/1754-6834-4-41
Moberg T, Sahlin K, Yao K et al (2017) Rheological properties of nanocellulose suspensions: effects of fibril/particle dimensions and surface characteristics. Cellulose 24:2499–2510. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1283-0
Nastaj J, Przewłocka A, Rajkowska-Myśliwiec M (2016) Biosorption of Ni(II), Pb(II) and Zn(II) on calcium alginate beads: equilibrium, kinetic and mechanism studies. Polish J Chem Technol 18:81–87. https://doi.org/10.1515/pjct-2016-0052
Olszewska A, Eronen P, Johansson LS et al (2011) The behaviour of cationic NanoFibrillar Cellulose in aqueous media. Cellulose 18:1213–1226. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-011-9577-0
Parhi R (2017) Cross-linked hydrogel for pharmaceutical applications: a review. Adv Pharm Bull 7:515–530. https://doi.org/10.15171/apb.2017.064
Peng N, Wang Y, Ye Q et al (2016) Biocompatible cellulose-based superabsorbent hydrogels with antimicrobial activity. Carbohydr Polym 137:59–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.10.057
Rebelo R, Fernandes M, Fangueiro R (2017) Biopolymers in medical implants: a brief review. Procedia Eng 200:236–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.07.034
Salajková M, Berglund LA, Zhou Q (2012) Hydrophobic cellulose nanocrystals modified with quaternary ammonium salts. J Mater Chem 22:19798–19805. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm34355j
Samal SK, Dash M, Vlierberghe S, Van et al (2012) Cationic polymers and their therapeutic potential. Chem Soc Rev 41:7147–7194. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cs35094g
Schenker M, Schoelkopf J, Gane P, Mangin P (2019) Rheology of microfibrillated cellulose (MFC) suspensions: influence of the degree of fibrillation and residual fibre content on flow and viscoelastic properties. Cellulose 26:845–860. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2117-4
Šebenik U, Krajnc M, Alič B, Lapasin R (2019) Ageing of aqueous TEMPO-oxidized nanofibrillated cellulose dispersions: a rheological study. Cellulose 26:917–931. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2128-1
Šebenik U, Lapasin R, Krajnc M (2020) Rheology of aqueous dispersions of Laponite and TEMPO-oxidized nanofibrillated cellulose. Carbohydr Polym 240:116330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116330
Sehaqui H, De Perez U, Tingaut P, Zimmermann T (2015) Humic acid adsorption onto cationic cellulose nanofibers for bioinspired removal of copper(ii) and a positively charged dye. Soft Matter 11:5294–5300. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5sm00566c
Siqueira P, Siqueira É, De Elza A et al (2019) Three-dimensional stable alginate-nanocellulose gels for biomedical applications: towards tunable mechanical properties and cell growing. Nanomaterials 9:78. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9010078
Spaic M, Small DP, Cook JR, Wan W (2014) Characterization of anionic and cationic functionalized bacterial cellulose nanofibres for controlled release applications. Cellulose 21:1529–1540. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0174-x
Tang Y, Wang X, Huang B et al (2018) Effect of cationic surface modification on the rheological behavior and microstructure of nanocrystalline cellulose. Polymers (Basel) 10:278. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10030278
Tavakoli J, Tang Y (2017) Hydrogel based sensors for biomedical applications: an updated review. Polymers (Basel) 9:364. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym9080364
Turpeinen T, Jäsberg A, Haavisto S et al (2020) Pipe rheology of microfibrillated cellulose suspensions. Cellulose 27:141–156. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02784-4
Udoetok IA, Wilson LD, Headley JV (2016) Quaternized cellulose hydrogels as sorbent materials and pickering emulsion stabilizing agents. Materials. 9(8):645. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma9080645
Velema J, Kaplan D (2006) Biopolymer-based biomaterials as scaffolds for tissue engineering. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 102:187–238. https://doi.org/10.1007/10_013
Wang X, Chang CH, Jiang J et al (2019) The crystallinity and aspect ratio of cellulose nanomaterials determine their pro-Inflammatory and immune adjuvant effects in vitro and in vivo. Small 15:1901642. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201901642
Zaman M, Xiao H, Chibante F, Ni Y (2012) Synthesis and characterization of cationically modified nanocrystalline cellulose. Carbohydr Polym 89:163–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.02.066
Zhang W, Zhang Y, Lu C, Deng Y (2012) Aerogels from crosslinked cellulose nano/micro-fibrils and their fast shape recovery property in water. J Mater Chem 22:11642–11650. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm30688c
Acknowledgment
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the Slovenian Research Agency (research core funding No. P2-0191).
Funding
This work was supported by Slovenian Research Agency (Grant No. P2-0191).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Tilen Kopač, Aleš Ručigaj; Methodology: Tilen Kopač; Formal analysis and investigation: Tilen Kopač, Aleš Ručigaj; Visualization: Tilen Kopač; Writing – original draft preparation: Tilen Kopač; Writing – review and editing: Matjaž Krajnc, Aleš Ručigaj; Funding acquisition: Matjaž Krajnc; Resources: Matjaž Krajnc; Supervision: Aleš Ručigaj.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Human or animals rights
Authors declare no humans and/or animals were involved in this study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kopač, T., Krajnc, M. & Ručigaj, A. A rheological study of cationic micro- and nanofibrillated cellulose: quaternization reaction optimization and fibril characteristic effects. Cellulose 29, 1435–1450 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04365-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04365-w