Abstract
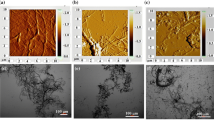
Lignocellulosic nanofibrils (LCNFs) are usually isolated from biomass with concentration less than 2.0 wt%. The low concentration limits the transportation and end-use applications of LCNFs. Therefore, the development of concentration process and the characteristics of concentrated LCNF become desirable and important for commercial deployment of LCNF application. In this study, 1.0 wt% LCNF suspension was prepared by mechanical fibrillation using a supermass grinder after enzymatic pretreatment, and then dewatered to solid concentrations of 5.9 wt%, 16.3 wt% and 25.9 wt% by a centrifuge. The un-concentrated LCNF suspension was obviously stable, being translucent, and well dispersed in water, while the concentrated LCNF suspensions exhibited the gel-like behavior or “solid-like” behavior depending on the concentration. Bundle-like fibrils were observed for the concentrated LCNFs, and average diameter of concentrated LCNF became large but still less than 100 nm. Un-concentrated and concentrated LCNFs had similar crystallinity and crystallite size, and the morphological changes were mainly in the amorphous regions of the fibrils. The concentrated LCNF films still had relatively good UV-blocking property, water absorption and oxygen permeability. The increasing basis weight of films was benefit for enhancing the surface smoothness of films and interweaves between fibrils, resulting in the tensile index and specific modulus of films higher than 71.7 kN·m·kg−1 and 6.8 MN·m·kg−1, respectively. In sum, the concentration process affected the morphology structure of LCNF, but the concentrated LCNF still kept relatively good properties. Concentration process of LCNF suspension may be a feasible strategy for large-scale LCNF production and storage.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bian HY, Dong ML, Chen LD, Zhou XL, Ni SZ, Fang GG, Dai HQ (2019) Comparison of mixed enzymatic pretreatment and post-treatment for enhancing the cellulose nanofibrillation efficiency. Bioresource Technol 293:122171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122171
Espinosa E, Rol F, Bras J, Rodríguez A (2020) Use of multi-factorial analysis to determine the quality of cellulose nanofibers: effect of nanofibrillation treatment and residual lignin content. Cellulose 27(18):10689–10705. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03136-3
Ferrer A, Quintana E, Filpponen I, Solala I, Vidal T, Rodriguez A, Laine J, Rojas OJ (2012) Effect of residual lignin and heteropolysaccharides in nanofibrillar cellulose and nanopaper from wood fibers. Cellulose 19:2179–2193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9788-z
Fu HC, Gao WH, Wang B, Zeng JS, Cheng Z, Xu J, Chen KF (2020) Effect of lignin content on the microstructural characteristics of lignocellulose nanofibrils. Cellulose 27:1327–1340. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02859-2
Heidarian P, Kaynak A, Paulino M, Zolfagharian A, Varley RJ, Kouzani AZ (2021) Dynamic nanocellulose hydrogels: recent advancements and future outlook. Carbohyd Polym 270:118357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118357
Hoeger IC, Nair SS, Ragauskas AJ, Deng YL, Rojas OJ, Zhu JY (2013) Mechanical deconstruction of lignocellulose cell walls and their enzymatic saccharification. Cellulose 20:807–818. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-013-9867-9
Horseman T, Tajvidi M, Diop CIK, Gardner DJ (2017) Preparation and property assessment of neat lignocellulose nanofibrils (LCNF) and their composite films. Cellulose 24:2455–2468. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1266-1
Huang YH, Nair SS, Chen HY, Fe BH, Yan N, Feng QM (2019) Lignin-rich nanocellulose fibrils isolated from parenchyma cells and fiber cells of western red cedar bark. Acs Sustain Chem Eng 7:15607–15616. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b03634
Isogai A (2021) Emerging nanocellulose technologies: recent developments. Adv Mater 33(28):2000630. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202000630
Miyamoto H, Schnupf U, Brady JW (2014) Water structuring over the hydrophobic surface of cellulose. J Agr Food Chem 62:11017–11023. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf501763r
Qian Y, Qiu XQ, Zhu SP (2015) Lignin: a nature-inspired sun blocker for broad-spectrum sunscreens. Green Chem 17:320–324. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4gc01333f
Qian Y, Zhong XW, Li Y, Qiu XQ (2017) Fabrication of uniform lignin colloidal spheres for developing natural broad-spectrum sunscreens with high sun protection factor. Ind Crop Prod 101:54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.03.001
Qing Y, Sabo R, Zhu JY, Agarwal U, Cai ZY, Wu YQ (2013) A comparative study of cellulose nanofibrils disintegrated via multiple processing approaches. Carbohyd Polym 97:226–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.04.086
Rojo E, Peresin MS, Sampson WW, Hoeger IC, Vartiainen J, Laine J, Rojas OJ (2015) Comprehensive elucidation of the effect of residual lignin on the physical, barrier, mechanical and surface properties of nanocellulose films. Green Chem 17:1853–1866. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4GC02398F
Segal L, Creely JJ, Martin AE, Conrad CM (1959) An empirical method for estimating the degree of crystallinity of native cellulose using the X-ray diffractometer. Text Res J 29(10):786–794. https://doi.org/10.1177/004051755902901003
Sethi J, Oksman K, Illikainen M, Sirvio JA (2018) Sonication-assisted surface modification method to expedite the water removal from cellulose nanofibers for use in nanopapers and paper making. Carbohyd Polym 197:92–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.05.072
Sim K, Lee J, Lee H, Youn HJ (2015) Flocculation behavior of cellulose nanofibrils under different salt conditions and its impact on network strength and dewatering ability. Cellulose 22:3689–3700. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0784-y
Sinquefield S, Ciesielski PN, Li K, Gardner DJ, Ozcan S (2020) Nanocellulose dewatering and drying: current state and future perspectives. Acs Sustain Chem Eng 8:9601–9615. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c01797
Spence KL, Venditti RA, Habibi Y, Rojas OJ, Pawlak JJ (2010a) The effect of chemical composition on microfibrillar cellulose films from wood pulps: mechanical processing and physical properties. Bioresource Technol 101:5961–5968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.02.104
Spence KL, Venditti RA, Rojas OJ, Habibi Y, Pawlak JJ (2010b) The effect of chemical composition on microfibrillar cellulose films from wood pulps: water interactions and physical properties for packaging applications. Cellulose 17:835–848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-010-9424-8
Spence KL, Venditti RA, Rojas OJ, Habibi Y, Pawlak JJ (2011) A comparative study of energy consumption and physical properties of microfibrillated cellulose produced by different processing methods. Cellulose 18:1097–1111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-011-9533-z
Thuy VTT, Hao LT, Jeon H, Koo JM, Park J, Lee ES, Hwang SY, Choi S, Park J, Oh DX (2021) Sustainable, self-cleaning, transparent, and moisture/oxygen-barrier coating films for food packaging. Green Chem 23:2658–2667. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0GC03647A
Wang SD, Gao WH, Chen KF, Xiang ZY, Zeng JS, Wang B, Xu J (2018) Deconstruction of cellulosic fibers to fibrils based on enzymatic pretreatment. Bioresource Technol 267:426–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.07.067
Wang QQ, Yao Q, Liu J, Sun JZ, Zhu QQ, Chen HL (2019) Processing nanocellulose to bulk materials: a review. Cellulose 26:7585–7617. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02642-3
Wetterling J, Jonsson S, Mattsson T, Theliander H (2017) The influence of ionic strength on the electroassisted filtration of microcrystalline cellulose. Ind Eng Chem Res 56:12789–12798. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.7b03575
Xiang ZY, Gao WH, Chen LH, Lan W, Zhu JY, Runge T (2016) A comparison of cellulose nanofibrils produced from Cladophora glomerata algae and bleached eucalyptus pulp. Cellulose 23:493–503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-015-0840-7
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31971603); Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangzhou (202102021212); Foundation of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Clean Pulp and Papermaking and Pollution Control, College of Light Industry and Food Engineering, Guangxi University, (No. 2019KF06); Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Plant Resources Biorefinery (2021B1212040011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Huang, L., He, L. et al. Characteristics of concentrated lignocellulosic nanofibril suspensions. Cellulose 29, 147–158 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04304-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04304-9