Abstract
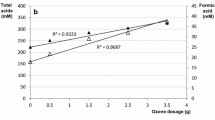
The black liquor (BL) obtained by straw pulping can hardly be applied to conventional alkali recovery systems because of its high concentration of silicon and viscosity. Soda-oxygen pulping can synchronously deposit silica on the surface of the cellulose to reduce the silicon content and viscosity of BL remarkably. In this paper, the BLs of wheat straw soda-oxygen pulping obtained at different end points (pH < 10, 11.5 < pH < 12) and conventional soda-anthraquinone (soda-AQ) were obtained. The extent of silicon removal and viscosity reduction before and after centrifugation or membrane filtration as well as the thermodynamic properties of the BLs were investigated. Compared with that achieved by soda-AQ, over 45% silicon was removed from BL after soda-oxygen cooking at a similar delignification level. The total solid (TS) concentration of the soda-oxygen BL was easily concentrated by up to approximately 50%. SiO2 can be further removed by simple centrifugation and membrane filtration, and its TS could be increased to 60% at 300 mp s. With cooking end point further decreased pH < 10, the centrifugated BL had the lowest silica content, the highest volumetric isothermal expansivity (VIE) value, and the lowest pyrolysis temperature.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belov NP, Lapshov SN, Mayorov EE, Sherstobitova AS, Yaskov AD (2012) Optical properties of black liquor and refractometric methods for monitoring the solid residue concentration in sulfate cellulose production. J Appl Spectrosc 79(3):499–502
Brown TR, Thilakaratne R, Brown RC, Hu G (2013) Techno-economic analysis of biomass to transportation fuels and electricity via fast pyrolysis and hydroprocessing. Fuel 106:463–469
Cardoso M, de Oliveira ED, Passos ML (2009) Chemical composition and physical properties of black liquors and their effects on liquor recovery operation in Brazilian pulp mills. Fuel 88(4):756–763
Danielewicz D, Surma-Slusarska B (2017) Properties and fibre characterisation of bleached hemp, birch and pine pulps: a comparison. Cellulose 24(11):5173–5186
Demirbas A, Pehlivan E, Altun T (2006) Potential evolution of Turkish agricultural residues as bio-gas, bio-char and bio-oil sources. Int J Hydrogen Energ 31(5):613–620
Guo D, Yuan H, Yin X, Wu C, Wu S, Zhou Z (2014) Effects of chemical form of sodium on the product characteristics of alkali lignin pyrolysis. Bioresource Technol 152:147–153
Jafari V, Labafzadeh SR, King A, Kilpelainen I, Sixta H, van Heiningen A (2014) Oxygen delignification of conventional and high alkali cooked softwood Kraft pulps, and study of the residual lignin structure. RSC Adv 4(34):17469–17477
Jiang S, Wang S (2009) Comprehensive harness measures to paper making with recycling pulp wastewater. Ind Water Treat 29(4):82–84
Jiang B, Zhang Y, Gu L, Wu W, Zhao H, Jin Y (2018) Structural elucidation and antioxidant activity of lignin isolated from rice straw and alkali oxygen black liquor. Int J Biol Macromol 116:513–519
Leite BS, Andreuccetti MT, Ferreira Leite SA, Hallak D’Angelo JV (2013) TG and DSC analyses of eucalyptus black liquor as alternative methods to estimate solids content. J Therm Anal Calorim 112(3):1539–1544
Li X, Huang Y, Gong J, Zhang X (2010) A study of the development of bio-energy resources and the status of eco-society in China. Energy 35:4451–4456
Li X, Jiao L, Fan Y, Chen L, Cai Y (2015) Effects of cellulose, xylan and lignin content on biomass pyrolysis characteristics and product distribution. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 31(13):236–243
Liu Q, Zhong Z, Wang S, Luo Z (2011) Interactions of biomass components during pyrolysis: A TG-FTIR study. J Anal Appl Pyrol 90(2):213–218
Liu C, Hu J, Zhang H, Xiao R (2016) Thermal conversion of lignin to phenols: Relevance between chemical structure and pyrolysis behaviors. Fuel 182:864–870
Lu J, Liu H, Song F, Xia F, Huang X, Zhang Z, Cheng Y, Wang H (2020) Combining hydrothermal-alkaline/oxygen pretreatment of reed with PEG 6, 000-assisted enzyme hydrolysis promote bioethanol fermentation and reduce enzyme loading. Ind Crop Prod 153:112615
Mohan D Jr, Pittman CU, Steele PH (2006) Pyrolysis of wood/biomass for bio-oil: A critical review. Energ Fuel 20(3):848–889
Oba Y, Naraoka H (2006) Carbon isotopic composition of acetic acid generated by hydrous pyrolysis of macromolecular organic matter from the Murchison meteorite. Meteorit Planet Sci 41(8):1175–1181
Pang C, Xie T, Lin L, Zhuang J, Liu Y, Shi J, Yang Q (2012) Changes of the surface structure of corn stalk in the cooking process with active oxygen and MgO-based solid alkali as a pretreatment of its biomass conversion. Bioresource Technol 103(1):432–439
Sun H, Zhang Y, Yang Y, Chen Y, Jeyakumar P, Shao Q, Zhou Y, Ma M, Zhu R, Qian Q, Fan Y, Xiang S, Zhai N, Li Y, Zhao Q, Wang H (2021) Effect of biofertilizer and wheat straw biochar application on nitrous oxide emission and ammonia volatilization from paddy soil. Environ Pollut 275:116640
Wang W, Gu F, Zhu JY, Sun K, Cai Z, Yao S, Wu W, Jin Y (2020) Fractionation of herbaceous biomass using a recyclable hydrotropic p-toluenesulfonic acid (p-TsOH)/choline chloride (ChCl) solvent system at low temperatures. Ind Crop Prod 150:112423
Wu C, Wang Z, Huang J, Williams PT (2013) Pyrolysis/gasification of cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin for hydrogen production in the presence of various nickel-based catalysts. Fuel 106:697–706
Xu Y, Sun H, Li X, Zhang D, Tian Y (2015) Method of black liquor combustion to remove silicon from wheat straw pulping. BioResources 10(2):1988–1997
Yang H, Xie Y, Zheng X, Pu Y, Huang F, Meng X, Wu W, Ragauskas A, Yao L (2016) Comparative study of lignin characteristics from wheat straw obtained by soda-AQ and kraft pretreatment and effect on the following enzymatic hydrolysis process. Bioresource Technol 207:361–369
Yang Y, Brammer JG, Wright DG, Scott JA, Serrano C, Bridgwater AV (2017) Combined heat and power from the intermediate pyrolysis of biomass materials: Performance, economics and environmental impact (vol 191, pg 639, 2017). Appl Energ 205:1610
Yue F, Chen K, Lu F (2016) Low Temperature soda-O2of bagasse. Molecules 21(1):85
Zhang L, Chen K (2017) pyrolysis behavior of the black liquor derived from soda-anthraquinone and soda-O2of rice straw at different reaction end points. Energ Fuel 31(1):514–522
Zhang L, Chen K, He L, Peng L (2018) Reinforcement of the bio-gas conversion from pyrolysis of wheat straw by hot caustic pre-extraction. Biotechnol Biofuels. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-018-1072-5
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21908127 and No. 21838006), National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFC1902101), and the Project Supported by the Foundation (No. KF201810) of Key Laboratory of Pulp and Paper Science and Technology of Ministry of Education/Shandong Province of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H., Chen, K., Zhang, L. et al. Synchronous silicon removal and viscosity reduction in the soda-oxygen pulping of wheat straw. Cellulose 28, 9081–9089 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04078-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-04078-0