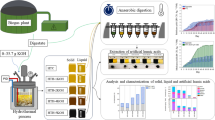
Abstract
Direct valorization of cellulosic biomass waste into energy is beneficial based on the concept of waste-to-energy. Pyrolysis of the biomass waste opens a chance to upgrade the valueless waste into value-added platform chemicals such as syngas (H2 and CO). This study focused on valorization of sesame seed waste (SSW), a biomass waste material collected after sesame oil extraction, into syngas. To enhance syngas production and make this process more environmentally benign, CO2 was added as co-reactant during SSW pyrolysis. In the presence of CO2, pyrolysis of SSW showed enhanced CO formation (670 %), comparing with pyrolysis under N2, due to the gas phase reactions (GPRs) between CO2 and volatile hydrocarbons resulted from pyrolysis of SSW. To enhance syngas production from SSW pyrolysis, mesoporous nickel-based catalyst was used for catalytic pyrolysis due to its known catalytic capability for chemical bond scissions of hydrocarbons and biomass-derived oxygenates. The enhanced production of syngas was proportionate to catalytic bed temperature (500, 600, and 700 °C) and catalyst loadings (0.2, 0.5, and 1 g), and the GPRs were independent with H2 formation. All experimental findings indicated that CO2-assisted catalytic pyrolysis significantly improved H2 and CO formations from a cellulosic biomass waste material, controlling the CO concentration with an introduction of CO2.
Graphic abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balat M (2011) Production of bioethanol from lignocellulosic materials via the biochemical pathway: a review. Energy Convers Manag 52:858–875. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2010.08.013
Banerjee A, Chakraborty R (2009) Parametric sensitivity in transesterification of waste cooking oil for biodiesel production: a review. Resour Conserv Recycl 53:490–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2009.04.003
Cho S-H, Oh J-I, Jung S, Park Y-K, Tsang YF, Ok YS, Kwon EE (2020) Catalytic pyrolytic platform for scrap tires using CO2 and steel slag. Appl Energy 259:114164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2019.114164
Chu S, Cui Y, Liu N (2017) The path towards sustainable energy. Nat Mater 16:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat4834
Cui X, Kær SK (2020) A comparative study on three reactor types for methanol synthesis from syngas and CO2. Chem Eng J 393:124632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124632
Cui X et al (2019) Room-temperature electrochemical water–gas shift reaction for high purity hydrogen production. Nat Commun 10:86. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07937-w
Eryilmaz T, Yesilyurt MK, Cesur C, Gokdogan O (2016) Biodiesel production potential from oil seeds in Turkey. Renew Sust Energy Rev 58:842–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.172
Foong SY et al (2020) Valorization of biomass waste to engineered activated biochar by microwave pyrolysis: progress, challenges, and future directions. Chem Eng J 389:124401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.124401
Hu Y, Du C, Leu S-Y, Jing H, Li X, Lin CSK (2018) Valorisation of textile waste by fungal solid state fermentation: an example of circular waste-based biorefinery. Resour Conserv Recycl 129:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2017.09.024
Huber GW, Iborra S, Corma A (2006) Synthesis of transportation fuels from biomass: chemistry, catalysts, and engineering. Chem Rev 106:4044–4098. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr068360d
Hunt J, Ferrari A, Lita A, Crosswhite M, Ashley B, Stiegman AE (2013) Microwave-specific enhancement of the carbon–carbon dioxide (boudouard) reaction. J Phys Chem C 117:26871–26880. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp4076965
Jung S, Park Y-K, Kwon EE (2019) Strategic use of biochar for CO2 capture and sequestration. J CO2 Util 32:128–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcou.2019.04.012
Jung S, Kim H, Fai Tsang Y, Andrew Lin K-Y, Park Y-K, Kwon EE (2020a) A new biorefinery platform for producing (C2–5) bioalcohols through the biological/chemical hybridization process. Bioresour Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.1235682020.123568
Jung S, Lee J, Park Y-K, Kwon EE (2020b) Bioelectrochemical systems for a circular bioeconomy. Bioresour Technol 300:122748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.122748
Jung S, Lee S, Park Y-K, Lee KH, Kwon EE (2020c) CO2-mediated catalytic pyrolysis of rice straw for syngas production and power generation. Energy Convers Manag 220:113057. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2020.113057
Kandola BK, Horrocks AR (1996) Complex char formation in flame-retarded fibre-intumescent combinations—II. Thermal analytical studies. Polym Degrad Stab 54:289–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0141-3910(96)00054-7
Khounani Z, Nazemi F, Shafiei M, Aghbashlo M, Tabatabaei M (2019) Techno-economic aspects of a safflower-based biorefinery plant co-producing bioethanol and biodiesel. Energy Convers Manag 201:112184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.112184
Kim S, Kwon EE, Kim YT, Jung S, Kim HJ, Huber GW, Lee J (2019a) Recent advances in hydrodeoxygenation of biomass-derived oxygenates over heterogeneous catalysts. Green Chem 21:3715–3743. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9GC01210A
Kim Y, Oh J-I, Vithanage M, Park Y-K, Lee J, Kwon EE (2019b) Modification of biochar properties using CO2. Chem Eng J 372:383–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.04.170
Kwon EE, Cho S-H, Kim S (2015) Synergetic sustainability enhancement via utilization of carbon dioxide as carbon neutral chemical feedstock in the thermo-chemical processing of biomass. Environ Sci Technol 49:5028–5034. https://doi.org/10.1021/es505744n
Kwon D, Lee SS, Jung S, Park Y-K, Tsang YF, Kwon EE (2020) CO2 to fuel via pyrolysis of banana peel. Chem Eng J 392:123774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.123774
Lahijani P, Zainal ZA, Mohammadi M, Mohamed AR (2015) Conversion of the greenhouse gas CO2 to the fuel gas CO via the Boudouard reaction: a review. Renew Sust Energy Rev 41:615–632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2014.08.034
Lee K-H (2009) Thermal and catalytic degradation of pyrolytic oil from pyrolysis of municipal plastic wastes. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 85:372–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2008.11.032
Lee T et al (2020) Using CO2 as an oxidant in the catalytic pyrolysis of peat moss from the North Polar Region. Environ Sci Technol 54:6329–6343. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c01862
Li J, Yan R, Xiao B, Liang DT, Du L (2008a) Development of nano-NiO/Al2O3 catalyst to be used for tar removal in biomass gasification. Environ Sci Technol 42:6224–6229. https://doi.org/10.1021/es800138r
Li J, Yan R, Xiao B, Liang DT, Lee DH (2008b) Preparation of nano-NiO particles and evaluation of their catalytic activity in pyrolyzing biomass components. Energy Fuels 22:16–23. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef700283j
Li X, Chen G, Liu C, Ma W, Yan B, Zhang J (2017) Hydrodeoxygenation of lignin-derived bio-oil using molecular sieves supported metal catalysts: a critical review. Renew Sust Energy Rev 71:296–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.12.057
Lim S, Lee K-T (2013) Influences of different co-solvents in simultaneous supercritical extraction and transesterification of Jatropha curcas L. seeds for the production of biodiesel. Chem Eng J 221:436–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.02.014
Muktham R, Ball AS, Bhargava SK, Bankupalli S (2016) Bioethanol production from non-edible de-oiled Pongamia pinnata seed residue-optimization of acid hydrolysis followed by fermentation. Ind Crop Prod 94:490–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2016.09.019
Nakomcic-Smaragdakis B, Cepic Z, Dragutinovic N (2016) Analysis of solid biomass energy potential in Autonomous Province of Vojvodina. Renew Sust Energy Rev 57:186–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.118
Norouzi O, Jafarian S, Safari F, Tavasoli A, Nejati B (2016) Promotion of hydrogen-rich gas and phenolic-rich bio-oil production from green macroalgae Cladophora glomerata via pyrolysis over its bio-char. Bioresour Technol 219:643–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.08.017
Pal N, Im S, Cho E-B, Kim H, Park J (2020) Superparamagnetic NiO-doped mesoporous silica flower-like microspheres with high nickel content. J Ind Eng Chem 81:99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2019.08.058
Papapetridis I, Goudriaan M, Vázquez Vitali M, de Keijzer NA, van den Broek M, van Maris AJA, Pronk JT (2018) Optimizing anaerobic growth rate and fermentation kinetics in Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains expressing Calvin-cycle enzymes for improved ethanol yield. Biotechnol Biofuels 11:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13068-017-1001-z
Park J, Lee Y, Ryu C, Park Y-K (2014) Slow pyrolysis of rice straw: analysis of products properties, carbon and energy yields. Bioresour Technol 155:63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2013.12.084
Ramachandran S, Singh SK, Larroche C, Soccol CR, Pandey A (2007) Oil cakes and their biotechnological applications: a review. Bioresour Technol 98:2000–2009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2006.08.002
Remón J, Casales M, Gracia J, Callén MS, Pinilla JL, Suelves I (2020) Sustainable production of liquid biofuels and value-added platform chemicals by hydrodeoxygenation of lignocellulosic bio-oil over a carbon-neutral Mo2C/CNF catalyst. Chem Eng J. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.1267052020.126705
Rezania S et al (2019) Review on transesterification of non-edible sources for biodiesel production with a focus on economic aspects, fuel properties and by-product applications. Energy Convers Manag 201:112155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.112155
Ruddy DA, Schaidle JA, Ferrell Iii JR, Wang J, Moens L, Hensley JE (2014) Recent advances in heterogeneous catalysts for bio-oil upgrading via “ex situ catalytic fast pyrolysis”: catalyst development through the study of model compounds. Green Chem 16:454–490. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3GC41354C
Sait HH, Hussain A, Salema AA, Ani FN (2012) Pyrolysis and combustion kinetics of date palm biomass using thermogravimetric analysis. Bioresour Technol 118:382–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.04.081
Salihu A, Alam MZ, AbdulKarim MI, Salleh HM (2012) Lipase production: an insight in the utilization of renewable agricultural residues. Resour Conserv Recycl 58:36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resconrec.2011.10.007
Santamaria L, Lopez G, Arregi A, Amutio M, Artetxe M, Bilbao J, Olazar M (2019) Stability of different Ni supported catalysts in the in-line steam reforming of biomass fast pyrolysis volatiles. Appl Catal B 242:109–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.09.081
Santamaria L, Arregi A, Lopez G, Artetxe M, Amutio M, Bilbao J, Olazar M (2020) Effect of La2O3 promotion on a Ni/Al2O3 catalyst for H2 production in the in-line biomass pyrolysis-reforming. Fuel 262:116593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116593
Serrano-Ruiz JC, Dumesic JA (2011) Catalytic routes for the conversion of biomass into liquid hydrocarbon transportation fuels. Energyy Environ Sci 4:83–99. https://doi.org/10.1039/C0EE00436G
Shahabuddin M, Krishna BB, Bhaskar T, Perkins G (2020) Advances in the thermo-chemical production of hydrogen from biomass and residual wastes: summary of recent techno-economic analyses. Bioresour Technol 299:122557. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122557
Shigarov A (2020) Modeling of low temperature steam reforming of flare gas to methane-rich fuel gas on Ni catalyst in different types of reactors. Chem Eng J 397:125313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125313
Trebbi D et al (2019) Identification and validation of SNP markers linked to seed toxicity in Jatropha curcas L. Sci Rep 9:10220. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46698-4
Zhang X et al (2017) Generalized two-dimensional correlation infrared spectroscopy to reveal mechanisms of CO2 capture in nitrogen enriched biochar. Proc Combust Inst 36:3933–3940. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proci.2016.06.062
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF- 2019R1A4A1027795). E.-B. Cho acknowledges supports under the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2020R1A2C1015117). This research was also conducted with the support of the Korea Environmental Industry and Technology Institute (KEITI) as a funding from the Ministry of Environment in 2020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, SH., Cho, EB., Lee, JH. et al. Synergistic benefits for hydrogen production through CO2-cofeeding catalytic pyrolysis of cellulosic biomass waste. Cellulose 28, 4781–4792 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03810-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-021-03810-0