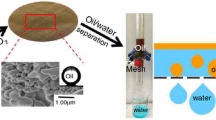
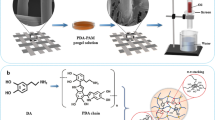
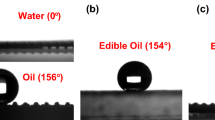
Abstract
The development of sustainable, low-cost, green and efficient oil–water separation materials is an attractive and challenging work. Oil/water separation process has been achieved by a variety of materials with special wettability, but most materials require complex instruments or involve toxic and corrosive chemicals, which might lead to some potential economic and environmental issues. Our work proposed here is a novel super-hydrophilic, underwater super-oleophobic cellulose hydrogel-coated mesh (CHCM) which produced by deep eutectic solvent, aimed for efficient gravity-driven oil/water separation. Based on this pre-wet CHCM, the separation efficiency of various oil–water mixtures was above 98.0%, and the results also showed that CHCM has good recyclability and durability, even after 20 cycles, the separation efficiency also maintained at 98.5%. Impressively, the prepared CHCM also exhibited good salt resistance; it can separate a high efficiency pump oil mixture from a saturated aqueous NaCl solution. Through XPS analysis of CHCM, the oil–water separation mechanism is due to the large number of super-hydrophilic groups on its surface. This simple, green, and efficient method overcomes an important barrier to the safe separation of oil–water mixtures and provides insights into the design of advanced materials for practical oil–water separation.
Graphic abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ao C, Yuan W, Zhao J, He X, Zhang X, Li Q, Xia T, Zhang W, Lu C (2017) Superhydrophilic graphene oxide@electrospun cellulose nanofiber hybrid membrane for high-efficiency oil/water separation. Carbohydr Polym 175:216–222
Ao C, Hu R, Zhao J, Zhang X, Li Q, Xia T, Zhang W, Lu C (2018) Reusable, salt-tolerant and superhydrophilic cellulose hydrogel-coated mesh for efficient gravity-driven oil/water separation. Chem Eng J 338:271–277
Cai D, Ma P (2019) Hydrogel-coated basalt fibre with superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic performance for oil–water separation. Compos Commun 14:1–6
Cao Y, Zhang X, Tao L, Li K, Xue Z, Feng L, Wei Y (2013) Mussel-inspired chemistry and michael addition reaction for efficient oil/water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:4438–4442
Chen F, Song J, Liu Z, Liu J, Zheng H, Huang S, Sun J, Xu W, Liu X (2016) Atmospheric pressure plasma functionalized polymer mesh: an environmentally friendly and efficient tool for oil/water separation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:6828–6837
Chen J, Shi X, Ren L, Wang Y (2017) Graphene oxide/PVA inorganic/organic interpenetrating hydrogels with excellent mechanical properties and biocompatibility. Carbon 111:18–27
De France KJ, Chan KJW, Cranston ED, Hoare T (2016) Enhanced mechanical properties in cellulose nanocrystal–poly(oligoethylene glycol methacrylate) injectable nanocomposite hydrogels through control of physical and chemical cross-linking. Biomacromol 17:649–660
De France KJ, Hoare T, Cranston ED (2017) Review of hydrogels and aerogels containing nanocellulose. Chem Mater 29:4609–4631
Ejaz Ahmed F, Lalia BS, Hilal N, Hashaikeh R (2014) Underwater superoleophobic cellulose/electrospun PVDF–HFP membranes for efficient oil/water separation. Desalination 344:48–54
Errokh A, Magnin A, Putaux J, Boufi S (2018) Morphology of the nanocellulose produced by periodate oxidation and reductive treatment of cellulose fibers. Cellulose 25:3899–3911
Feng L, Zhang Z, Mai Z, Ma Y, Liu B, Jiang L, Zhu D (2004) A super-hydrophobic and super-oleophilic coating mesh film for the separation of oil and water. Angew Chem 116:2046–2048
Gao X, Xu L, Xue Z, Feng L, Peng J, Wen Y, Wang S, Zhang X (2014) Dual-scaled porous nitrocellulose membranes with underwater superoleophobicity for highly efficient oil/water separation. Adv Mater 26:1771–1775
Ge J, Zhao H, Zhu H, Huang J, Shi L, Yu S (2016) Advanced sorbents for oil-spill cleanup: recent advances and future perspectives. Adv Mater 28:10459–10490
Gu J, Xiao P, Chen J, Zhang J, Huang Y, Chen T (2014) Janus polymer/carbon nanotube hybrid membranes for oil/water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:16204–16209
Huang Y, Li H, Wang L, Qiao Y, Tang C, Jung C, Yoon Y, Li S, Yu M (2015) Ultrafiltration membranes with structure-optimized graphene-oxide coatings for antifouling oil/water separation. Adv Mater Interfaces 2:1400433
Ju H, McCloskey BD, Sagle AC, Wu Y, Kusuma VA, Freeman BD (2008) Crosslinked poly(ethylene oxide) fouling resistant coating materials for oil/water separation. J Membr Sci 307:260–267
Li J, Shi L, Chen Y, Zhang Y, Guo Z, Su B, Liu W (2012) Stable superhydrophobic coatings from thiol-ligand nanocrystals and their application in oil/water separation. J Mater Chem 22:9774
Li L, Zhang G, Su Z (2016a) One-step assembly of phytic acid metal complexes for superhydrophilic coatings. Angew Chem Int Ed 55:9093–9096
Li Y, Zhang H, Fan M, Zhuang J, Chen L (2016b) A robust salt-tolerant superoleophobic aerogel inspired by seaweed for efficient oil–water separation in marine environments. Phys Chem Chem Phys PCCP 18:25394–25400
Li P, Sirviö JA, Haapala A, Liimatainen H (2017) Cellulose nanofibrils from nonderivatizing urea-based deep eutectic solvent pretreatments. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:2846–2855
Liu L, Chen C, Yang S, Xie H, Gong M, Xu X (2016) Fabrication of superhydrophilic-underwater superoleophobic inorganic anti-corrosive membranes for high-efficiency oil/water separation. Phys Chem Chem Phys 18:1317–1325
Liu Y, Guo B, Xia Q, Meng J, Chen W, Liu S, Wang Q, Liu Y, Li J, Yu H (2017) Efficient cleavage of strong hydrogen bonds in cotton by deep eutectic solvents and facile fabrication of cellulose nanocrystals in high yields. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:7623–7631
Ma Q, Cheng H, Fane AG, Wang R, Zhang H (2016) Recent development of advanced materials with special wettability for selective oil/water separation. Small 12:2186–2202
Ma Q, Cheng H, Yu Y, Huang Y, Lu Q, Han S, Chen J, Wang R, Fane AG, Zhang H (2017) Preparation of superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic nanofiber-based meshes from waste glass for multifunctional oil/water separation. Small 13:1700391
Maguire-Boyle SJ, Barron AR (2011) A new functionalization strategy for oil/water separation membranes. J Membr Sci 382:107–115
Obaid M, Barakat NAM, Fadali OA, Motlak M, Almajid AA, Khalil KA (2015) Effective and reusable oil/water separation membranes based on modified polysulfone electrospun nanofiber mats. Chem Eng J 259:449–456
Pan Q, Wang M, Wang H (2008) Separating small amount of water and hydrophobic solvents by novel superhydrophobic copper meshes. Appl Surf Sci 254:6002–6006
Phiri I, Eum KY, Kim JW, Choi WS, Kim SH, Ko JM, Jung H (2019) Simultaneous complementary oil–water separation and water desalination using functionalized woven glass fiber membranes. J Ind Eng Chem 73:78–86
Su B, Tian Y, Jiang L (2016) Bioinspired interfaces with superwettability: from materials to chemistry. J Am Chem Soc 138:1727–1748
Tao M, Xue L, Liu F, Jiang L (2014) An intelligent superwetting PVDF membrane showing switchable transport performance for oil/water separation. Adv Mater 26:2943–2948
Thoniyot P, Tan MJ, Karim AA, Young DJ, Loh XJ (2015) Nanoparticle–hydrogel composites: concept, design, and applications of these promising, multi-functional materials. Adv Sci 2:1400010
Wang B, Liang W, Guo Z, Liu W (2015) Biomimetic super-lyophobic and super-lyophilic materials applied for oil/water separation: a new strategy beyond nature. Chem Soc Rev 44:336–361
Wang X, Xu S, Tan Y, Du J, Wang J (2016a) Synthesis and characterization of a porous and hydrophobic cellulose-based composite for efficient and fast oil–water separation. Carbohydr Polym 140:188–194
Wang X, Yu J, Sun G, Ding B (2016b) Electrospun nanofibrous materials: a versatile medium for effective oil/water separation. Mater Today 19:403–414
Xue Z, Wang S, Lin L, Chen L, Liu M, Feng L, Jiang L (2011) A novel superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic hydrogel-coated mesh for oil/water separation. Adv Mater 23:4270–4273
Xue C, Ji P, Zhang P, Li Y, Jia S (2013) Fabrication of superhydrophobic and superoleophilic textiles for oil–water separation. Appl Surf Sci 284:464–471
Xue Z, Cao Y, Liu N, Feng L, Jiang L (2014) Special wettable materials for oil/water separation. J Mater Chem A 2:2445–2460
Yin K, Chu D, Dong X, Wang C, Duan J, He J (2017) Femtosecond laser induced robust periodic nanoripple structured mesh for highly efficient oil–water separation. Nanoscale 9:14229–14235
Yoon H, Na S, Choi J, Latthe SS, Swihart MT, Al-Deyab SS, Yoon SS (2014) Gravity-driven hybrid membrane for oleophobic–superhydrophilic oil–water separation and water purification by graphene. Langmuir 30:11761–11769
Yu Z, Yun FF, Gong Z, Yao Q, Dou S, Liu K, Jiang L, Wang X (2017) A novel reusable superhydrophilic NiO/Ni mesh produced by a facile fabrication method for superior oil/water separation. J Mater Chem A 5:10821–10826
Zhang J, Seeger S (2011) Polyester materials with superwetting silicone nanofilaments for oil/water separation and selective oil absorption. Adv Funct Mater 21:4699–4704
Zhang S, Lu F, Tao L, Liu N, Gao C, Feng L, Wei Y (2013a) Bio-inspired anti-oil-fouling chitosan-coated mesh for oil/water separation suitable for broad pH range and hyper-saline environments. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:11971–11976
Zhang X, Li Z, Liu K, Jiang L (2013b) Bioinspired multifunctional foam with self-cleaning and oil/water separation. Adv Funct Mater 23:2881–2886
Zhang Q, Liu N, Wei Y, Feng L (2018) Facile fabrication of hydrogel coated membrane for controllable and selective oil-in-water emulsion separation. Soft Matter 14:2649–2654
Zhou X, Zhang Z, Xu X, Guo F, Zhu X, Men X, Ge B (2013) Robust and durable superhydrophobic cotton fabrics for oil/water separation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 5:7208–7214
Zhou K, Zhang QG, Li HM, Guo NN, Zhu AM, Liu QL (2014) Ultrathin cellulose nanosheet membranes for superfast separation of oil-in-water nanoemulsions. Nanoscale 6:10363
Zhou C, Cheng J, Hou K, Zhao A, Pi P, Wen X, Xu S (2016a) Superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic titania nanowires surface for oil repellency and oil/water separation. Chem Eng J 301:249–256
Zhou S, Liu P, Wang M, Zhao H, Yang J, Xu F (2016b) Sustainable, reusable, and superhydrophobic aerogels from microfibrillated cellulose for highly effective oil/water separation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:6409–6416
Zhou C, Cheng J, Hou K, Zhu Z, Zheng Y (2017) Preparation of CuWO4@ Cu2O film on copper mesh by anodization for oil/water separation and aqueous pollutant degradation. Chem Eng J 307:803–811
Zhu X, Tu W, Wee K, Bai R (2014) Effective and low fouling oil/water separation by a novel hollow fiber membrane with both hydrophilic and oleophobic surface properties. J Membr Sci 466:36–44
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21978248, 21676223), the special fund for Fujian Ocean High-Tech Industry Development (No. FJHJF-L-2018-1), China, and the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian, China (No. 2019J06005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 2 (MP4 36295 kb)
Supplementary material 3 (MP4 54423 kb)
Supplementary material 4 (MP4 27257 kb)
Supplementary material 5 (MP4 22381 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Li, J., Yu, X. et al. Facile fabrication of super-hydrophilic cellulose hydrogel-coated mesh using deep eutectic solvent for efficient gravity-driven oil/water separation. Cellulose 28, 949–960 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03578-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03578-9