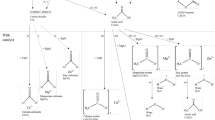
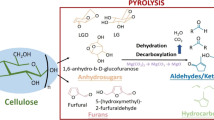
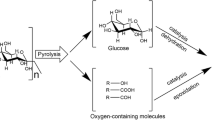
Abstract
Reaction atmosphere is one of the principle reaction parameters affecting the pyrolysis of biomass. At elevated temperatures, in addition to gases, organics are also regarded as part of the reaction atmosphere. In this study, the impacts of the co-feeding of formic acid or acetic acid on the pyrolysis behaviour of cellulose were investigated at 400 and 600 °C, respectively. The results showed that the co-feeding of the acids significantly affected properties of both the resulting bio-oil and biochar. Co-feeding of acetic acid remarkably promoted formation of heavier organics with π-conjugated structures, while the presence of formic acid suppressed their evolution, especially at the lower pyrolysis temperature of 400 °C. The co-feeding of the carboxylic acids increased the yields of biochar. Furthermore, the co-feeding of formic acid or acetic acid also affected the elemental composition, the defective structure, the crystallinity and the thermal stabilities of the resulting biochar at varied pyrolysis temperature in the distinct ways. The carboxylic acids or their derivatives interfered with the formation of the volatiles or reacted directly with the organic components on surface of biochar, which substantially modified the physiochemical properties of the biochar.
Graphic abstract

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali N, Saleem M, Shahzad K, Hussain S, Chughtai A (2016) Effect of operating parameters on production of bio-oil from fast pyrolysis of maize stalk in bubbling fluidized bed reactor. Pol J Chem Technol 18:88–96. https://doi.org/10.1515/pjct-2016-0053
Bridgwater AV (2012) Review of fast pyrolysis of biomass and product upgrading. Biomass Bioenerg 38:68–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2011.01.048
Borrego AG, Garavaglia L, Kalkreuth WD (2009) Characteristics of high heating rate biomass chars prepared under N2 and CO2 atmospheres. Int J Coal Geol 77:409–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coal.2008.06.004
Baldauf W, Balfanz U, Rupp M (1994) Upgrading of flash pyrolysis oil and utilization in refineries. Biomass Bioenerg 7(1–6):237–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/0961-9534(94)00065-2
Carpenter D, Westover TL, Czernika S, Jablonski W (2014) Biomass feedstocks for renewable fuel production: a review of the impacts of feedstock and pretreatment on the yield and product distribution of fast pyrolysis bio-oils and vapors. Green Chem 16:384–406. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3GC41631C
Dickerson T, Soria J (2013) Catalytic fast pyrolysis: a review. Energies 6(1):514–538. https://doi.org/10.3390/en6010514
Elliott DC (2007) Historical developments in hydroprocessing bio-oils. Energ Fuel 21(3):1792–1815. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef070044u
Elliott DC, Hart TR, Neuenschwander GG, Rotness LJ, Zacher AH (2009) Catalytic hydroprocessing of biomass fast pyrolysis bio-oil to produce hydrocarbon products. Environ Prog Sustain 28(3):441–449. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.10384
Fermoso J, Hernando H, Jana P, Moreno I, Prech J, Hernandez O, Pizarro P, Coronado JM, Cejka J, Serrano DP (2016) Lamellar and pillared ZSM-5 zeolites modified with MgO and ZnO for catalytic fastpyrolysis of eucalyptus woodchips. Catal Today 277:171–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2015.12.009
Gholizadeh M, Gunawan R, Hu X, de Miguel MF, Westerhof R, Chaitwat W, Li C-Z (2016a) Effects of temperature on the hydrotreatment behaviour of pyrolysis bio-oil and coke formation in a continuous hydrotreatment reactor. Fuel Process Technol 148:175–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2016.03.002
Gholizadeh M, Gunawan R, Hu X, Hasan MM, Kersten S, Westerhof R, Li C-Z (2016b) Different reaction behaviours of the light and heavy components of bio-oil during the hydrotreatment in a continuous pack-bed reactor. Fuel Process Technol 146:76–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2016.01.026
Gholizadeh M, Gunawan R, Hu X, Kadarwati S, Westerhof R, Chaiwat W, Li C-Z (2016c) Importance of hydrogen and bio-oil inlet temperature during the hydrotreatment of bio-oil. Fuel Process Technol 150:132–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2016.05.014
Gholizadeh M, Hu X, Liu Q (2019) A mini review of the specialties of the bio-oils produced from pyrolysis of 20 different biomasses. Renew Sust Energ Rev 114:109313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109313
Gunawan R, Li X, Lievens C, Gholizadeh M, Chaiwat W, Hu X, Li C-Z (2013) Upgrading of bio-oil into advanced biofuels and chemicals. Part I. Transformation of GC-detectable light species during the hydrotreatment of bio-oil using Pd/C catalyst. Fuel 111:709–717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2013.04.002
Goyal HB, Seal D, Saxena RC (2008) Bio-fuels from thermochemical conversion of renewable resources: a review. Renew Sust Energ Rev 12:504–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2006.07.014
Guizani C, Sanz FE, Salvador S (2014) Effects of CO2 on biomass fast pyrolysis: reaction rate, gas yields and char reactive properties. Fuel 116:310–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2013.07.101
Hu X, Gholizadeh M (2019) Biomass pyrolysis: A review of the process development and challenges from initial researches up to the commercialisation stage. J Energy Chem 39:109–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jechem.2019.01.024
Hu X, Gunawan R, Mourant D, Hasan MDM, Wu L, Song Y, Lievens C, Li C-Z (2017) Upgrading of bio-oil via acid-catalyzed reactions in alcohols-a mini review. Fuel Process Technol 155:2–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2016.08.020
Hu X, Gunawan R, Mourant D, Lievens C, Li X, Zhang S, Chaiwat W, Li C-Z (2012a) Acid-catalysed reactions between methanol and the bio-oil from the fast pyrolysis of mallee bark. Fuel 97:512–522. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2012.02.032
Hu X, Guo HY, Gholizadeh M, Sattari B, Liu Q (2019) Pyrolysis of different wood species: impacts of C/H ratio in feedstock on distribution of pyrolysis products. Biomass Bioenerg 120:28–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2018.10.021
Hu X, Lievens C, Mourant D, Wang Y, Wu L, Gunawan R, Song Y, Li C-Z (2013) Investigation of deactivation mechanisms of a solid acid catalyst during esterification of the bio-oils from mallee biomass. Appl Energ 111:94–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.04.078
Hu X, Wang Y, Mourant D, Gunawan R, Lievens C, Chaiwat W, Gholizadeh M, Wu L, Li X, Li C-Z (2012b) Polymerization on heating up of bio-oil: a model compound study. AIChE J 59:888–900. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.13857
Hasan MDM, Wang XS, Mourant D, Gunawan R, Yu C, Hu X, Kadarwati S, Gholizadeh M, Wu H, Li B, Zhang L, Li C-Z (2017) Grinding pyrolysis of Mallee wood: effects of pyrolysis conditions on the yields of bio-oil and biochar. Fuel Process Technol 167:215–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2017.07.004
Iliopoulou EF, Antonakou EV, Karakoulia SA, Vasalos IA, Lappas AA, Triantafyllidis KS (2007) Catalytic conversion of biomass pyrolysis products by mesoporous materials: effect of steam stability and acidity of Al-MCM-41 catalysts. Chem Eng J 134:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2007.03.066
Iliopoulou EF, Triantafyllidis KS, Lappas AA (2018) Overview of catalytic upgrading of biomass pyrolysis vapors toward the production of fuels and high-value chemicals. Wires Energy Environ 1:1–29. https://doi.org/10.1002/wene.322
Kwon EE, Jeon YJ, Yi H (2012) New candidate for biofuel feedstock beyond terrestrial biomass for thermo-chemical process (pyrolysis/gasification) enhanced by carbon dioxide (CO2). Bioresource Technol 123:637–677. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2012.07.035
Kan T, Strezov V, Evans TJ (2016) Lignocellulosic biomass pyrolysis: a review of product properties and effects of pyrolysis parameters. Renew Sust Energ Rev 57:1126–1140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.185
Li X, Hayashi JI, Li C-Z (2006) FT-Raman spectroscopic study of the evolution of char structure during the pyrolysis of a Victorian brown coal. Fuel 85:1700–1707. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2006.03.008
Lievens C, Mourant D, He M, Gunawan R, Li X, Li C-Z (2011) An FT-IR spectroscopic study of carbonyl functionalities in bio-oils. Fuel 90(11):3417–3423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2011.06.001
Montoya JI, Chejne-Janna F, Garcia-Pérez M (2015) Fast pyrolysis of biomass: A review of relevant aspects: Part I: Parametric study. DYNA 82(192):239–248. https://dx.doi.org/10.15446/dyna.v82n192.44701
Onal E, Uzun BB, Putun AE (2017) The effect of pyrolysis atmosphere on bio-oil yields and structure. Int J Green Energy 14:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/15435075.2014.952421
Putun E, Ates F, Putun AE (2008) Catalytic pyrolysis of biomass in inert and steam atmospheres. Fuel 87:815–824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2007.05.042
Qiang L, Wen-Zhi L, Xi-Feng Z (2009) Overview of fuel properties of biomass fast pyrolysis oils. Energ Convers Manage 50:1376–1383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2009.01.001
Ragucci R, Giudicianni P, Cavaliere A (2013) Cellulose slow pyrolysis products in a pressurized steam flow reactor. Fuel 107:122–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2013.01.057
Venderbosch RH, Ardiyanti AR, Wildschut J, Oasmaa A, Heeres HJ (2010) Stabilization of biomass-derived pyrolysis oils. J Chem Technol Biot 85(5):674–686. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.2354
Xu Z, Liang L, Zhang Q, Wang X, Liu J, Shen H, Huang W (2019) A study on catalytic depolymerization of a typical perhydrous coal for improving tar yield. J Anal Appl Pyrol 138:242–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2019.01.001
Xiong W-M, Zhu M-Z, Deng L, Fu Y, Guo Q-X (2009) Esterification of organic acid in bio-oil using acidic ionic liquid catalysts. Energ Fuel 23:2278–2283. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef801021j
Yang X, Zhao Y, Li R, Wu Y, Yang M (2018) A modified kinetic analysis method of cellulose pyrolysis based on TG–FTIR technique. Thermochim Acta 665:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tca.2018.05.008
Zhang Q, Chang J, Wang T, Xu Y (2007) Review of biomass pyrolysis oil properties and upgrading research. Energ Convers Manage 48(1):87–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2006.05.010
Zhang C, Hu X, Guo H, Wei T, Dong D, Hu G, Hu S, Xiang J, Liu Q, Wang Y (2018a) Pyrolysis of poplar, cellulose and lignin: Effects of acidity and alkalinity of the metal oxide catalysts. J Anal Appl Pyrol 134:590–605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2018.08.009
Zhang LJ, Hu GZ, Hu S, Xiang J, Hu X, Wang Y, Geng DS (2018b) Hydrogenation of fourteen biomass-derived phenolics in water and in methanol: their distinct reaction behaviours. Sustainable Energ Fuel 2:751–758. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8SE00006A
Zhang Z, Wang Q, Yang X, Chatterjee S, Pittman CU (2010) Sufonic acid resin-catalyzed addition of phenols, carboxylic acids, and water to olefins: model reactions for catalytic upgrading of bio-oil. Bioresource Technol 101:3685–3695. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2009.12.100
Zhang H, Xiao R, Wang D, He G, Shao S, Zhang J, Zhong Z (2011) Biomass fast pyrolysis in a fluidized bed reactor under N2, CO2, CO, CH4 and H2 atmospheres. Bioresource Technol 102:4258–4264. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2010.12.075
Zhang CT, Zhang L, Li Q, Wang Y, Liu Q, Wei T, Dong D, Salavati S, Gholizadeh M, Hu X (2019) Catalytic pyrolysis of poplar wood over transition metal oxides: correlation of catalytic behaviors with physiochemical properties of the oxides. Biomass Bioenerg 124:125–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2019.03.017
Zhang CT, Zhang Z, Zhang L, Li Q, Li C, Chen G, Zhang S, Liu Q, Hu X (2020a) Evolution of the functionalities and structures of biochar in pyrolysis of poplar in a wide temperature range. Bioresource Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123002
Zhang Z, Zhang X, Zhang L, Wang Y, Li X, Zhang S, Liu Q, Wei T, Gao G, Hu X (2020b) Steam reforming of guaiacol over Ni/SiO2 catalyst modified with basic oxides: impacts of alkalinity on properties of coke. Energ Convers Manage 205:112301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2019.112301
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51876080), the Strategic International Scientific and Technological Innovation Cooperation Special Funds of National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2016YFE0204000), the Program for Taishan Scholars of Shandong Province Government, the Recruitment Program of Global Experts (Thousand Youth Talents Plan), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2017BB002) and the Key Research and Development Program of Shandong Province (2018GSF116014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Z., Zhang, C., Zhang, L. et al. Pyrolysis of cellulose with co-feeding of formic or acetic acid. Cellulose 27, 4909–4929 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03118-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03118-5