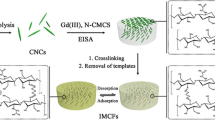
Abstract
Rare earth elements are a treasure trove of new materials in the twenty-first century, however, the similar radii of the lanthanide metals make it difficult for the ionic rare earth elements to be selectively separated. Ion-imprinted technology can help to selectively separate rare earth elements, nevertheless, most materials used for ion-imprinted are expensive. Chitosan has a wide range of sources, low cost, and a large quantity of amino and hydroxyl groups, which is advantageous for adsorbing heavy metals. Most scholars have made chitosan into a shape such as microspheres, which does not exert the great value of chitosan and is difficult to recycle, which greatly affects the adsorption rate. There are few studies on increasing the specific surface area of chitosan, so there is still much room for improvement in the adsorption capacity of chitosan. In order to improve the performance of chitosan-based materials, this research reports the preparation of imprinted nanofiber chitosan films (INFCF) by ion-imprinted technique and low-temperature thermal phase separation. These methods not only make the material have a high BET surface area, but also enable the material to have selective adsorption capacity. The BET surface area of the film is 203.6 m2 g−1. The maximum adsorption capacity of INFCF for Gd(III) was 71.00 mg g−1 at pH 7.0. The adsorption mechanism is summarized as a single layer of chemical adsorption. The excellent selectivity and repeatability of INFCF make it a high-quality material for the selective recovery of rare earth ions in industrial production.
Graphic abstract













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baroni P, Vieira R, Meneghetti E, Da Silva M, Beppu M (2008) Evaluation of batch adsorption of chromium ions on natural and crosslinked chitosan membranes. J Hazard Mater 152(3):1155–1163
El-Nadi Y (2017) Solvent extraction and its applications on ore processing and recovery of metals: classical approach. Sep Purif Rev 46(3):195–215
Erdeng D, Jiaqi L, Siqi Z, Lu Z, Xinxin F (2018) Transformation of naproxen during the chlorination process: products identification and quantum chemistry validation. Chemosphere 211:1007–1017
Fu J, Chen L, Li J, Zhang Z (2015) Current status and challenges of ion imprinting. J Mater Chem A 3(26):13598–13627
Habashi F (2013) Extractive metallurgy of rare earths. Can Metall Q 52(3):224–233
Hao X, Chen R, Liu Q, Liu J, Zhang H, Yu J, Li Z, Wang J (2018) A novel U (vi)-imprinted graphitic carbon nitride composite for the selective and efficient removal of U (vi) from simulated seawater. Inorg Chem Front 5(9):2218–2226
Ide T, Suzuki A, Imada T (2016) Lanthanide selective adsorption by ion-imprinted polymer with chelidonic acid monoamide groups. Sep Sci Technol 51(18):2887–2895
Jha MK, Kumari A, Panda R, Kumar JR, Yoo K, Lee JY (2016) Review on hydrometallurgical recovery of rare earth metals. Hydrometallurgy 165:2–26
Kim GM, Lach R, Michler GH, Chang YW (2005) The mechanical deformation process of electrospun polymer nanocomposite fibers. Macromol Rapid Commun 26(9):728–733
Kim JF, Kim JH, Lee YM, Drioli E (2016) Thermally induced phase separation and electrospinning methods for emerging membrane applications: a review. AIChE J 62(2):461–490
Liu C, Bai R (2006) Adsorptive removal of copper ions with highly porous chitosan/cellulose acetate blend hollow fiber membranes. J Membr Sci 284(1–2):313–322
Liu L, Li C, Bao C, Jia Q, Xiao P, Liu X, Zhang Q (2012) Preparation and characterization of chitosan/graphene oxide composites for the adsorption of Au(III) and Pd (II). Talanta 93:350–357
Liu Z, Liu Y, Gong A (2019) Preparation of diglycolamide polymer modified silica and its application as adsorbent for rare earth ions. Des Monomers Polym 22(1):1–7
Martinez AM, Kjos O, Skybakmoen E, Solheim A, Haarberg GM (2013) Extraction of rare earth metals from Nd-based scrap by electrolysis from molten salts. ECS Trans 50(11):453–461
Negrea A, Gabor A, Davidescu CM, Ciopec M, Negrea P, Duteanu N, Barbulescu A (2018) Rare earth elements removal from water using natural polymers. Sci Rep-UK 8(1):316
Ngah WW, Teong L, Hanafiah M (2011) Adsorption of dyes and heavy metal ions by chitosan composites: a review. Carbohydr Polym 83(4):1446–1456
Pan JM, Zeng J, Cao Q, Gao HP, Gen YC, Peng YX, Dai XH, Yan YS (2016) Hierarchical macro and mesoporous foams synthesized by HIPEs template and interface grafted route for simultaneous removal of λ-cyhalothrin and copper ions. Chem Eng J 284:1361–1372
Raebiger JW, Bolskar RD (2008) Improved production and separation processes for gadolinium metallofullerenes. J Phys Chem C 112(17):6605–6612
Rinaudo M (2006) Chitin and chitosan: properties and applications. Prog Polym Sci 31(7):603–632
Shafaei A, Ashtiani FZ, Kaghazchi T (2007) Equilibrium studies of the sorption of Hg(II) ions onto chitosan. Chem Eng J 133(1–3):311–316
Sun X, Peng B, Ji Y, Chen J, Li D (2008) The solid–liquid extraction of yttrium from rare earths by solvent (ionic liquid) impreganated resin coupled with complexing method. Sep Purif Technol 63(1):61–68
Suquila FA, de Oliveira LL, Tarley CR (2018) Restricted access copper imprinted poly (allylthiourea): the role of hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) and bovine serum albumin (BSA) on the sorptive performance of imprinted polymer. Chem Eng J 350(15):714–728
Tavlarides L, Bae J, Lee C (1987) Solvent extraction, membranes, and ion exchange in hydrometallurgical dilute metals separation. Sep Sci Technol 22(2–3):581–617
Wei X, Xu G, Gong C, Qin F, Gong X, Li C (2018a) Fabrication and evaluation of sulfanilamide-imprinted composite sensors by developing a custom-tailored strategy. Sens Actuator B Chem 255:2697–2703
Wei X, Yu M, Li C, Gong X, Qin F, Wang Z (2018b) Magnetic nanoparticles coated with a molecularly imprinted polymer doped with manganese-doped ZnS quantum dots for the determination of 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol. Microchim Acta 185(4):208
Wei X, Zhang Z, Wang Z (2019) A simple dopamine detection method based on fluorescence analysis and dopamine polymerization. Microchem J 145:55–58
Yu P, Wang H-Q, Bao R-Y, Liu Z, Yang W, Xie B-H, Yang M-B (2017) Self-assembled sponge-like chitosan/reduced graphene oxide/montmorillonite composite hydrogels without cross-linking of chitosan for effective Cr(VI) sorption. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(2):1557–1566
Zheng X, Liu E, Zhang F, Dai J, Yan Y, Li C (2016) Selective adsorption and separation of gadolinium with three-dimensionally interconnected macroporous imprinted chitosan films. Cellulose 24(2):977–988
Zheng X, Zhang Y, Zhang F, Li Z, Yan Y (2018) Dual-template docking oriented ionic imprinted bilayer mesoporous films with efficient recovery of neodymium and dysprosium. J Hazard Mater 353:496–504
Zheng X, Wang Y, Qiu F, Li Z, Yan Y (2019a) Dual-functional mesoporous films templated by cellulose nanocrystals for the selective adsorption of lithium and rubidium. J Chem Eng Data 64(3):926–933
Zheng X, Zhang Y, Bian T, Zhang Y, Zhang F, Yan Y (2019b) Selective extraction of gadolinium using free-standing imprinted mesoporous carboxymethyl chitosan films with high capacity. Cellulose 26(2):1209–1219
Zhu C, Hu T, Tang L, Zeng G, Deng Y, Lu Y, Fang S, Wang J, Liu Y, Yu J (2018) Highly efficient extraction of lead ions from smelting wastewater, slag and contaminated soil by two-dimensional montmorillonite-based surface ion imprinted polymer absorbent. Chemosphere 209:246–257
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21876015, 21808018, 21822807), Applied Basic Research of Changzhou (No. CJ20180055), Natural Science Research of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (No. 18KJB610002), Science and Technology Support Program of Changzhou (No. CE20185015), and Postgraduate Research & Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (No. SJCX18_0958). The authors would like to thank Wang Liang from Shiyanjia Lab (www.shiyanjia.com) for the XPS analysis. Also, the author would like to thank the researchers at the Analytical Testing Center of Changzhou University for their assistance in SEM, FTIR, and BET analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, X., Bian, T., Zhang, Y. et al. Construction of ion-imprinted nanofiber chitosan films using low-temperature thermal phase separation for selective and efficiency adsorption of Gd(III). Cellulose 27, 455–467 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02804-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02804-3