Abstract
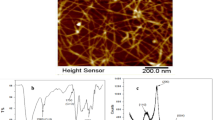
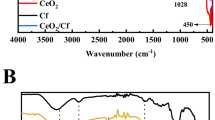
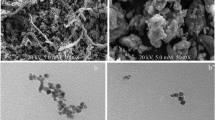
Cellulose micro-fibrils (CMF), which are green, sustainable and are made from abundant renewable biomass, have attracted much attention in the research community for various applications. In this study, we presented a novel magnetic cellulose composite catalyst (HKUST-1/Fe3O4/CMF) for pollution remedy purpose. The main function of CMF is to improve the dispersion of metal organic framework (MOF) crystals (HKUST-1) and Fe3O4 nanoparticles (NPs) so that the catalytic performance of resultant HKUST-1/Fe3O4/CMF composite is enhanced. The as-prepared HKUST-1/Fe3O4/CMF catalyst was characterized by TEM, EDX, BET, XRD, FTIR, TGA and VSM analytical techniques. Results have showed that HKUST-1 and Fe3O4 NPs are anchored onto the surface of CMF. The adsorption efficiency of HKUST-1/Fe3O4/CMF composite has enhanced because of the porous MOF structures. Furthermore, the composite catalyst has a large surface area and exhibits good magnetic and catalytic properties in the Fenton system. When used as a catalyst in the degradation of dye model compound (methylene blue, MB), the composite catalyst shows a high catalytic activity. In addition, the composite catalyst reveals a good reusability, durability in the recycling and reuse testing. These results support to conclude that the as-prepared HKUST-1/Fe3O4/CMF composite is a green, sustainable, effective and potential catalyst system for pollutant remedy.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alaerts L, Séguin E, Poelman H et al (2006) Probing the Lewis acidity and catalytic activity of the metal–organic framework [Cu3(btc)2] (BTC = benzene-1,3,5-tricarboxylate). Chem Eur J 12:7353–7363. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.200600220
An X, Wen Y, Cheng D et al (2016) Preparation of cellulose nano-crystals through a sequential process of cellulase pretreatment and acid hydrolysis. Cellulose 23:2409–2420
An X, Cheng D, Dai L et al (2017) Synthesis of nano-fibrillated cellulose/magnetite/titanium dioxide (NFC@Fe3O4@TNP) nanocomposites and their application in the photocatalytic hydrogen generation. Appl Catal B Environ 206:53–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.01.021
Arslan I, Balcioǧlu IA, Bahnemann DW (2000) Advanced chemical oxidation of reactive dyes in simulated dyehouse effluents by ferrioxalate-Fenton/UV-A and TiO2/UV-A processes. Dyes Pigments 47:207–218
Castro CS, Guerreiro MC, Oliveira LCA et al (2009) Iron oxide dispersed over activated carbon: support influence on the oxidation of the model molecule methylene blue. Appl Catal Gen 367:53–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2009.07.032
Challagulla S, Nagarjuna R, Ganesan R, Roy S (2016) Acrylate-based polymerizable sol–gel synthesis of magnetically recoverable TiO2 supported Fe3O4 for Cr(VI) photoreduction in aerobic atmosphere. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:974–982
Chui SS-Y, Lo SM-F, Charmant JP et al (1999) A chemically functionalizable nanoporous material [Cu3 (TMA)2 (H2O)3]n. Science 283:1148–1150
Costa RC, Lelis MF, Oliveira LC et al (2006) Novel active heterogeneous Fenton system based on Fe3−xMxO4 (Fe Co, Mn, Ni): the role of M2+ species on the reactivity towards H2O2 reactions. J Hazard Mater 129:171–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.08.028
da Silva Pinto M, Sierra-Avila CA, Hinestroza JP (2012) In situ synthesis of a Cu-BTC metal–organic framework (MOF 199) onto cellulosic fibrous substrates: cotton. Cellulose 19:1771–1779. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9752-y
Dai L, Zhang L, Wang B et al (2017) Multifunctional self-assembling hydrogel from guar gum. Chem Eng J 330:1044–1051. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.08.041
Duarte F, Maldonado-Hódar FJ, Madeira LM (2011) Influence of the characteristics of carbon materials on their behaviour as heterogeneous Fenton catalysts for the elimination of the azo dye Orange II from aqueous solutions. Appl Catal B Environ 103:109–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2011.01.016
Erdem B, Hunsicker RA, Simmons GW et al (2001) XPS and FTIR surface characterization of TiO2 particles used in polymer encapsulation. Langmuir 17:2664–2669
Fu L, You S-J, Zhang G et al (2010) Degradation of azo dyes using in situ Fenton reaction incorporated into H2O2-producing microbial fuel cell. Chem Eng J 160:164–169
Gao Y, Hu C, Zheng WJ et al (2016) Fe3O4 anisotropic nanostructures in hydrogels: efficient catalysts for the rapid removal of organic dyes from wastewater. ChemPhysChem 17:1999–2007. https://doi.org/10.1002/cphc.201600117
Georgi A, Schierz A, Trommler U et al (2007) Humic acid modified Fenton reagent for enhancement of the working pH range. Appl Catal B Environ 72:26–36
Gong X, Wang Y, Kuang T (2017) ZIF-8-based membranes for carbon dioxide capture and separation. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:11204–11214. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b03613
Habila MA, Alothman ZA, El-Toni AM et al (2017) Carbon-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles with surface amido groups for magnetic solid phase extraction of Cr(III), Co(II), Cd(II), Zn(II) and Pb(II) prior to their quantitation by ICP-MS. Microchim Acta 184:2645–2651. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2283-3
Haque E, Jun JW, Jhung SH (2011) Adsorptive removal of methyl orange and methylene blue from aqueous solution with a metal–organic framework material, iron terephthalate (MOF-235). J Hazard Mater 185:507–511
Hasan Z, Jhung SH (2015) Removal of hazardous organics from water using metal–organic frameworks (MOFs): plausible mechanisms for selective adsorptions. J Hazard Mater 283:329–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.09.046
Hua Y, Wang S, Xiao J et al (2017) Preparation and characterization of Fe3O4/gallic acid/graphene oxide magnetic nanocomposites as highly efficient Fenton catalysts. RSC Adv 7:28979–28986. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra23939k
Huang T, Zhang G, Zhang N et al (2018) Fe0-H2O2 for advanced treatment of citric acid wastewater: detailed study of catalyst after several times use. Chem Eng J 336:233–240
Jabbari V, Veleta JM, Zarei-Chaleshtori M et al (2016) Green synthesis of magnetic MOF@GO and MOF@CNT hybrid nanocomposites with high adsorption capacity towards organic pollutants. Chem Eng J 304:774–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.06.034
Jahan MS, Saeed A, He Z, Ni Y (2011) Jute as raw material for the preparation of microcrystalline cellulose. Cellulose 18:451–459
Karra JR, Walton KS (2010) Molecular simulations and experimental studies of CO2, CO, and N2 adsorption in metal–organic frameworks. J Phys Chem C 114:15735–15740. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp105519h
Ke F, Yuan Y-P, Qiu L-G et al (2011) Facile fabrication of magnetic metal–organic framework nanocomposites for potential targeted drug delivery. J Mater Chem 21:3843–3848
Khataee A, Sajjadi S, Rahim Pouran S, Hasanzadeh A (2017) Efficient electrochemical generation of hydrogen peroxide by means of plasma-treated graphite electrode and activation in electro-Fenton. J Ind Eng Chem 56:312–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2017.07.024
Kim JW, Ki CS, Um IC, Park YH (2017) A facile fabrication method and the boosted adsorption and photodegradation activity of CuO nanoparticles synthesized using a silk fibroin template. J Ind Eng Chem 56:335–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2017.07.029
Koyuncu I (2002) Reactive dye removal in dye/salt mixtures by nanofiltration membranes containing vinylsulphone dyes: effects of feed concentration and cross flow velocity. Desalination 143:243–253
Li Y, Zhu H, Gu H et al (2013) Strong transparent magnetic nanopaper prepared by immobilization of Fe3O4 nanoparticles in a nanofibrillated cellulose network. J Mater Chem A 1:15278. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ta12591b
Liu J, Sun Z, Deng Y et al (2009) Highly water-dispersible biocompatible magnetite particles with low cytotoxicity stabilized by citrate groups. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 121:5989–5993
Lu H, Zhang L, Liu C et al (2018) A novel method to prepare lignocellulose nanofibrils directly from bamboo chips. Cellulose 25:7043–7051. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2067-x
Lu H, Zhang L, Ma J et al (2019) Nano-cellulose/MOF derived carbon doped CuO/Fe3O4 nanocomposite as high efficient catalyst for organic pollutant remedy. Nanomaterials 9:277. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9020277
Majano G, Perez-Ramirez J (2013) Scalable room-temperature conversion of copper(II) hydroxide into HKUST-1 (Cu3 (btc)2). Adv Mater 25:1052–1057. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201203664
Mehdinia A, Jahedi Vaighan D, Jabbari A (2018) Cation exchange superparamagnetic Al-based metal organic framework (Fe3O4/MIL-96(Al)) for high efficient removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:3176–3186. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b03301
Mesquita I, Matos LC, Duarte F et al (2012) Treatment of azo dye-containing wastewater by a Fenton-like process in a continuous packed-bed reactor filled with activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 237–238:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.07.066
Michael I, Rizzo L, McArdell CS et al (2013) Urban wastewater treatment plants as hotspots for the release of antibiotics in the environment: a review. Water Res 47:957–995
Moghaddam SS, Moghaddam MA, Arami M (2010) Coagulation/flocculation process for dye removal using sludge from water treatment plant: optimization through response surface methodology. J Hazard Mater 175:651–657
Nguyen TD, Phan NH, Do MH, Ngo KT (2011) Magnetic Fe2MO4 (M: Fe, Mn) activated carbons: fabrication, characterization and heterogeneous Fenton oxidation of methyl orange. J Hazard Mater 185:653–661
Panella B, Hirscher M, Pütter H, Müller U (2006) Hydrogen adsorption in metal-organic frameworks: Cu-MOFs and Zn-MOFs compared. Adv Funct Mater 16:520–524. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200500561
Pearce CI, Lloyd JR, Guthrie JT (2003) The removal of colour from textile wastewater using whole bacterial cells: a review. Dyes Pigments 58:179–196
Răcuciu M, Creangă DE, Airinei A (2006) Citric-acid-coated magnetite nanoparticles for biological applications. Eur Phys J E Soft Matter Biol Phys 21:117–121
Sing KS (1985) Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity (Recommendations 1984). Pure Appl Chem 57:603–619
Sun B, Hou Q, He Z et al (2014) Cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) as carriers for a spirooxazine dye and its effect on photochromic efficiency. Carbohydr Polym 111:419–424
Tan P, Xie XY, Liu XQ et al (2017) Fabrication of magnetically responsive HKUST-1/Fe3O4 composites by dry gel conversion for deep desulfurization and denitrogenation. J Hazard Mater 321:344–352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.09.026
Tang C, Wang Y, Long Y et al (2017) Anchoring 20 (R)-ginsenoside Rg3 onto cellulose nanocrystals to increase the hydroxyl radical scavenging activity. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:7507–7513
Wang N, Zheng T, Zhang G, Wang P (2016) A review on Fenton-like processes for organic wastewater treatment. J Environ Chem Eng 4:762–787. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.12.016
Wang Y, Huang H, Duan S et al (2018) A new application of a mesoporous hybrid of tungsten oxide and carbon as an adsorbent for elimination of Sr2+ and Co2+ from an aquatic environment. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6:2462–2473. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b03818
Xi Y, Sun Z, Hreid T et al (2014) Bisphenol A degradation enhanced by air bubbles via advanced oxidation using in situ generated ferrous ions from nano zero-valent iron/palygorskite composite materials. Chem Eng J 247:66–74
Yan A-X, Yao S, Li Y-G et al (2014) Incorporating polyoxometalates into a porous MOF greatly improves its selective adsorption of cationic dyes. Chem Eur J 20:6927–6933
Yang Q, Zhang M, Song S, Yang B (2017) Surface modification of PCC filled cellulose paper by MOF-5 (Zn3(BDC)2) metal–organic frameworks for use as soft gas adsorption composite materials. Cellulose 24:3051–3060. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1331-9
Zaman M, Xiao H, Chibante F, Ni Y (2012) Synthesis and characterization of cationically modified nanocrystalline cellulose. Carbohydr Polym 89:163–170
Zhang A, Shen J (2016) Adding growth-promoting ingredients in activated sludge process as a troubleshooting strategy for pulp and paper mill wastewater treatment. BioResources 11:8119–8122. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.11.4.8119-8122
Zhang C-F, Qiu L-G, Ke F et al (2013) A novel magnetic recyclable photocatalyst based on a core–shell metal–organic framework Fe3O4@ MIL-100 (Fe) for the decolorization of methylene blue dye. J Mater Chem A 1:14329–14334
Zhang L, Lu H, Yu J et al (2017) Dissolution of lignocelluloses with a high lignin content in a N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide monohydrate solvent system via simple glycerol-swelling and mechanical pretreatments. J Agric Food Chem 65:9587–9594. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b03429
Zhao X, Liu S, Tang Z et al (2015) Synthesis of magnetic metal-organic framework (MOF) for efficient removal of organic dyes from water. Sci Rep 5:11849
Zhuang H, Han H, Ma W et al (2015) Advanced treatment of biologically pretreated coal gasification wastewater by a novel heterogeneous Fenton oxidation process. J Environ Sci 33:12–20
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support from (1) the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31570576), (2) the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Provincial University (16KJA220005), (3) the Postgraduate Research and Practice Innovation Program of Jiangsu Province (KYCX17_0835), (4) the Doctorate Fellowship Foundation of Nanjing Forestry University, (5) the Priority Academic Program Development (PAPD) of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions, and the Canada Research Chairs program of the Government of Canada. Also, the authors acknowledge Mr. Mike Johnson (Department of Chemistry and Institute for Research in Materials, Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS, Canada) for the acquisition and interpretation of the PPMS data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, H., Zhang, L., Wang, B. et al. Cellulose-supported magnetic Fe3O4–MOF composites for enhanced dye removal application. Cellulose 26, 4909–4920 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02415-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-019-02415-y