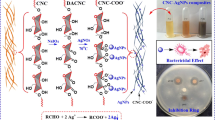
Abstract
The preparation method of Silver (Ag)-loaded cellulose paper based on the formation of seed nuclei has been proposed as a functional material with high antibacterial performance. Metal palladium (Pd) was employed for the formation of seed nuclei, followed by sodium potassium tartrate tetrahydrate reduction to create Pd–Ag-cellulose paper. The properties in term of micro morphology, distribution of silver particles, antibacterial activity and silver release behavior were investigated. The results verified the formation of Pd-nucleus on surface of fiber, and revealed that silver particles were steadily deposited on the fibers based on the seed nuclei embedded. Pd–Ag-cellulose paper, comparing with Ag-cellulose paper produced with direct deposition method, exhibited a thick closely silver layer and uniform distribution of silver particles. The antibacterial test indicated that the lethality rate of Pd–Ag-cellulose paper against E. coli is 99.92% which is very close to that of Ag-cellulose paper (99.93%). Nevertheless, the silver release regression equation provided a high slope value (0.075) to Ag-cellulose paper, which explains a rapid release of silver. Pd–Ag-cellulose paper, by contrast, the slope value is only 0.021, and that indicates the silver slower release was achieved. Ag-loaded cellulose paper prepared using the proposed method shows the prominent properties in silver loading, antibacterial and silver slow-release.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao XG, Liang CL, Xia SM (2016) Preparation and conductivity of carbon fiber coated with silver. Mater Sci Forum 847:137–142
Jafta CJ, Petzold A, Risse S, Clemens D, Ballauff M (2017) Correlating pore size and shape to local disorder in microporous carbon: a combined small angle neutron and X-ray scattering study. Carbon 123:440–447
Khalil HA, Davoudpour Y, Chaturbhuj K, Saurabh M, Hossain S (2016) A review on nanocellulosic fibres as new material for sustainable packaging: process and applications. Renew Sust Energ Rev 64:823–836
Maneerung T, Tokura S, Rujiravanit R (2008) Impregnation of silver nanoparticles into bacterial cellulose for antimicrobial wound dressing. Carbohyd Polym 72:43–51
Mihaly-Cozmuta A, Peter A, Craciun G, Falup A, Mihaly-Cozmuta L, Nicula C, Vulpoi A, Baia M (2017) Preparation and characterization of active cellulose-based papers modified with TiO2, Ag and zeolite nanocompositesfor bread packaging application. Cellulose 1:1–8
Nie CX, Cheng C, Zhang P, Ma L, He C, Xia Y, Zhao CS (2016) Mussel-inspired coatings on Ag nanoparticle conjugated carbon nanotubes: bactericidal activity and mammal cell toxicity. J Mater Chem B 4:2749–2756
Nie CX, Yang Y, Cheng C, Ma L, Deng J, Wang LR, Zhao CS (2017) Bioinspired and biocompatible carbon nanotube-Ag nanohybrid coatings for robust antibacterial applications. Acta Biomater 51:479–494
Shah MSAS, Nag M, Kalagara T, Singh S, Manorama SV (2008) Silver on PEG-PU-TiO2 polymer nanocomposite films: an excellent system for antibacterial applications. Chem Mater 20(7):2455–2460
Shahriary L, Nair R, Sabharwal SG, Athawale MAA (2015) One-step synthesis of Ag–reduced graphene oxide–multiwalled carbon nanotubes for enhanced antibacterial activities. New J Chem 39:4583–4590
Song XJ, Shi XY (2017) Bioreductive deposition of highly dispersed Ag nanoparticles on carbon nanotubes with enhanced catalytic degradation for 4-nitrophenol assisted by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:3038–3044
Tian T, Zhong Y, Deng C, Wang H, He Y, Ge Y, Song G (2017) Brightly near-infrared to blue emission tunable silver-carbon dot nanohybrid for sensing of ascorbic acid and construction of logic gate. Talanta 162:135–142
Wang W, Liang T, Bai H, Dong W, Liu X (2018) All cellulose composites based on cellulose diacetate and nanofibrillated cellulose prepared by alkali treatment. Carbohyd Polym 179:297–304
Zhao X, Muench F, Schaefer S, Brötz J, Liu SX, Ensinger W (2016) Electroless decoration of macroscale foam with nickel nano-spikes: a scalable route toward efficient catalyst electrodes. Electrochem Commun 65:39–43
Zivic F, Grujovic N, Mitrovic S, Ahad IU, Brabazon D (2017) Characteristics and applications of silver nanoparticles. In: Brabazon D, Pellicer E, Zivic F, Sort J, Baró MD, Grujovic N, Choy K-L (eds) Commercialization of nanotechnologies—a case study approach. Springer, Cham, pp 227–273
Acknowledgments
The present work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong (ZR2017LEM009), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 31600472, 31570566, 31500489, 31770626, 31670590) and the Taishan Scholars Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, H., Zhao, X., Liu, Y. et al. Facile synthesis of elemental silver by the seed nucleus embedding method for antibacterial applications. Cellulose 25, 5289–5296 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1952-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1952-7