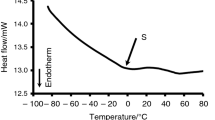
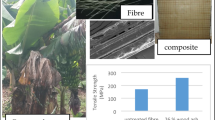
Abstract
An alkali based method has been optimised and proposed to extract the cellulosic fibres from the corn husks. Physicochemical and morphological properties of the fibres extracted from corn husk have been studied in detail, and compared with the well-explored cellulosic fibre, like cotton and ligno-cellulosic fibre, like jute. Scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray were used to study the surface and cross-sectional morphology and the elemental analysis of the corn-husk fibres and compared with cotton and jute fibres. The analysis showed that the morphological and the physico-chemical properties of the extracted corn husk fibres are comparable with ligno-cellulosic jute fibre. Also, improvement in thermal stability of corn husk fibre was obtained by application of the agro-waste banana pseudostem sap (BPS). BPS treated corn husk fibre showed the limiting oxygen index (LOI) value of 32 against the LOI value of 21 for the control corn fibre. In vertical burning test BPS treated corn yarn showed self extinguishing behaviour and 50 mm char length whereas control corn yarn was burnt within 1 min with flame and afterglow. TG analysis of the BPS treated corn yarn showed more than 30% weight retention at 450 °C compared to the 20% weight retention of the control corn yarn at the said temperature. In addition, major mass loss peak in TG curve has been shifted from 350 to 300 °C after BPS treatment (signature of the dehydration effect of the treated corn yarn). The flame retardant treatment process is comparatively simple and cost-effective, as add-on remains only at 8% and the BPS is available in large quantity in many countries.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Basak S, Ali SW (2018) Fire resistant behaviour of cellulosic textile functionalized with wastage plant bio-molecules: a comparative scientific report. Int J Biol Macromol 114:169–180
Basak S, Samanta KK, Chattopadhyay SK (2014a) Fire retardant property of the cotton fabric treated with herbal extract. J Text Inst 106:1338–1347
Basak S, Samanta KK, Chattopadhyay SK, Das S, Narkar R, Desouza C, Saikh AH (2014b) Fire retardant and antimicrobial jute fabric using sodium metasilicate nonahydrate. Pol J Chem Technol 16:106–113
Basak S, Samanta KK, Saxena S, Chattopadhyay SK, Narkar R, Mahangade R (2015a) Fire retardant cellulosic textile using banana pseudostem sap. Pol J Chem Technol 17:123–133
Basak S, Samanta KK, Chattopadhyay SK, Narkar R (2015b) Self-extinguishing ligno-cellulosic fibre using banana pseudostem sap. Current Sci 108:372–383
Basak S, Samanta KK, Chattopadhyay SK, Narkar R (2015c) Thermally stable cellulosic paper made using banana pseudostem sap, a wasted by-product. Cellulose 22:2767–2776
Basak S, Samanta KK, Saxena S, Chattopadhyay SK, Narkar R, Mahangade R (2015d) Fire retardant cellulosic substrate using banana pseudostem sap. Int J Cloth Sci Technol 27:245–263
Basak S, Patil PG, Shaikh AJ, Samanta KK (2016) Green coconut shell extract and boric acid: new formulation for making thermal stable cellulosic paper. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 91:2871–2881
Biagiotti J, Puglia D, Kenny JM (2004) A Review on Natural Fibre-Based Composites-Part I: structure, processing and properties of vegetable fibres. J Nat Fibers 1(2):37–68
Canetta E, Montiel K, Adya AK (2009) Morphological changes in textile fibres exposed to environmental stresses: atomic force microscopic examination. Forensic Sci Int 191:6–14
Ebisike K, AttahDaniel BE, Babatope B, Olusence SOO (2013) Studies on the extraction of naturally occurring banana fibres. Int J Eng Sci 2:95–99
Fidelis MEA, Pereira TVS, Gomes OFM, Silva FA, Filho RDT (2013) The effect of fiber morphology on the tensile strength of natural fibers. J Mater Res Technol 13:149–157
French AD, Santiago Cintron M (2013) Cellulose polymorphy, crystallite size, and the Segal Crystallinity Index. Cellulose 20:583–588
Hady AAE, Farouk A, Sharaf S (2013) Flame retardancy and UV protection of cotton based fabrics using nano ZnO and polycarboxylic acid. Carbohyd Polym 92:400–407
Halliwell G (1959) Cellulose In: HU Bergmeyer (ed) (1965) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Verlog Chemie GmBH Weinheim/Bergstr, Academic Press, New York and London, pp 66–67
Hong B, Chen F, Xue G (2016) Preparation and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from bamboo pulp. Cellulose chem. Technol. 50:225–231
Horrocks AR (2014) Flame retardant challanges for textiles and fibres: new chemistry versus innovatory solutions. Polym Degrad Stabil 96:377–382
Kambli N, Basak S, Samanta KK, Deshmukh RR (2016) Extraction of natural cellulosic fibres from cornhusk and its physico-chemical properties. Fibres Polym 17(5):687–694
Kambli ND, Mageshwaran V, Patil Prashant G, Saxena Sujata, Deshmukh Rajendra R (2017) Synthesis and characterization of microcrystalline cellulose powder from corn husk fibres using bio-chemical route. Cellulose 24(12):5355–5369
Kei SCH (2010) The effect of atmospheric pressure plasma on flame retardant property of cotton. Institute of Textile and Clothing, Bachelor of Arts in Fashion Technology thesis, Hong Kong Polytechnic University
Li J, Wei X, Wang Q, Chen J, Chang G, Kong L, Su J, Liu Y (2012) Homogeneous isolation of nanocellulose from sugarcane bagasse by high pressure homogenization. Carbohyd Polym 90:1609–1613
Morais JPS, Rosa MF, Filho MMS, Nascimento LD, Nascimento DM, Cassales AR (2013) Extraction and characterization of nanocellulose structures from raw cotton linter. Carbohyd Polym 91:229–235
Neto WPF, Silverio HA, Dantas NO, Pasquini D (2013) Extraction and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from agro-industrial residue—Soy hulls. Ind Crops Prod 42:480–488
Reddy N, Yang Y (2005a) Long natural cellulosic fibres from cornhusks: structure and properties. AATCC review 24–27
Reddy N, Yang Y (2005b) Properties and potential applications of natural cellulose fibers from cornhusks. Green Chem 7:190–195
Reddy N, Yang Y (2006) Properties of high quality long natural cellulosic fibres from rice straw. J Agric Food Chem 54:8077–8081
Reddy N, Yang Y (2014) Biofibres from agricultural byproducts for industrial applications. Trends Biotechnol 23:25–30
Reddy N, Yang Y, Alister III DD (2006) Processability and properties of yarns produced from cornhusk fibres and their blends with other fibres. Indian J Fibre Text Res 31:537–542
Rosa MF, Medeiros ES, Malmonge JA, Gregorski KS, Wood DF, Mattoso LHC, Glenn G, Orts WJ, Imam SH (2010) Cellulose nanowhiskers from coconut husk fibers: effect of preparation conditions on their thermal and morphological behavior. Carbohyd Polym 81:83–92
Samanta KK, Basak S, Chattopadhyay SK (2016) Potential of ligno-cellulosic and protein fibres in sustainable fashion. In: Muthu SS, Gardetti MA (eds) Sustainable fibres for fashion industry, vol 2. Springer, Singapore, pp 61–110
Santos RM, Neto WPF, Silvério HA, Martins DF, Dantas NO, Pasquini D (2013) Cellulose nanocrystals from pineapple leaf, a new approach for there use of this agro-waste. Ind Crops Prod 50:707–714
Serad GA, Sanders JR (1984) In: Grayson M (ed) Encyclopaedia of textiles, fibers and nonwoven fabrics. Wiley, New York, pp 62–89 (ISBN-13: 978-0471814610)
Shukla A, Basak A, Ali SW, Chattopadhyay R (2017) Development of fire retardant sisal yarn. Cellulose 24:423–434
Silverio HA, Neto WPF, Dantas NO, Pasquini D (2013) Extraction and characterization of cellulose nanocrystals from corncob for application as reinforcing agent in nanocomposites. Ind Crops Prod 44:427–436
Ward K (1950) Crystallinity of cellulose and its significance for the fiber properties. Text Res J 20(6):363–372
Yilmaz ND (2013) Effect of chemical extraction parameters on corn husk fibres characteristics. Indian J Fibre Text Res 38:29–34
Yilmaz ND, Cahskan E, Yilmaz K (2014) Effect of xylanase enzyme on mechanical properties of fibres extracted from undried and dried corn husks. Indian J Fibre Text Res 39:60–64
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge necessary experimental and testing supports provided by Institute of Chemical Technology (ICT), Mumbai and ICAR-Central Institute for Research on Cotton Technology (ICAR-CIRCOT), Mumbai and also, the SAIF, IIT-Bombay for EDX characterization.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kambli, N.D., Samanta, K.K., Basak, S. et al. Characterization of the corn husk fibre and improvement in its thermal stability by banana pseudostem sap. Cellulose 25, 5241–5257 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1931-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1931-z