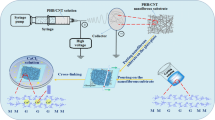
Abstract
A novel nanofiber composite nano-filtration membrane was prepared by combination of grafting, electrospinning and surface coating. First, carboxyl multi-walled carbon nanotubes were grafted onto bacterial cellulose molecular chains by solution reaction. The grafting products were characterized by TEM, FTIR, Raman, XPS and TGA measurements. Then, they were electrospun into nanofibers to be the supporting layer, and a coating of denser chitosan hydrogel thin film was used as the barrier layer. The morphology of the electrospun nanofibers and composite membrane were observed by SEM. The mechanical behavior of the composite membrane was investigated in dry and wet state. The filtration properties were evaluated in term of the pure water flux (PWF), dye rejection rate and anti-fouling properties. Results showed that the chitosan hydrogel coated electrospun nanofiber composite membrane had higher tensile strength and Young’s Modulus with the value of 11.75, 10.11 and 244, 211 MPa in dry and wet state, respectively. The PWF was increased from 52.1 to 140.7 L/m2 h with the operation pressure increasing from 0.1 to 0.6 MPa. Direct Orange S, Procion Red mx-5B, Stilbene Yellow and Methylene Blue with molecular weight ranged from 300 to 800 g/mol were selected for dye removal test. The rejection rate could maintain over 90% for dyes with the molecular weight larger than 600 g/mol under 0.5 MPa. The chitosan hydrogel coated electrospun nanofiber composite membrane exhibited good anti-fouling properties for both oil and protein. These results indicate that these membranes are efficient for dye removal from wastewater, with high flux and rejection rate at high pressure.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed FE, Lalia BS, Hashaikeh R (2015) A review on electrospinning for membrane fabrication: challenges and applications. Desalination 356:15–30
Cai Z, Song X, Zhang Q, Liu Y (2017a) Amidoxime surface modification of polyindole nanofiber membrane for effective removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. J Mater Sci 52:5417–5434
Cai Z, Zhang Q, Zhu C, Song X, Liu Y (2017b) Development of a sodium/electrospun poly(5-cyanoindole) nanofiber secondary battery system with high performance. Synth Met 231:15–18
Cai Z, Zhu C, Guo J, Zhang Q, Zhao K (2018) Electrospun carboxyl multi-walled carbon nanotubes grafted polyhydroxybutyrate composite nanofibers membrane scaffolds: preparation, characterization and cytocompatibility. Mater Sci Eng, C 82:29–40
Gasemloo S, Sohrabimm MR, Khosravimm M, Dastmalchim S, Gharbani P (2016) Fabrication of sulfated nanofilter membrane based on carboxymethyl cellulose. Water Sci Technol 74:2611–2619
Guo J, Zhang Q, Cai Z, Zhao KY (2016) Preparation and dye filtration property of electrospun polyhydroxybutyrate–calcium alginate/carbon nanotubes composite nanofibrous filtration membrane. Sep Purif Technol 161:69–79
Huang Y, Huang QL, Liu H, Zhang CX, You YW, Li NN (2017) Preparation, characterization, and applications of electrospun ultrafine fibrous PTFE porous membranes. J Membrane Sci 523:317–326
Jorio A, Pimenta MA, Filho AGS, Saito R, Dresselhaus G, Dresselhaus MS (2003) Characterizing carbon nanotube samples with resonance Raman scattering. New J Phys 5:139.1–139.17
Kaur S, Rana D, Matsuura T, Sundarrajan S, Ramakrishna S (2012a) Preparation and characterization of surface modified electrospun membranes for higher filtration flux. J Membr Sci 390–391:235–242
Kaur S, Sundarrajan S, Rana D, Matsuura T, Ramakrishna S (2012b) Influence of electrospun fiber size on the separation efficiency of thin film nanofiltration composite membrane. J Membr Sci 392–393:101–111
Kebria MRS, Jahanshahi M, Rahimpour A (2015) SiO2 modified polyethyleneimine-based nanofiltration membranes for dye removal from aqueous and organic solutions. Desalination 367:255–264
Khorshidi S, Solouk A, Mirzadeh H, Mazinani S, Lagaron JM, Sharifi S (2016) A review of key challenges of electrospun scaffolds for tissue-engineering applications. J Tissue Eng Regen Med 10:715–738
Lalia BS, Kochkodan V, Hashaikeh R, Hilal N (2013) A review on membrane fabrication: structure, properties and performance relationship. Desalination 326:77–95
Li XP, Chen YB, Hu XY, Zhang YF, Hu LJ (2014) Desalination of dye solution utilizing PVA/PVDF hollow fiber composite membrane modified with TiO2 nanoparticles. J Membr Sci 471:118–129
Liang CZ, Sun SP, Li FY, Ong YK, Chung TS (2014) Treatment of highly concentrated wastewater containing multiple synthetic dyes by a combined process of coagulation/flocculation and nanofiltration. J Membr Sci 469:306–315
Liu W, Zhu L, Huang C, Jin X (2016) Direct electrospinning of ultrafine fibers with interconnected macropores enabled by in situ mixing microfluidics. Appl Mater Interf 8:34870–34878
Makaremi M, Lim CX, Pasbakhsh P, Sui ML, Goh KL, Chang H (2016) Electrospun functionalized polyacrylonitrile-chitosan bi-layer membranes for water filtration applications. RSC Adv 6:53882–53893
Rajesh S, Senthilkumar S, Jayalakshmi A, Nirmala MT, Ismail AF, Mohan D (2013) Preparation and performance evaluation of poly (amide–imide) and TiO2 nanoparticles impregnated polysulfone nanofiltration membranes in the removal of humic substances. Colloid Surface A 418:92–104
Rezzadori K, Penha FM, Proner MC, Zin G, Petrus JCC, Prádanos P, Palacio L, Hernández A, Luccio MD (2015) Evaluation of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes performance in the permeation of organic solvents. J Membr Sci 492:478–489
Rosa RM, Silva JC, Sanches IS, Henriques C (2017) Simultaneous photo-induced cross-linking and silver nanoparticle formation in a PVP electrospun wound dressing. Mater Lett 207:145–148
Urban J (2016) Current trends in the development of porous polymer monoliths for the separation of small molecules. J Sep Sci 39:51–68
Wang XF, Zhang K, Yang Y, Wang LL, Zhou Z, Zhu MF, Hsiao BS, Chu B (2010) Development of hydrophilic barrier layer on nanofibrous substrate as composite membrane via a facile route. J Membr Sci 356:110–116
Wenhui S, Zhen Z, Weiliang T, Xinling W (2007) A facile approach to covalently functionalized carbon nanotubes with biocompatible polymer. Polymer 48:3658–3663
Wu D, Huang Y, Yu S, Lawless D, Feng X (2014) Thin film composite nanofiltration membranes assembled layer-by-layer via interfacial polymerization from polyethylenimine and trimesoyl chloride. J Membr Sci 472:141–153
Xu L, Du LS, Wang C, Xu W (2012) Nanofiltration coupled with electrolytic oxidation in treating simulated dye wastewater. J Membr Sci 409–410:329–334
Yang S, Shao D, Wang X, Hou G, Nagatsu M, Tan X (2015) Design of chitosan-grafted carbon nanotubes: evaluation of how the –OH functional group affects Cs+ adsorption. Mar Drugs 13:3116–3131
Yoon K, Hsiao BS, Chu B (2009) High flux nanofiltration membranes based on interfacially polymerized polyamide barrier layer on polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous scaffolds. J Membr Sci 326:484–492
Yoon JT, Lee SC, Jeong YG (2010) Effects of grafted chain length on mechanical and electrical properties of nanocomposites containing polylactide-grafted carbon nanotubes. Compos Sci Technol 70:776–782
Zeng G, He Y, Zhan Y, Zhang L, Pan Y, Zhang C, Yu Z (2016) Novel polyvinylidene fluoride nanofiltration membrane blended with functionalized halloysite nanotubes for dye and heavy metal ions removal. J Hazard Mater 317:60–72
Zhang XX, Lin BB, Zhao KY, Wei JF, Guo J, Cui WK, Jiang S, Liu D, Li JX (2015) A free-standing calcium alginate/polyacrylamide hydrogel nanofiltration membrane with high anti-fouling performance: preparation and characterization. Desalination 365:234–241
Zhang M, Zhao X, Zhang G, Wei G, Su Z (2017) Electrospinning design of functional nanostructures for biosensor applications. J Mater Chem B 5:1699–1711
Zhao S, Wang Z (2017) A loose nano-filtration membrane prepared by coating HPAN UF membrane with modified PEI for dye reuse and desalination. J Membr Sci 524:214–224
Zheng YP, Yao GH, Cheng QB, Yu SC, Liu MH, Gao CJ (2013) Positively charged thin-film composite hollow fiber nanofiltration membrane for the removal of cationic dyes through submerged filtration. Desalination 328:42–50
Zhou CM, Shi YL, Sun CS, Yu SC, Liu MH, Gao CJ (2014) Thin-film composite membranes formed by interfacial polymerization with natural material sericin and trimesoyl chloride for nanofiltration. J Membr Sci 471:381–391
Zhu H, Szymczyk A, Balannec B (2011) On the salt rejection properties of nanofiltration polyamide membranes formed by interfacial polymerization. J Membr Sci 379:215–223
Zhu WP, Gao J, Sun SP, Zhang S, Chung TS (2015) Poly(amidoamine) dendrimer (PAMAM) grafted on thin film composite (TFC) nanofiltration (NF) hollow fiber membranes for heavy metal removal. J Membr Sci 487:117–126
Zhu M, Han J, Wang F, Shao W, Xiong R, Zhang Q (2017) Electrospun nanofibers membranes for effective air filtration. Macromol Mater Eng 302:1600353
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Tianjin Science Technology Research Funds of China (16JCZDJC37500) and The Project of Tianjin Science and Technology Correspondent (16JCTPJC44800).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhijiang, C., Ping, X., Cong, Z. et al. Preparation and characterization of a bi-layered nano-filtration membrane from a chitosan hydrogel and bacterial cellulose nanofiber for dye removal. Cellulose 25, 5123–5137 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1914-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1914-0