Abstract
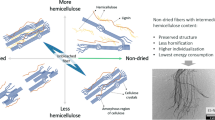
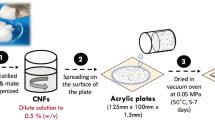
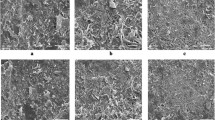
In this study, oil palm mesocarp fiber (OPMF) was pretreated with (1) superheated steam (SHS) and (2) potassium hydroxide (KOH) to remove hemicellulose. Both SHS–OPMF and KOH–OPMF underwent delignification step to isolate the cellulose and dissolved in selected ionic liquid and its co-solvent before being electrospun to obtain microfibrillated cellulose (MFC). FE-SEM images showed that SHS–OPMF cellulose produced discontinuous MFC fiber with diameter ranging from 100 to 500 nm, of which 15.5% were in the range of 100–200 nm; while KOH–OPMF cellulose produced continuous MFC with sizes larger than 200 nm. The differences in fiber size and continuity of fiber produced were due to incomplete removal of hemicellulose from SHS–OPMF sample that inhibited fiber re-coalescence and resulted in interruption in fiber formation.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahrin EK, Baharuddin AS, Ibrahim MF, Razak MNA, Sulaiman A, Abd-Aziz S, Hassan MA, Shirai Y, Nishida H (2012) Physiochemical property changes and enzymatic hydrolysis enhancement of oil palm empty fruit bunches treated with superheated steam. BioResources 7:1784–1801
Chung DE, Um IC (2014) Effect of molecular weight and concentration on crystallinity and post drawing of wet spun silk fibroin fiber. Fibers Polym 15:153–160
Fahma F, Iwamoto S, Hori N, Iwata T, Takemura A (2010) Isolation, preparation, and characterization of nanofibers from oil palm empty-fruit-bunch (OPEFB). Cellulose 17:977–985
Freire MG, Teles ARR, Ferreira RAS, Carlos LD, Lopes-da-Silva JA, Coutinho JAP (2011) Electrospun nanosized cellulose fibers using ionic liquids at room temperature. Green Chem 13:3173–3180
Haafiz MKM, Eichhorn SJ, Hassan A, Jawaid M (2013) Isolation and characterization of microcrystalline cellulose from oil palm biomass residue. Carbohyd Polym 95:628–634
Hardelin L, Thunberg J, Perzon E, Westman G, Walkenstrom P, Gatenholm P (2012) Electrospinning of cellulose nanofibers from ionic liquids: the effect of different cosolvents. J Appl Polym Sci 125:1901–1909
Heijnesson-Hultén A, Guo S, Basta J, Daniel G, Zhan H, Germgard U (2013) Impact of drying on the quality of bamboo kraft pulps. BioResources 8:245–1257
Iwamoto S, Abe K, Yano H (2008) The effect of hemicellulose on wood pulp nanofibrillation and nanofiber network characteristic. Biomacromol 9:1022–1026
Kang Y, Ahn Y, Lee SH, Hong JH, Ku MK, Kim H (2013) Lignocellulosic nanofiber prepared by alkali treatment and electrospinning using ionic liquid. Fibers Polym 14:530–536
Mahmud NAN, Baharuddin S, Bahrin EK, Sulaiman A, Naim MN, Zakaria R, Hassan MA, Nishida H, Shirai Y (2013) Enzymatic saccharification of oil palm mesocarp fiber (OPMF) treated with superheated steam. BioResources 8:1320–1331
Mohaiyiddin MS, Lin OH, Owi WT, Chan CH, Chia CH, Zakaria S, Villagracia AR, Akil HM (2016) Characterization of nanocellulose recovery from Elaeis guineensis frond for sustainable development. Clean Technol Environ Policy 18:2503–2512
Nordin NIAA, Ariffin H, Andou Y, Hassan MA, Shirai Y, Nishida H, Yunus WMZW, Karuppuchamy S, Ibrahim NA (2013) Modification of oil palm mesocarp fiber characteristic using superheated steam treatment. Molecules 18:9132–9146
Otsuka I, Njinang CN, Borsali R (2017) Simple fabrication of cellulose nanofibers via electrospinning of dissolving pulp and tunicate. Cellulose 24:3281–3288
Stieger N, Liebenberg W, Wessels JC (2009) UV spectrophotometric method for the identification and solubility determination of nevirapine. Pharmazie 64:690–691
Syamsu K, Maddu A, Bahmid NA (2016) Synthesis of nanofiber from oil palm empty fruit bunches cellulose acetate for bioplastics production. J Chem Mater Res 8:56–62
Wahab ANH, Tahir MP, Yunus MNY, Ashaari Z, Yong ACC, Ibrahim NA (2013) Influence of resin molecular weight on curring and thermal degradation of polywood made from phenolic prepreg palm veneers. J Adhes 90:210–229
Wang H, Gurau G, Rogers RD (2012) Ionic liquid processing of cellulose. Chem Soc Rev 41:1519–1537
Warid MNM, Ariffin H, Hassan MA, Shirai Y (2016) Optimization of superheated steam treatment to improve surface modification of oil palm biomass fiber. BioRes 11:5780–5796
Yasim-Anuar TAT, Ariffin H, Norrrahim MNF, Hassan MA (2017) Factors affecting spinnability of oil palm mesocarp fiber cellulose solution for the production of microfiber. BioResources 12:715–734
Zakaria MR, Fujimoto S, Hirata S, Hassan MA (2014a) Ball milling pretreatment of oil palm biomass for enhancing enzymatic hydrolysis. Appl Biochem Biotech 173:1778–1789
Zakaria MR, Hirata S, Hassan MA (2014b) Combined pretreatment using alkaline hydrothermal and ball milling to enhance enzymatic hydrolysis of oil palm mesocarp fiber. Bioresources Technol 169:236–243
Zhu N, Chen X (2013) Biofabrication of Tissue Scaffolds. Advances in Biomaterials Science and Biomedical Applications. INTECH, United Kingdom, pp 315–328. https://doi.org/10.5772/54125
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Ministry of Higher Education Malaysia (MOHE) for funding this research and for the provision of MyBrain 15 scholarship to the first and third authors. Authors would like to thank Seri Ulu Langat Palm Oil Mill for the provision of oil palm biomass.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Norrrahim, M.N.F., Ariffin, H., Yasim-Anuar, T.A.T. et al. Superheated steam pretreatment of cellulose affects its electrospinnability for microfibrillated cellulose production. Cellulose 25, 3853–3859 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1859-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-1859-3