Abstract
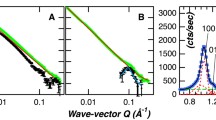
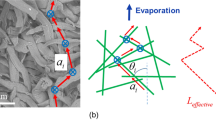
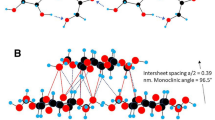
Water diffusion in cellulose was studied via two-phase Kärger model and the propagator method. In addition to ruling out anomalous diffusion, the mean squared displacements obtained at different diffusion times from the Kärger model allowed to characterize the system’s phases by their average confining sizes, average connectivity and average apparent diffusion coefficients. The two-phase scheme was confirmed by the propagator method, which has given insights into the confining phase-geometry, found consistent with a parallel-plane arrangement. Final results indicate that water in cellulose is confined in two different types of amorphous domains, one placed at fiber surfaces, the other at fiber cores. This picture fully corresponds to the phenomenological categories so far used to identify water in cellulose fibers, namely, free and bound water, or freezing and non-freezing water.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Callaghan P (2011) Translational dynamics and magnetic resonance: principles of pulsed gradient spin echo nmr. Oxford University Press, New York
Calvini P (2005) The influence of levelling-off degree of polymerisation on the kinetics of cellulose degradation. Cellulose 12:445. doi:10.1007/s10570-005-2206-z
Calvini P, Gorassini A, Merlani A (2008) On the kinetics of cellulose degradation: looking beyond the pseudo zero order rate equation. Cellulose 15:193. doi:10.1007/s10570-007-9162-8
Casieri C, Monaco A, De Luca F (2010) Evidence of temperature-induced subdiffusion of water on the micrometer scale in a Nafion membrane. Macromolecules 43(2):638–642. doi:10.1021/ma902323t
Conti A, Poggi G, Baglioni P, De Luca F (2014) On the macromolecular cellulosic network of paper: changes induced by acid hydrolysis studied by NMR diffusometry and relaxometry. Phys Chem Chem Phys 16:8409. doi:10.1039/C4CP00377B
English N, MacElroy J (2003) Molecular dynamics simulations of microwave heating of water. J Chem Phys 118:1589. doi:10.1063/1.1538595
Fengel D, Wegener G (1984) Wood: chemistry, ultrastructure, reactions. In: Walter de Gruyter. Berlin and New York. doi:10.1002/pol.1985.130231112
Horner A, Milchev A, Argyrakis P (1995) Role of percolation in diffusion on random lattices. Phys Rev E 52:3570. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.52.3570
Kaerger J, Pfeifer H, Heink W (1988) Principles and applications of self-diffusion measurements by nuclear magnetic resonance. Adv Magn Res 12:1
Kimmich R (1997) NMR—tomography, diffusometry, relaxometry. Springer, Berlin
Lepore A, Baccaro S, Casieri C, Cemmi A, De Luca F (2012) Role of water in the ageing mechanism of paper. Chem Phys Lett 531:206. doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2012.01.083
Long F, Bagley E, Wilkens J (2004) Anomalous diffusion of acetone into cellulose acetate. J Chem Phys 21:1412. doi:10.1063/1.1699249
Mueller M, Riekel C, Vuong R, Chanzy H (2000) Skin/core micro-structure in viscose rayon fibres analysed by X-ray microbeam and electron diffraction mapping. Polymer 41:2627. doi:10.1016/S0032-3861(99)00433-4
Nakamura K, Hatakeyama T, Hatakeyama H (1981) Studies on bound water of cellulose by differential scanning calorimetry. Text Res J 51:607. doi:10.1177/004051758105100909
Nisizawa K (1973) Mode of action of cellulases. J Ferment Technol 51:267
Niskanen K (1998) Paper physics. Fapet Oy, Helsinky
Palombo M, Gabrielli A, Servedio V, Ruocco G, Capuani S (2013) Structural disorder and anomalous diffusion in random packing of spheres. Sci Rep 3:2631
Price W (2009) NMR studies of translational motion. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Proietti N, Capitani D, Pedemonte E, Blumich B, Segre A (2004) Monitoring degradation in paper: non-invasive analysis by unilateral NMR, part II. J Magn Reson 170:113. doi:10.1016/j.jmr.2004.06.006
Schuster K, Aldred P, Villa M, Baron M, Loidl R, Biganska O, Patlazhan S, Navard P, Ruef H, Jericha E (2003) Characterising the emerging lyocell fibres structures by ultra small angle neutron scattering (USANS). Lenzinger Ber 82:107
Stephens C, Whitmore P, Morris H, Bier M (2008) Hydrolysis of the amorphous cellulose in cotton-based paper. Biomacromolecules 9:1093. doi:10.1021/bm800049w
Topgaard D, Soderman O (2001) Diffusion of water absorbed in cellulose fibers studied with \(^1\)H-NMR. Langmuir 17:2694. doi:10.1021/la000982l
UNI 8282 (1994) cellulose in dilute solutions—determination of limiting viscosity number—method in cupri-ethylenediamine (CED) solution—equivalent to the ISO standard 5351/1
Zhao H, Kwak J, Zhang Z, Brown H, Arey B, Holladay J (2007) Studying cellulose fiber structure by SEM, XRD, NMR and acid hydrolysis. Carbohydr Polym 68:235. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2006.12.013
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Conti, A., Palombo, M., Parmentier, A. et al. Two-phase water model in the cellulose network of paper. Cellulose 24, 3479–3487 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1338-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-017-1338-2