Abstract
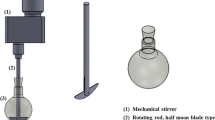
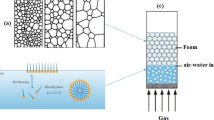
This article describes the preparation of novel aqueous spongy foams that are composed of three-dimensionally distributed wood-fiber networks stabilized with nanofibrillate cellulose (NFC) and/or microfibrillated cellulose (MFC). The free standing aqueous spongy foams were prepared with the entrapment of NFC and/or MFC—stabilized air-in-water (A/W) capillary foams using “gel trapping technique”. The stability of spongy foams could be controlled by manipulating the volume fraction of NFC and/or MFC and a secondary liquid immiscible with the continuous phase of the NFC and/or MFC suspension. Possible morphology and mechanical distribution of NFC and/or MFC within spongy foams were verified with optical microscope, SEM, and functional load-bearing method. Owing to three-dimensionally dispersed wood-fiber structure, ultra-lightweight (0.01–0.06 g/cm3), high porosity (>90%), and microporous (10–80 μm), the NFC and/or MFC reinforced spongy foams, improved compressional strength-vertical direction obviously, from 0.0 to more than 13.78 kPa.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akartuna I, Studart AR, Tervoort E, Gonzenbach UT, Gauckler LJ (2008) Stabilization of oil-in-water emulsions by colloidal particles modified with short amphiphiles. Langmuir ACS J Surf Colloids 24:7161–7168
Ali ZM, Gibson LJ (2013) The structure and mechanics of nanofibrillar cellulose foams. Soft Matter 9:1580–1588. doi:10.1039/c2sm27197d
Al-Qararah AM, Hjelt T, Koponen A, Harlin A, Ketoja JA (2013) Bubble size and air content of wet fibre foams in axial mixing with macro-instabilities. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 436:1130–1139. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfa.2013.08.051
Baillis D, Coquard R, Moura LM (2015) Heat transfer in cellulose-based aerogels: analytical modelling and measurements. Energy 84:732–744. doi:10.1016/j.energy.2015.03.039
Cervin NT, Andersson L, Ng JB, Olin P, Bergstrom L, Wagberg L (2013) Lightweight and strong cellulose materials made from aqueous foams stabilized by nanofibrillated cellulose. Biomacromolecules 14:503–511. doi:10.1021/bm301755u
Chen L, Rende D, Schadler LS, Ozisik R (2013) Polymer nanocomposite foams. J Mater Chem A 1:3837. doi:10.1039/c2ta00086e
Demitri C, Giuri A, Raucci MG, Giugliano D, Madaghiele M, Sannino A, Ambrosio L (2014) Preparation and characterization of cellulose-based foams via microwave curing. Interface Focus 4:20130053. doi:10.1098/rsfs.2013.0053
Denkov N, Ivanov I, Kralchevsky P, Wasan D (1992) A possible mechanism of stabilization of emulsions by solid particles. J Colloid Interface Sci 150:589–593
Dittmann J, Koos E, Willenbacher N (2013) Ceramic capillary suspensions: novel processing route for macroporous ceramic materials. J Am Ceram Soc 96:391–397
Dorcheh AS, Abbasi M (2008) Silica aerogel; synthesis, properties and characterization. J Mater Process Technol 199:10–26
Fernandez JE (2007) Materials for aesthetic, energy-efficient, and self-diagnostic buildings. Science 315:1807–1810. doi:10.1126/science.1137542
Gonzenbach UT, Studart AR, Tervoort E, Gauckler LJ (2007) Macroporous ceramics from particle-stabilized wet foams. J Am Ceram Soc 90:16–22. doi:10.1111/j.1551-2916.2006.01328.x
Heydarifard S, Nazhad MM, Xiao H, Shipin O, Olson J (2016) Water-resistant cellulosic filter for aerosol entrapment and water purification, Part I: production of water-resistant cellulosic filter. Environ Technol. doi:10.1080/09593330.2015.1130174
Hoffmann S, Koos E, Willenbacher N (2014) Using capillary bridges to tune stability and flow behavior of food suspensions. Food Hydrocoll 40:44–52
Jabbari M, Akesson D, Skrifvars M, Taherzadeh MJ (2015) Novel lightweight and highly thermally insulative silica aerogel-doped poly(vinyl chloride)-coated fabric composite. J Reinf Plast Compos 34:1581–1592. doi:10.1177/0731684415578306
Jelle BP (2011) Traditional, state-of-the-art and future thermal building insulation materials and solutions—properties, requirements and possibilities. Energy Build 43:2549–2563. doi:10.1016/j.enbuild.2011.05.015
Koos E (2014) Capillary suspensions: particle networks formed through the capillary force. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 19:575–584. doi:10.1016/j.cocis.2014.10.004
Koos E, Willenbacher N (2011) Capillary forces in suspension rheology. Science 331:897–900
Lehmonen J, Jetsu P, Kinnunen K, Hjelt T (2013) Potential of foam-laid forming technology in paper applications. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 28:392–398
Liu X, Fatehi P, Ni Y (2011) Adsorption of lignocellulosic materials dissolved in pre-hydrolysis liquor of kraft-based dissolving pulp production process on polymer-modified activated carbons. J Sci Technol Prod Proc 1(1):46–54
Madani A, Zeinoddini S, Varahmi S, Turnbull H, Phillion AB, Olson JA, Martinez DM (2014) Ultra-lightweight paper foams: processing and properties. Cellulose 21:2023–2031. doi:10.1007/s10570-014-0197-3
Nam YS, Park TG (1999) Biodegradable polymeric microcellular foams by modified thermally induced phase separation method. Biomaterials 20:1783–1790
Paunov VN (2003) Novel method for determining the three-phase contact angle of colloid particles adsorbed at air-water and oil-water interfaces. Langmuir ACS J Surf Colloids 19:7970–7976
Pham TN et al (2014) Industrially benign super-compressible piezoresistive carbon foams with predefined wetting properties: from environmental to electrical applications. Sci Rep 4:6933. doi:10.1038/srep06933
Pouyan Jahangiri RK, Zeinoddini Sadaf S, Madani Ario, Sharma Yash, Andre Phillion D, Martinez Mark, Olson James A (2014) On filtration and heat insulation properties of foam formed cellulose based materials. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 29:584–591
Stocco A, Rio E, Binks BP, Langevin D (2011) Aqueous foams stabilized solely by particles. Soft Matter 7:1260–1267
Tasset S, Cathala B, Bizot H, Capron I (2014) Versatile cellular foams derived from CNC-stabilized pickering emulsions. RSC Adv 4:893–898. doi:10.1039/c3ra45883k
Tzoumaki MV, Karefyllakis D, Moschakis T, Biliaderis CG, Scholten E (2015) Aqueous foams stabilized by chitin nanocrystals. Soft Matter 11:6245–6253
Wang Q, Liu S, Yang G, Chen J, Ni Y (2015) Cationic polyacrylamide enhancing cellulase treatment efficiency of hardwood kraft-based dissolving pulp. Bioresour Technol 183:42–46. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2015.02.011
Wege HA, Kim S, Paunov VN, Zhong Q, Velev OD (2008) Long-term stabilization of foams and emulsions with in situ formed microparticles from hydrophobic cellulose. Langmuir ACS J Surf Colloids 24:9245–9253
Wei G, Liu Y, Zhang X, Yu F, Du X (2011) Thermal conductivities study on silica aerogel and its composite insulation materials. Int J Heat Mass Transf 54:2355–2366
Wicklein B, Kocjan A, Salazar-Alvarez G, Carosio F, Camino G, Antonietti M, Bergström L (2015) Thermally insulating and fire-retardant lightweight anisotropic foams based on nanocellulose and graphene oxide. Nat Nanotechnol 10:277–283
Zhang Y, Wu J, Wang H, Meredith JC, Behrens SH (2014) Stabilization of liquid foams through the synergistic action of particles and an immiscible liquid. Angew Chem 53:13385–13389. doi:10.1002/anie.201405816
Zhang Y, Allen MC, Zhao R, Deheyn DD, Behrens SH, Meredith JC (2015) Capillary foams: stabilization and functionalization of porous liquids and solids. Langmuir ACS J Surf colloids 31:2669–2676. doi:10.1021/la504784h
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to NSERC Strategic Network—Innovative Green Wood Fibre Products (Canada) and Guangxi Key Laboratory of Clean Pulp & Papermaking and Pollution Control (China) for part of funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Lu, P., Xiao, H. et al. Novel aqueous spongy foams made of three-dimensionally dispersed wood-fiber: entrapment and stabilization with NFC/MFC within capillary foams. Cellulose 24, 241–251 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1103-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-016-1103-y