Abstract
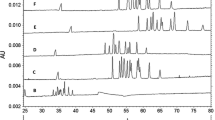
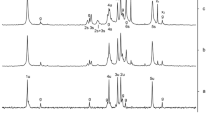
Hemicelluloses such as xylans play an increasing role as renewable raw materials for technological applications. The complex and variable composition of hemicelluloses requires powerful analytical techniques in order to assess their composition. In the present study, the neutral fraction of hydrothermally isolated xylan from beech wood was characterized by capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection (CE-LIF) upon derivatization with 8-aminopyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid. Reproducible separation of the xylo-oligosaccharides was achieved using a polyvinyl alcohol coated capillary and a 25 mM sodium acetate buffer, pH 4.75, as background electrolyte at an applied voltage of −30 kV. Intermediate precision expressed as relative standard deviation was below 2.0 % for migration times and below 10 % for relative peak areas except for the oligomers present at very low concentrations only. At the same time, derivatization conditions proved to be robust as well. Samples obtained by fractionation of the xylan were subsequently characterized by CE-LIF. In addition, capillary electrophoresis with mass spectrometry detection indicated the presence of small amounts of xylo-oligosaccharides containing additional sugar moieties such as 4-O-methylglucuronic acid. Moreover, minor components containing acetyl groups could be detected. The presence of these impurities was confirmed by nuclear magnetic resonance analysis of the fractions. In conclusion, although none of the techniques applied here gave a complete picture of the composition of the investigated xylan or its fractions, the combination provided insight into the complexity of the sample.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- APTS:
-
8-Aminopyrene-1,3,6-trisulfonic acid
- BGE:
-
Background electrolyte
- CE:
-
Capillary electrophoresis
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- DP:
-
Degree of polymerization
- EACA:
-
ε-Aminocaproic acid
- ESI-MS:
-
Electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry
- G:
-
Gluco-oligomer (numbers indicate degree of polymerization)
- HPAEC-PAD:
-
High performance anion-exchange chromatography with pulsed amperometric detection
- HTX:
-
Hydrothermally treated beech wood xylan
- HTX-n:
-
Neutral fraction of hydrothermally treated beech wood xylan
- LIF:
-
Laser-induced fluorescence
- MALDI-MS:
-
Matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry
- MGA:
-
4-O-methylglucuronic acid
- NMR:
-
Nuclear magnetic resonance
- PGC-ELSD:
-
Porous graphitized carbon liquid chromatography with evaporative light scattering detection
- PVA:
-
Polyvinyl alcohol
- RP-HPLC:
-
Reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography
- RSD:
-
Relative standard deviation
- SEC:
-
Size-exclusion chromatography
- THF:
-
Tetrahydrofuran
- X:
-
Xylo-oligomer (numbers indicate degree of polymerization)
References
Bunz S-C, Cutillo F, Neusüß C (2013a) Analysis of native and APTS-labeled N-glycans by capillary electrophoresis/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:8277–8284
Bunz S-C, Rapp E, Neusüss C (2013b) Capillary electrophoresis/mass spectrometry of APTS-labeled glycans for the identification of unknown glycan species in capillary electrophoresis/laser-induced fluorescence systems. Anal Chem 85:10218–10224
Chong SL, Nissilä T, Ketola RA, Koutaniemi S, Derba-Maceluch M, Mellerowicz EJ, Tenkanen M, Tuomainen P (2011) Feasibility of using atmospheric pressure matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization with ion trap mass spectrometry in the analysis of acetylated xylooligosaccharides derived from hardwoods and Arabidopsis thaliana. Anal Bioanal Chem 401:2995–3009
Daus S, Petzold-Welcke K, Kötteritzsch M, Baumgaertel A, Schubert US, Heinze T (2011) Homogeneous sulfation of xylan from different sources. Macromol Mater Eng 296:551–561
DeLong EA (1978) Verfahren zur Behandlung von Lignocellulosematerial und dadurch gewonnenes Lignocelluloseprodukt in Teilchenform. DE Patent 2830476C2 (in German)
Deutschmann R, Dekker RFH (2012) From plant biomass to bio-based chemicals: latest developments in xylan research. Biotechnol Adv 30:1627–1640
Doliška A, Strnad S, Ribitsch V, Kleinschek KS, Willför S, Saake B (2009) Analysis of galactoglucomannans from spruce wood by capillary electrophoresis. Cellulose 16:1089–1097
Ebringerová A, Heinze T (2000) Xylan and xylan derivatives—biopolymers with valuable properties, 1. Macromol Rapid Commun 21:542–556
Ebringerová A, Hromádková Z (1999) Xylans of industrial and biomedical importance. Biotechnol Genet Eng 16:325–346
Ebringerová A, Hromádková Z, Heinze T (2005) Hemicellulose. Adv Polym Sci 186:1–67
El Rassi Z (1999) Recent developments in capillary electrophoresis and capillary electrochromatography of carbohydrate species. Electrophoresis 20:3134–3144
Garrote G, Parajó JC (2002) Non-isothermal autohydrolysis of Eucalyptus wood. Wood Sci Technol 36:111–123
Guttman A, Cooke N, Starr CM (1994) Capillary electrophoresis separation of oligosaccharides: I. Effect of operational variables. Electrophoresis 15:1518–1522
Guttman A, Chen FTA, Evangelista RA, Cooke N (1996) High-resolution capillary gel electrophoresis of reducing oligosaccharides labeled with 1-aminopyrene-3,6,8-trisulfonate. Anal Biochem 233:234–242
Harvey DJ (2011) Derivatization of carbohydrates for analysis by chromatography, electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 879:1196–1225
Hiltunen S, Sirén H (2013) Analysis of monosaccharides and oligosaccharides in the pulp and paper industry by use of capillary zone electrophoresis: a review. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:5773–5784
Hilz H, de Jong LE, Kabel MA, Schols HA, Voragen AGJ (2006) A comparison of liquid chromatography, capillary electrophoresis, and mass spectrometry methods to determine xyloglucan structures in black currants. J Chromatogr A 1133:275–286
Hoffman M, Jia Z, Pena MJ, Cash M, Harper A, Blackburn AR, Darvill A, York WS (2005) Structural analysis of xyloglucans in the primary cell walls of plants in the subclass Asteridae. Carbohydr Res 340:1826–1840
Kabel MA, Carvalheiro F, Garrote G, Avgerinos E, Koukios E, Parajo JC, Girio FM, Schols HA, Voragen AGJ (2002a) Hydrothermally treated xylan rich by-products yield different classes of xylo-oligosaccharids. Carbohydr Polym 50:47–56
Kabel MA, Schols HA, Voragen AGJ (2002b) Complex xylo-oligosaccharides identified from hydrothermally treated Eucalyptus wood and brewery´s spent grain. Carbohydr Polym 50:191–200
Kabel MA, Heijnis WH, Bakx EJ, Kuijpers R, Voragen AGJ, Schols HA (2006) Capillary electrophoresis fingerprinting, quantification and mass-identification of various 9-aminopyrene-1,4,6-trisulfonate-derivatized oligomers derived from plant polysaccharides. J Chromatogr A 1137:119–126
Metsämuuronen S, Lyytikäinen K, Backfolk K, Sirén H (2013) Determination of xylo-oligosaccharides in enzymatically hydrolysed pulp by liquid chromatography and capillary electrophoresis. Cellulose 20:1121–1133
Mittermayr S, Guttman A (2012) Influence of molecular configuration and conformation on the electromigration of oligosaccharides in narrow bore capillaries. Electrophoresis 33:1000–1007
O’Shea MG, Samuel MS, Konik CM, Morell MK (1998) Fluorophore-assisted carbohydrate electrophoresis (FACE) of oligosaccharides: efficiency of labeling and high-resolution separation. Carbohydr Res 307:1–12
Pabst M, Kolarich D, Pöltl G, Dalik T, Lubec G, Hofinger A, Altmann F (2009) Comparison of fluorescent labels for oligosaccharides and introduction of a new postlabeling purification method. Anal Biochem 384:263–273
Puls J, Dietrichs HH (1991) Separation of lignocelluloses into highly accessible fibre materials and hemicellulose fraction by the steaming-extraction process. Communication for European communities, EUR7091, energy biomass conference, pp 348–353
Ruhaak LR, Zauner G, Huhn C, Bruggink C, Deelder AM, Wuhrer M (2010) Glycan labeling strategies and their use in identification and quantification. Anal Bioanal Chem 397:3457–3481
Teleman A, Tenkanen M, Jacobs A, Dahlman O (2002) Characterization of O-acetyl-(4-O-methylglucuruno)xylan isolated from birch and beech. Carbohydr Res 337:373–377
Vismeh R, Humpula JF, Chundawat SPS, Balan V, Dale BE, Jones AD (2013) Profiling of soluble neutral oligosaccharides from treated biomass using solid phase extraction and LC-TOF MS. Carbohydr Polym 94:791–799
Westphal Y, Kühnel S, Schols HA, Voragen AGJ, Gruppen H (2010) LC/CE-MS tools for the analysis of complex arabino-oligosaccharides. Carbohydr Res 345:2239–2251
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jáč, P., Elschner, T., Reiter, C. et al. Characterization of hydrothermally isolated xylan from beech wood by capillary electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence and mass spectrometry detection. Cellulose 21, 3993–4007 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0456-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-014-0456-3