Abstract
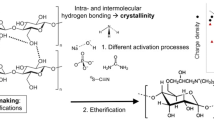
The direct acylation of cellulose and different pulps with various acid chlorides was systematically screened. The syntheses were started in a heterogeneous solid–liquid reaction medium in hot pyridine with aliphatic and aromatic acid chlorides. After a few hours, depending on the reagent used, a homogenous solution was obtained. The obtained cellulose esters usually show a high degree of substitution (DS) and polymerization and are soluble in organic solvents. Esterification of softwood dissolving pulp, hardwood kraft pulp and hardwood kraft pulp-hemicellulose poor were also studied. The results show that almost identical DS were obtained for pulp derivatives compared to esters of microcrystalline cellulose. Thermogravimetric analysis and differential scanning calorimetry of the synthesized materials showed an improved thermal stability and various discrete thermal transitions compared to the original cellulose. The scanning electron microscopy images of derivatives showed a relatively flat and smooth surface with an absence of fibrous structure. The reactive dissolution of cellulose or pulp in pyridine is a straightforward and easy route to obtain long-chain aliphatic and aromatic cellulose esters.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayitou AJ-L, Jesuraj JL, Barooah N, Ugrinov A, Sivaguru J (2009) Enantiospecific photochemical norrish/yang type II reaction of nonbiaryl atropchiral α-oxoamides in solution: axial to point chirality transfer. J Am Chem Soc 131(32):11314–11315. doi:10.1021/ja9050586
Barthel S, Heinze T (2006) Acylation and carbanilation of cellulose in ionic liquids. Green Chem 8(3):301–306. doi:10.1039/B513157J
Bras J, Vaca-Garcia C, Borredon M-E, Glasser W (2007) Oxygen and water vapor permeability of fully substituted long chain cellulose esters (LCCE). Cellulose 14(4):367–374. doi:10.1007/s10570-007-9123-2
Cheng HN, Dowd MK, Selling GW, Biswas A (2010) Synthesis of cellulose acetate from cotton byproducts. Carbohydr Polym 80(2):449–452. doi:10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.11.048
Crépy L, Chaveriat L, Banoub J, Martin P, Joly N (2009) Synthesis of cellulose fatty esters as plastics: influence of the degree of substitution and the fatty chain length on mechanical properties. ChemSusChem 2(2):165–170. doi:10.1002/cssc.200800171
Edgar KJ, Pecorini TJ, Glasser WG (1998) Long-chain cellulose esters: Preparation, properties, and perspective. In: ACS symposium series 688. Cellulose derivatives: Modification, characterization, and nanostructures. American Chemical Society, p 38
Forstall F (2002) Industry and trade summary: wood pulp and waste paper. United States International Trade Commission, Washington
Garcés J, Franco P, Oliveros L, Minguillón C (2003) Mixed cellulose-derived benzoates bonded on allylsilica gel as HPLC chiral stationary phases: influence of the introduction of an aromatic moiety in the fixation substituent. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 14(9):1179–1185. doi:10.1016/s0957-4166(03)00176-9
Granström M, Kavakka J, King A, Majoinen J, Mäkelä V, Helaja J, Hietala S, Virtanen T, Maunu S-L, Argyropoulos D, Kilpeläinen I (2008) Tosylation and acylation of cellulose in 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. Cellulose 15(3):481–488. doi:10.1007/s10570-008-9197-5
Heinze T, Liebert T, Koschella A (2006) Esterification of polysaccharides. Springer, Berlin
King AWT, Jalomaki J, Granström M, Argyropoulos DS, Heikkinen S, Kilpeläinen I (2010) A new method for rapid degree of substitution and purity determination of chloroform-soluble cellulose esters, using 31P NMR. Anal Methods 2(10):1499–1505
Malm CJ, Mench JW, Kendall DL, Hiatt GD (1951) Aliphatic acid esters of cellulose. Preparation by acid-chloride-pyridine procedure. Ind Eng Chem 43(3):684–688. doi:10.1021/ie50495a033
Peydecastaing J, Girardeau S, Vaca-Garcia C, Borredon M (2006) Long chain cellulose esters with very low DS obtained with non-acidic catalysts. Cellulose 13(1):95–103. doi:10.1007/s10570-005-9012-5
Stampfli H, Patil G, Sato R, Quon CY (1990) Separation of R(+)-and S(−)-benzyl-3-tetrahydrofuroates using two different chiral columns. J Liq Chromatogr 13(7):1285–1290. doi:10.1080/01483919008049249
Swatloski RP, Spear SK, Holbrey JD, Rogers RD (2002) Dissolution of cellose with ionic liquids. J Am Chem Soc 124(18):4974–4975. doi:10.1021/ja025790m
Vaca-Garcia C, Thiebaud S, Borredon M, Gozzelino G (1998) Cellulose esterification with fatty acids and acetic anhydride in lithium chloride/N,N-dimethylacetamide medium. J Am Oil Chem Soc 75(2):315–319. doi:10.1007/s11746-998-0047-2
Vaca-Garcia C, Borredon ME, Gaseta A (2001) Determination of the degree of substitution (DS) of mixed cellulose esters by elemental analysis. Cellulose 8(3):225–231. doi:10.1023/a:1013133921626
Vassel B, Skelly WG (1963) N-chlorobetainyl chloride. Org Synth 4:154
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Forest Cluster Ltd. as a part of the Future Biorefinery (FuBio) project and by the Academy of Finland (grants 122534 and 132150).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Spectroscopic data and thermal analysis results of the prepared cellulose and pulp derivatives are presented. This material is available free of charge via the Internet.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Labafzadeh, S.R., Kavakka, J.S., Sievänen, K. et al. Reactive dissolution of cellulose and pulp through acylation in pyridine. Cellulose 19, 1295–1304 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9720-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-012-9720-6