Abstract
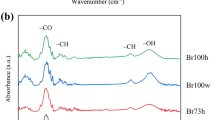
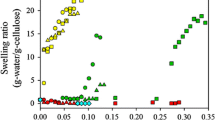
Ethylene diamine (EDA)/salt solvent systems can dissolve cellulose without any pretreatment. A comparison of the electrical conductivity of different salts in EDA was made at 25 °C, and conductivity decreased in the order of KSCN>KI>NaSCN at the same molar concentration. Among the salts tested, potassium thiocyanate (KSCN) was capable of dissolving both high molecular weight (DP>1000) and low molecular weight (DP = 210) cellulose, and this was confirmed by polarized light microscopy. 39K and 14N NMR experiments were conducted at 70 °C as a function of cellobiose concentration with EDA/KSCN as the solvent. The results showed that the K+ ion interacts with cellobiose more than the SCN− ion does. Recovered cellulose was studied by infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and wide angle X-ray diffraction (WAXD). Changes in the FTIR absorption bands at 1,430 and 1,317 cm−1 were associated with a change in the conformation of the C-6CH2OH group. The changes in positions and/or intensities of absorption bands at 2,900, 1,163, and 8,97cm−1 were related to the breaking of hydrogen bonds in cellulose. X-ray diffraction studies revealed that cellulose, recovered by precipitating cellulose solutions with water, underwent a polymorphic transformation from cellulose I to cellulose II.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bochek AM (2003) Effect of hydrogen bonding on cellulose solubility in aqueous and nonaqueous solvents. Russ J Appl Chem 76(11):1711–1719
Boerstoel H, Maatman H et al (2001) Liquid crystalline solutions of cellulose in phosphoric acid. Polymer 42(17):7371–7379
Cadars S, Lesage A et al (2005) Chemical shift correlations in disordered solids. J Am Chem Soc 127(12):4466–4476
Cai J, Zhang L (2005) Rapid dissolution of cellulose in LiOH/Urea and NaOH/Urea aqueous solutions. Macromol Biosci 5(6):539–548
Cuculo JA, Smith CB et al (1994a) A Study on the Mechanism of Dissolution of the Cellulose/ NH3/NH4SCN System .1. J Polym Sci Part a-Polym Chem 32(2):229–239
Cuculo JA, Smith CB et al (1994b) A Study on the Mechanism of Dissolution of the Cellulose/NH3/NH4SCN System .2. J Polym Sci Part a-Polym Chem 32(2):241–247
Fischer S, Leipner H et al (2003) Inorganic molten salts as solvents for cellulose. Cellulose 10(3):227–236
Fischer S, Leipner H et al (2000) Structural changes of cellulose dissolved in molten salt hydrates. Abstr Paper Am Chem Soc 219:U281–U281
Frey M, Joo Y et al (2003) New solvents for cellulose electrospinning and preliminary nanofiber spinning results. Polym Preprint 44(2):168–169
Frey MW, Chan H et al (2005) Rheology of cellulose/KSCN/ethylenediamine solutions and coagulation into filaments and films. J Polym Sci Part B-Polym Phys 43(15):2013–2022
Frey MW, Li L et al (2006) Dissolution of cellulose in ethylene diamine/salt solvent systems. Cellulose 13(2):147–155
Frey MW, Theil MH (2004) Calculated phase diagrams for cellulose/ammonia/ammonium thiocyanate solutions in comparison to experimental results. Cellulose 11(1):53–63
Hattori K, Abe E et al (2004) New solvents for cellulose. II. Ethylenediamine/thiocyanate salt system. Polym J 36(2):123–130
Hattori K, Cuculo JA et al (2002) New solvents for cellulose: Hydrazine/thiocyanate salt system. J Polym Sci Part A-Polym Chem 40(4):601–611
Hattori M, Koga T et al (1998) Aqueous calcium thiocyanate solution as a cellulose solvent. Structure and interactions with cellulose. Polym J 30(1):43–48
Henrissat B, Marchessault RH et al (1987) A solid-state C-13 NMR-study of the Cellulose-I-Ethylenediamine complex. Polymer Communications 28(4):113–115
Horii F, Hirai A et al (1983) Solid-state C-13-NMR study of conformations of oligosaccharides and cellulose—Conformation of CH2OH group about the exo-cyclic C–C bond. Polymer Bull 10(7–8):357–361
Isbin HS, Kobe KA (1945) The solubility of some salts in ethylenediamine, monoethanolamine and ethylene glycol. J Am Chem Soc 67(3):464–465
Isogai A, Ishizu A et al (1987) Dissolution mechanism of cellulose in SO2-Amine-Dimethylsulfoxide. J Appl Polym Sci 33(4):1283–1290
Isogai A, Usuda M et al (1989) Solid-state CP/ MAS C-13 NMR-study of cellulose polymorphs. Macromolecules 22(7):3168–3172
McCormick CL, Callais PA et al (1985) Solution studies of cellulose in lithium-chloride and N,N-dimethylacetamide. Macromolecules 18(12):2394–2401
Michael M, Ibbett RN et al (2000) Interaction of cellulose with amine oxide solvents. Cellulose 7(1):21–33
Moulthrop JS, Swatloski RP et al (2005) High-resolution C-13 NMR studies of cellulose and cellulose oligomers in ionic liquid solutions. Chem Commun (12):1557–1559
Nehls I, Wagenknecht W et al (1994) Characterization of cellulose and cellulose derivatives in solution by high-resolution C-13-NMR spectroscopy. Prog Polym Sci 19(1):29–78
Nelson ML, O’Connor RT (1964) Relation of certain infrared bands to cellulose crystallinity and crystal lattice type. I. Spectra of lattice types I, II, III, and of amorphous cellulose. J Appl Polym Sci 8(3):1311–1324
Numata Y, Kono H et al (2003) Cross-polarization/magic-angle spinning C-13 nuclear magnetic resonance study of cellulose I-ethylenediamine complex. J Biosci Bioeng 96(5):461–466
Oh SY, Yoo DI et al (2005) Crystalline structure analysis of cellulose treated with sodium hydroxide and carbon dioxide by means of X-ray diffraction and FTIR spectroscopy. Carbohydrate Res 340(15):2376–2391
Striegel AM (2003) Advances in the understanding of the dissolution mechanism of cellulose in DMAc/LiCl. J Chile Chem Soc 48(1):73–77
Swatloski RP, Spear SK et al (2002a) Dissolution of cellulose with ionic liquids. J Am Chem Soc 124(18):4974–4975
Swatloski RP, Spear SK et al (2002b) Ionic liquids: New solvents for non-derivitized cellulose dissolution. Abstr Paper Am Chem Soc 224:U622–U622
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the NTC (National Textile Center) for funding this project, Dr. Ivan Keresztes, NMR Instruments Laboratory, Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, for technical support regarding the NMR measurements, and Prof. David B. Zax, Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, and Prof. David B. Wilson, Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics, Cornell University, for reviewing this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, M., Frey, M.W. The role of salt on cellulose dissolution in ethylene diamine/salt solvent systems. Cellulose 14, 225–234 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-007-9110-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-007-9110-7