Abstract
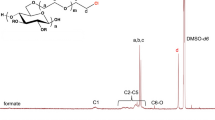
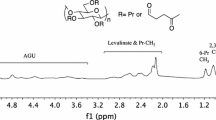
Functional thiomethyl and thiosulfate derivatives of carboxymethylcellulose (CMC, DS = 0.9) were synthesized by nucleophilic displacement reactions. Alkylation of CMC by allyl glycidyl ether took mainly place at the primary positions of the cellulose backbone and yielded a 6-O-(3′-allyloxy-2′-hydroxypropyl)-CMC 1 with a partial DS of 3′-allyloxy-2′-hydroxypropyl substituents DSallyl of up to 0.43. Addition of tetrathionate to the allyl groups gave rise to 6-O-(2′′,3′′-bis(thiosulfato)propoxy-2′-hydroxypropyl)-CMC 2. As the addition of tetrathionate was sluggish and incomplete, alternatively bromine was added and the resulting dibromide was substituted by thiosulfate. A 40% conversion of the allyl groups was achieved by this two-step procedure. On the other hand, the addition of bromine to 1 in aqueous solution almost quantitatively yielded the bromohydrin derivative which was converted by displacement reaction with thiosulfate to 6-O-(2′′-hydroxy-3′′-thiosulfatopropoxy-2′-hydroxypropyl)-CMC 4. 6-Thiomethyl-6-deoxy-CMC 6 was synthesized by displacement reaction of 6-O-tosylcellulose with sodium methylsulfide and subsequent carboxymethylation of the cellulose backbone. A partial DS of thiomethyl substituents DSThM=0.65 exclusively at the primary positions was obtained. All functional CMC derivatives, 2, 4, and 6 were readily available in gram quantities, rather stable and highly water soluble for pH > 3. On gold surfaces they form self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) with thicknesses of 1.2 to 2.4 nm as determined by surface plasmon resonance (SPR).
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c:
-
weight concentration
- CMC:
-
carboxymethylcellulose
- d:
-
days
- DMAc:
-
N,N-dimethylacetamide
- DMSO:
-
dimethylsulfoxide
- DP:
-
degree of polymerization
- DS:
-
degree of substitution
- EA:
-
elemental analysis
- h:
-
hours
- m:
-
mol/l
- MALLS:
-
multi angle laser light scattering
- min:
-
minutes
- mdeg:
-
millidegrees
- MW:
-
weight average molecular weight
- n:
-
refractive index
- r.t.:
-
room temperature
- s:
-
seconds
- SAM:
-
self-assembled monolayer
- SPR:
-
surface plasmon resonance
- λ:
-
wavelength
References
R.E.A.V. Axen J.O. Porath P.J.E. Carlsson (1975) ArticleTitleThiopolymers and derivatives. Patent DE 2523793, Exploaterings AB T.B.F Chem. Abstr. 84 151744
A.A. Baker W. Helbert J. Sugiyama M.J. Miles (2000) ArticleTitleNew insight into cellulose structure by atomic force microscopy shows the Iα crystal phase at near-atomic resolution Biophys. J. 79 1139–1145
M.W.J. Beulen B.-H. Huisman P.A. van der Heijden F.C.J.M. van Veggel M.G. Simons E.M.E.F. Biemond P.J. de Lange D.N. Reinhoudt (1996) ArticleTitleEvidence for nondestructive adsorption of dialkyl sulfides on gold Langmuir 12 6170–6172
S. Choi H. Lauer G. Wenz M. Bruns D.F.S. Petri (2000) ArticleTitleFormation of dense cellulose monolayers on silver surfaces J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 11 11–15
H. Distler (1967) ArticleTitleThe chemistry of bunte salts Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 6 544–553
E. Heuser M. Heath W.H. Shochley (1950) ArticleTitleThe rate of esterification of primary and secondary hydroxyls of cellulose with p-toluenesulfonyl (tosyl) chloride J. Am. Chem. Soc. 72 670–674
F.F.L. Ho D.W. Klosiewicz (1980) ArticleTitleProton nmr spectrometry for determination of substituents and their distribution in carboxymethylcellulose Anal. Chem. 52 913–916
T. Itoh Y. Tsujii H. Suzuki T. Fukuda T. Miyamoto (1992) ArticleTitleMono- and multilayer Langmuir–Blodgett films of cellulose tri-n-alkyl esters study by transmission electron microscopy Polym. J. 24 641–652
E. Jaehne T. Kowalik H.-J. Adler A. Plagge M. Stratmann (2002) ArticleTitleUltra-thin layers of phosphorylated cellulose derivatives on metal surfaces Macromol. Symp. 177 97–109
K. Kamide M. Saito (1983) ArticleTitlePersistence length of cellulose and cellulose derivatives in solution Macromol. Chem. Rapid Commun. 4 33–39
T. Kawaguchi H. Nakahara K. Fukuda (1985) ArticleTitleMono- and multilayers of amphiphilic cellulose esters and some novel comblike polymers J. Colloid Interface Sci. 104 290–293
A.R. Khan L. Barton V. T. D’Souza (1996) ArticleTitleEpoxides of the secondary side of cyclodextrins J. Am. Chem. Soc. 61 8301–8303
D. Klemm T. Heinze B. Philipp W. Wagenknecht (1997) ArticleTitleNew approaches to advanced polymers by selective cellulose functionalization Acta Polym. 48 277–297
T. Kowalik H.-J. Adler A. Plagge M. Stratmann (2000) ArticleTitleUltrathin layers of phosphorylated cellulose derivatives on aluminium surfaces Macromol. Chem. Phys. 15 2064–2069
W.-M. Kulicke A.H. Kull W. Kull H. Thielking J. Engelhardt J.-B. Pannek (1996) ArticleTitleCharacterization of aqueous carboxymethylcellulose solutions in terms of their molecular structure and its influence on rheological behaviour Polymer 37 2723–2731
B. Lehr M. Seufert G. Wenz G. Decher (1996) ArticleTitleFabrication of poly(p-phenylene vinylene) (ppv) nano-heterocomposite films via layer-by-layer adsorption Supramol. Sci. 2 199–207
D.W. Lynch W.R. Hunter (1985) Optical constants of metals E.D. Palik (Eds) Handbook of Optical Constants of Solids Academic Press San DiegoCA 286–295
J.W. Mays (1988) ArticleTitleSolution properties and chain stiffness of (cyanoethyl) (hydroxypropyl)cellulose Macromolecules 21 3179–3183
S. Michielsen (1999) Specific refractive index of polymers in dilute solution/c. Refractometric calibration data J. Brandrup E.H. Immergut E.A. Grulke (Eds) Polymer Handbook J. Wiley & Sons New York VII/500
K. Rahn M. Diamantoglou D. Klemm H. Berghmans T. Heinze (1996) ArticleTitleHomogeneous synthesis of cellulose p-toluenesulfonates in NN-dimethylacetamide/LiCl solvent system Angew. Makromol. Chem. 238 143–163
M. Schaub K. Mathauer S. Schwiegk P.A. Albouy G. Wenz G. Wegner (1992) ArticleTitleInvestigation of molecular superstructures of hairy rodlike polymers by X-ray reflection Thin Solid Films 210 397–400
M. Schaub G. Wenz G. Wegner A. Stein D. Klemm (1993) ArticleTitleUltrathin films of cellulose on silicon wafers Adv. Mater. 12 919–921
S.I. Takahashi T. Fujimoto B.M. Barua T. Miyamoto (1986) ArticleTitle13-C-nmr spectral studies on the distribution of substituents in some cellulose derivatives J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. Ed. 24 2981–2993
G. Wenz S. Choi M. Bruns T. Schimmel H. Beyer D.F. Siqueira Petri (1999) ArticleTitleSynthesis of a cellulose thiosulfate and its immobilization on gold surfaces Polymer 40 1593–1601
Wenz G., Petri D.F. and Choi S.W. 2001. Polymer thiosulfates for coating of metals. Patent US 6,245,579 B1 Universität KarlsruheChem. Abstr. 130, 183895.
S.A. Zynio A.V. Samoylov E.R. Surovtseva V.M. Mirsky Y.M. Shirshov (2002) ArticleTitleBimetallic layers increase sensitivity of affinity sensors based on surface plasmon resonance Sensors 2 62–70
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wenz, G., Liepold, P. & Bordeanu, N. Synthesis and SAM formation of water soluble functional carboxymethylcelluloses: thiosulfates and thioethers. Cellulose 12, 85–96 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-004-0199-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-004-0199-7