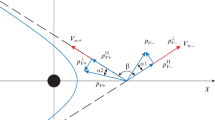
Abstract
Designing optimal spacecraft trajectories is a critical task for any mission design. In particular, mission designers seek to exploit from the combined effects of planetary gravity-assist maneuvers and electric propulsions systems to reduce both the flight time and propellant consumption. In order to obtain more realistic results, disturbances such as (1) gravitational force of secondary bodies, (2) Solar radiation pressure, and (3) non-spherical gravity models have to be considered. Mission designers are, thus, faced with the task of solving a constrained optimal control problem where the complexities are compounded due to the nonlinearity of the dynamical models as well as the existence of intermediate constraints (e.g., gravity-assist constraints). This investigation presents a methodology to incorporate all of the enumerated factors in planetary trajectory design using the indirect optimization method. In order to demonstrate the utility of the method, an interplanetary trajectory from the Earth to Jupiter is considered, while the spacecraft performs a gravity-assist maneuver with the Earth en route to Jupiter. An appealing feature of the developed tool is the flexibility in adding or removing any of the disturbances, which allows us to assess the impact of each item on the final solution. The results are compared against two existing solutions in the literature and demonstrate the utility of the method.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/horizons.cgi [Retrieved on: Dec. 21, 2018].
References
Batliss, S.: Precision targeting for multiple swingby interplanetary trajectories. J. Spacecr. Rockets 8(9), 927–931 (1971)
Bertrand, R., Epenoy, R.: New smoothing techniques for solving bang–bang optimal control problems-numerical results and statistical interpretation. Optim. Control Appl. Methods 23(4), 171–197 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1002/oca.709
Betts, J.: Survey of numerical methods for trajectory optimization. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 21(2), 193–207 (1998). https://doi.org/10.2514/2.4231
Bryson, A.E.: Applied Optimal Control: Optimization, Estimation and Control. Routledge, London (2018)
Conway, B.A.: A survey of methods available for the numerical optimization of continuous dynamic systems. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 152(2), 271–306 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10957-011-9918-z
Dellnitz, M., Ober-Blöbaum, S., Post, M., Schütze, O., Thiere, B.: A multi-objective approach to the design of low thrust space trajectories using optimal control. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 105(1–3), 33 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-009-9229-y
Enright, P.J., Conway, B.A.: Discrete approximations to optimal trajectories using direct transcription and nonlinear programming. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 15(4), 994–1002 (1992). https://doi.org/10.2514/3.20934
Guo, T., Jiang, F., Baoyin, H., Li, J.: Fuel optimal low thrust rendezvous with outer planets via gravity assist. Sci. China Phys. Mech. Astron. 54(4), 756–769 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11433-011-4291-3
Hans, S., Renjith, R.K.: Finite difference scheme for automatic costate calculation. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 19(1), 231–239 (1996). https://doi.org/10.2514/3.21603
Jiang, F., Baoyin, H., Li, J.: Practical techniques for low-thrust trajectory optimization with homotopic approach. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 35(1), 245–258 (2012). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.52476
Kawaguchi, J., Fujiwara, A., Uesugi, T.K.: The ion engines cruise operation and the earth swingby of “Hayabusa” (Muses-C). Space Technol. 25(2), 105–115 (2005). https://doi.org/10.2514/6.IAC-04-Q.5.02
Kugelberg, J., Bodin, P., Persson, S., Rathsman, P.: Accommodating electric propulsion on SMART-1. Acta Astronaut. 55(2), 121–130 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2004.04.003
Li, H., Chen, S., Baoyin, H.: J2-Perturbed multitarget rendezvous optimization with low thrust. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 41(3), 802–808 (2018). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.G002889
Lieske, J.H.: Galilean satellites and the Galileo space mission. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 66(1), 13–20 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00048819
Longuski, J.M., Williams, S.N.: Automated design of gravity-assist trajectories to Mars and the outer planets. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 52(3), 207–220 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00048484
Martell, C.A., Lawton, J.A.: Adjoint variable solutions via an auxiliary optimization problem. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 18(6), 1267–1272 (1995). https://doi.org/10.2514/3.21540
McInnes, C.R.: Solar Sailing: Technology, Dynamics and Mission Applications. Springer, Berlin (2013). Chap. 2
Negri, R.B., de Almeida Prado, A.F.B., Sukhanov, A.: Studying the errors in the estimation of the variation of energy by the “patched-conics” model in the three-dimensional swing-by. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 129(3), 269–284 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-017-9779-3
Ocampo, C.: An architecture for a generalized spacecraft trajectory design and optimization system. In: Libration Point Orbits and Applications, pp. 529–571 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1142/9789812704849_0023
Polsgrove, T., Kos, L., Hopkins, R., Crane, T.: Comparison of performance predictions for new low-thrust trajectory tools. In: AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference and Exhibit, 6742 (2006). https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2006-6742
Racca, G.D.: New challenges to trajectory design by the use of electric propulsion and other new means of wandering in the solar system. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 85(1), 1–24 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021787311087
Rayman, M.D., Varghese, P., Lehman, D.H., Livesay, L.L.: Results from the deep space 1 technology validation mission. Acta Astronaut. 47(2), 475–487 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0094-5765(00)00087-4
Rayman, M.D., Fraschettia, T.C., Raymonda, C.A., Russellb, C.T.: Dawn: a mission in development for exploration of main belt asteroids Vesta and Ceres. Acta Astronaut. 58(11), 605–616 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2006.01.014
Saghamanesh, M., Novinzadeh, A.: Optimal guidance of spacecraft rendezvous via free initial velocity vector. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part G J. Aerosp. Eng. 228(7), 1020–1032 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1177/0954410013483224
Saghamanesh, M., Baoyin, H.: A robust homotopic approach for continuous variable low-thrust trajectory optimization. Adv. Space Res. 62(11), 3095–3113 (2018a). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2018.08.046
Saghamanesh, M., Baoyin, H.: Optimal gravity-assist low-thrust trajectory using a robust homotopic approach. In: IEEE/CSAA Guidance, Navigation and Control (2018c)
Saghamanesh, M., Baoyin, H.: Practical mission design for mars trajectory optimization based on the ephemeris model and full perturbation system. Adv. Astronaut. Sci. 165, 1293–1313 (2018b)
Saghamanesh, M., Taheri, E., Baoyin, H.: Systematic low-thrust trajectory design to Mars based on a full ephemeris modelling. Adv. Space Res. 64(11), 2356–2378 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asr.2019.08.013
Sarli, B.V., Kawakatsu, Y.: Selection and trajectory design to mission secondary targets. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 127(2), 233–258 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-016-9724-x
Sentinella, M.R., Casalino, L.: Cooperative evolutionary algorithm for space trajectory optimization. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 105(1–3), 211 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-009-9223-4
Taheri, E., Junkins, J.L.: Generic smoothing for optimal bang-off-bang spacecraft maneuvers. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 41(11), 2470–2475 (2018). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.G003604
Taheri, E., Kolmanovsky, I., Atkins, E.: Enhanced smoothing technique for indirect optimization of minimum-fuel low-thrust trajectories. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 39(11), 2500–2511 (2016). https://doi.org/10.2514/1.G000379
Taheri, E., Junkins, J.L.: How man impulses redux. J. Astronaut. Sci. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40295-019-00203-1
Vallado, D.A.: Fundamentals of Astrodynamics and Applications, vol. 12. Springer, Berlin (2001)
Whiffen, G.: Mystic: Implementation of the static dynamic optimal control algorithm for high-fidelity, low-thrust trajectory design. In: AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference and Exhibit, 6741 (2006). https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2006-6741
Whiffen, G.J., Lam, T.: The Jupiter icy moons orbiter reference trajectory. In: AAS/AIAA SpaceFlight Mechanics Meeting (2006)
Yam, C.H., McConaghy, T.T., Chen, K.J., Longuski, J.M.: Preliminary design of nuclear electric propulsion missions to the outer planets. In: AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Specialist Conference, AIAA Paper, 5393, 16–19 (2004). https://doi.org/10.2514/6.2004-5393
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saghamanesh, M., Taheri, E. & Baoyin, H. Interplanetary gravity-assist fuel-optimal trajectory optimization with planetary and Solar radiation pressure perturbations. Celest Mech Dyn Astr 132, 16 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-020-9955-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-020-9955-8