Abstract
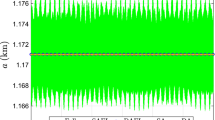
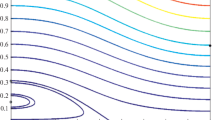
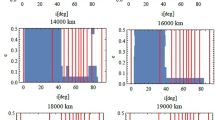
The long-term effects of a distant third-body on a massless satellite that is orbiting an oblate body are studied for a high order expansion of the third-body disturbing function. This high order may be required, for instance, for Earth artificial satellites in the so-called MEO region. After filtering analytically the short-period angles via averaging, the evolution of the orbital elements is efficiently integrated numerically with very long step-sizes. The necessity of retaining higher orders in the expansion of the third-body disturbing function becomes apparent when recovering the short-periodic effects required in the computation of reliable osculating elements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anselmo L., Pardini C.: Long-term dynamical evolution of high area-to-mass ratio debris released into high earth orbits. Acta Astronaut. 67, 204–216 (2010)
Boccaletti D., Pucacco G.: Theory of Orbits. 2: Perturbative and Geometrical Methods, pp. 10. Springer, Berlin (1998)
Broucke R.A.: Long-term third-body effects via double averaging. J. Guidance Control Dyn. 26(1), 27–32 (2003)
Brouwer D.: Solution of the problem of aritifical satellite theory without drag. Astron. J. 64(1274), 378–396 (1959)
Brouwer D., Clemence G.M.: Methods of Celestial Mechanics, pp. 296ff. Academic Press, New York (1961)
Campbell J.A., Jefferys W.H.: Equivalence of the perturbation theories of Hori and Deprit. Celest. Mech. 2(4), 467–473 (1970)
Cefola, P., Broucke, R.: On the Formulation of the Gravitational Potential in Terms of Equinoctial Variables. Paper AIAA 75-9, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (1975)
Cefola, P.J., Yurasov, V.S., Folcik, Z.J., Phelps, E.B., Proulx, R.J., Nazarenko, A.I.: Comparison of the DSST and the USM Semi-Analytical Orbit Propagators. Paper AAS 03-236, American Astronautical Society (2003)
Chao C.C., Gick R.A.: Long-term evolution of navigation satellite orbits: GPS/GLONASS/Galileo. Adv. Space Res. 34, 1221–1226 (2004)
Coffey S.L., Deprit A., Miller B.R.: The critical inclination in artificial satellite theory. Celest. Mech. 39(4), 365–406 (1986)
Collins, S.K.: Long Term Prediction of High Altitude Orbits. PhD Thesis, MIT (1981)
Collins, S.K., Cefola, P.J.: Double Averaged Third Body Model for Prediction of Super-Synchronous Orbits over Long Time Spans, p. 63. Paper AAS 79-135, American Astronautical Society (1979)
Deprit A.: Canonical transformations depending on a small parameter. Celest. Mech. 1(1), 12–30 (1969)
Deprit A.: Delaunay normalisations. Celest. Mech. 26(1), 9–21 (1982)
Deprit A., Rom A.: The main problem of artificial satellite theory for small and moderate eccentricities. Celest. Mech. 2, 166–206 (1970)
Ely T.A.: Eccentricity impact on east-west stationkeeping for global positioning system class orbits. J. Guidance Control Dyn. 25(2), 352–357 (2002)
Ely T.A., Howell K.C.: Long term evolution of artificial satellite orbits due to resonant tesseral harmonics. J. Astronaut. Sci. 44, 167–190 (1996)
Ely T.A., Howell K.C.: Dynamics of artificial satellite orbits with tesseral resonances including the effects of luni-solar perturbations. Int. J. Dyn. Stab. Syst. 12(4), 243–269 (1997)
Gedeon G.S.: Tesseral resonance effects on satellite orbits. Celest. Mech. 1(2), 167–189 (1969)
Giacaglia G.: Lunar perturbations of artificial satellites of the earth. Celest. Mech. 9, 239–267 (1974)
Green, A.J.: Orbit Determination and Prediction Processes for Low Altitude Satellites. PhD Thesis, MIT (1979)
Hori G.-i.: Theory of general perturbation with unspecified canonical variable. Publ. Astron. Soc. Jpn. 18(4), 287–296 (1966)
Kelly T.S.: A note on first-order normalizations of perturbed Keplerian systems. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 46, 19–25 (1989)
Kozai, Y.: On the Effects of the Sun and the Moon upon the Motion of a Close Earth Satellite, p. 10, SAO Special Report #22 Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory, Cambridge, MA (1959)
Kozai Y.: Second-order solution of artificial satellite theory without air drag. Astron. J. 67(7), 446–461 (1962)
Lara M., Palacián J.F., Russell R.P: Mission design through averaging of perturbed Keplerian systems: the paradigm of an enceladus orbiter. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 108(1), 1–22 (2010)
Laskar J., Boué G.: Explicit expansion of the three-body disturbing function for arbitrary eccentricities and inclinations. Astron. Astrophys. 522(A60), 11 (2010)
McClain, W.D.: A Recursively Formulated First-Order Semianalytic Artificial Satellite Theory Based on the Generalized Method of Averaging, Volume 1: The Generalized Method of Averaging Applied to the Artificial Satellite Problem, Computer Sciences Corporation CSC/TR-77/6010 (1977)
Métris G.: Mean values of particular functions in the elliptic motion. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 52, 79–84 (1991a)
Métris, G.: Théorie du mouvement des satellites artificiels—Développement des équations du mouvement moyen—Application à l’étude des longues périodes, p. 188, PhD Thesis, Observatoire de Paris (1991b)
Métris G., Exertier P.: Semi-analytical theory of the mean orbital motion. Astron. Astrophys. 294, 278–286 (1995)
Meyer K.R., Hall G.R.: Introduction to Hamiltonian Dynamical Systems and the N-Body Problem, Vol. 90. Springer, New York (1992)
Montenbruck O., Gill E.: Satellite Orbits Models Methods and Applications. Springer, New york (2001)
Osácar C., Palacián J.F.: Decomposition of functions for elliptic orbits. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 60, 207–223 (1994)
Palacián J.F.: Dynamics of a satellite orbiting a planet with an inhomogeneous gravitational field. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 98, 219–249 (2007)
Prado A.F.B.A.: Third-body perturbation in orbits around natural satellites. J. Guidance Control Dyn. 26(1), 33–40 (2003)
Proulx, R., McClain, W.C., Early, L., Cefola, P.: A Theory for the Short Periodic Motion due to the Tesseral Harmonic Gravity Field, p. 20, Paper AAS 81-180, American Astronautical Society, (1981)
Rossi A.: Resonant dynamics of Medium earth orbits: space debris issues. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 100(4), 267–286 (2008)
Slutsky, M.: First Order Short Periodic Motion of and Artificial Satellite Due to Third-Body Perturbations: Numerical Evaluation, p. 22, Paper 83-393, American Astronautical Society (1983)
Steichen, D.: An averaging method to study the motion of lunar artificial satellites. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 68, 205–224; (part I) and 225–247 (part II) (1998)
Valk S., Lemaître A., Deleflie F.: Semi-analytical theory of mean orbital motion for geosynchronous space debris under gravitational influence. Adv. Space Res. 43, 1070–1082 (2009)
Vashkov’yak M.A.: A numerical-analytical method for studying the orbital evolution of distant planetary satellites. Astron. Lett. 31(1), 64–72 (2005)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lara, M., San-Juan, J.F., López, L.M. et al. On the third-body perturbations of high-altitude orbits. Celest Mech Dyn Astr 113, 435–452 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-012-9433-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-012-9433-z