Abstract
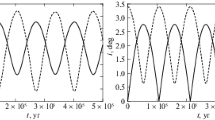
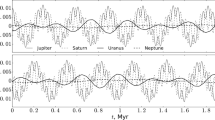
The stability in the sense of Lagrange of the Sun–Jupiter–Saturn system and 47 UMa system with respect to masses on a time scale of 106 years was studied using the method of averaging and numerical methods. When the masses of Jupiter and Saturn increase by 20 times (approximately, more accurate value depends on a time-scale of stable motion), these planets can have close approaches. Close approaches appear when analyzing osculating elements; they are absent in the mean elements. A similar situation takes place in the case of 47 UMa and other exoplanetary systems. The study of Lagrange stability with respect to masses allows us to obtain upper limits for masses of extrasolar planets.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Butler R.P., Marcy G.W.: A planet orbiting 47 Ursae Majoris. Astrophys. J. 464, L153–L156 (1996)
Butler R.P., Wright J.T., Marcy G.W. et al.: Catalog of nearby exoplanets. Astrophys. J. 646, 505–522 (2006)
Chambers J.E.: A hybrid symplectic integrator that permits close encounters between massive bodies. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 304, 793–799 (1999)
Chetaev, N.G.: Stability of motion. Gostekhisdat, Moscow – Leningrad (4th edition: 1990, Nauka, Moscow) (1946) (in Russian)
Everhart E.: Implicit single methods for integrating orbits. Celest. Mech. 10, 35–55 (1974)
Fischer D.A. et al.: A second planet orbiting 47 Ursae Majoris. Astrophys. J. 564, 1028–1034 (2002)
Georgakarakos N.: Stability criteria for hierarchical triple systems. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 100, 151–168 (2008)
Gladman B.: Dynamics of systems of two close planets. Icarus 106, 247–263 (1993)
Goldstein, D.: The near-optimality of Stormer methods for long time integrations of y′′ = g(y). Ph.D. Dissertation, Univ. of California, Los Angeles, Dept. of Mathematics (1996)
Goździewski K.: Stability of the 47 UMa planetary system. Astron. Astrophys. 393, 997–1013 (2002)
Hairer, E., Norsett, S.P., Wanner, G.: Solving ordinary differential equations I. Nonstiff problems. Second revised edition (1993)
Ito, T., Miyama, Sh.M.: An estimation of upper limit masses of υ And planets. In: Proceedings of 32nd Symposium Celest. Mech. University Advanced Studies, pp. 194–205. Hayama, Kanagawa, Japan (2000)
Ito T., Miyama Sh.M.: An estimation of upper limit masses of υ And planets. Astrophys. J. 552, 372–379 (2001)
Kuznetsov E.D., Kholshevnikov K.V.: Planet mass stability margin of two-planetary systems. Sol. Syst. Res. 43, 220–228 (2009)
Laughlin G., Chambers J., Fisher D.: A dynamical analysis of the 47 Ursae Majoris planetary system. Astrophys. J. 579, 455–467 (2002)
Marchal C., Bozis G.: Hill stability and distance curves for the general three-body problem. Celest. Mech. 26, 311–333 (1982)
Milani A., Nobili A.M.: On topological stability in the general three-body problem. Celest. Mech. 31, 213–240 (1983)
Nacozy P.E.: On the stability of the Solar System. Astron. J. 81, 787–791 (1976)
Nacozy P.E.: A discussion of long-term numerical solutions of the Jupiter–Saturn–Sun system. Celest. Mech. 16, 77–86 (1977)
Naef D., Mayor M., Beuzit J.L. et al.: The ELODIE survey for northern extra-solar planets. III. Three planetary candidates detected with ELODIE. Astron. Astrophys. 414, 351–359 (2004)
Pitjeva E.V.: The dynamical model of the planet motions and EPM ephemerides. Highlights Astron. 14, 470 (2007)
Standish, E.M.: JPL planetary and lunar ephemerides, DE405/LE405. Interoffice Memorandum. 312.F-98-048. JPL. 18 p. (1998)
Sukhotin A.A., Kholshevnikov K.V.: Planetary orbits evolution for 200 000 years calculated by the method of Halphen–Goriachev. Astronomia i geodesia. Tomsk, Tomsk University Publ. 14, 5–21 (1986) (in Russian)
Varadi, F.: NBI. A set of numerical integrators for the gravitational N-body problem. http://www.atmos.ucla.edu/~varadi (1999)
Wittenmyer R.A., Endl M., Cochran W.D.: Long-period objects in the extrasolar planetary systems 47 Ursae Majoris and 14 Herculis. Astrophys. J. 654, 625–632 (2007)
Wittenmyer R.A., Endl M., Cochran W.D. et al.: A search for multi-planet systems using the Hobby-Eberly telescope. Astrophys. J. Suppl. Ser. 182, 97–119 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kholshevnikov, K.V., Kuznetsov, E.D. Stability of planetary systems with respect to masses. Celest Mech Dyn Astr 109, 201–210 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-010-9324-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-010-9324-0