Abstract
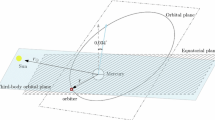
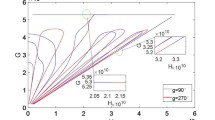
We hereby study the stability of a massless probe orbiting around an oblate central body (planet or planetary satellite) perturbed by a third body, assumed to lay in the equatorial plane (Sun or Jupiter for example) using a Hamiltonian formalism. We are able to determine, in the parameters space, the location of the frozen orbits, namely orbits whose orbital elements remain constant on average, to characterize their stability/unstability and to compute the periods of the equilibria. The proposed theory is general enough, to be applied to a wide range of probes around planet or natural planetary satellites. The BepiColombo mission is used to motivate our analysis and to provide specific numerical data to check our analytical results. Finally, we also bring to the light that the coefficient J 2 is able to protect against the increasing of the eccentricity due to the Kozai-Lidov effect and the coefficient J 3 determines a shift of the equilibria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson J.D., Colombo G., Espsitio P.B., Lau E.L., Trager G.B.: The mass, gravity field, and ephemeris of mercury. Icarus 71, 337–349 (1987)
Breiter S., Elipe A.: Critical inclination in the main problem of a massive satellite. Cel. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 95, 287–297 (2006)
Brouwer D., Clemence G.: Methods of Celestial Mechanics. Academic Press, NY (1961)
D’Hoedt S., Lemaître A.: Planetary long periodic terms in Mercury’s rotation: a two dimensional adiabatic approach. Cel. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 101, 127–139 (2008)
D’Hoedt S., Noyelles B., Dufey J., Lemaître A.: A secondary resonance in Mercury’s rotation. Cel. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 107, 93–100 (2010)
Dufey J., Noyelles B., Rambaux N., Lemaître A.: Latitudinal librations of Mercury with a fluid core. Icarus 203, 1–12 (2009)
Farago F., Laskar J.: High-inclination orbits in the secular quadrupolar three-body problem. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 401, 1189–1198 (2009)
Garcia D., de Pascale P., Jehn R.: Bepicolombo mercury cornerstone consolidated report on mission analysis. Tech. rep., MAO Working Paper No. 466, (2007)
Hairer E., Norsett S., Wanner G.: Solving Ordinary Differential Equations I. Nonstiff Problems, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1993)
Kozai Y.: Secular perturbations of asteroids with high inclination and eccentricity. Astro. J. 67, 591–598 (1962)
Lara M., Russell R.P.: Computation of a science orbit about Europa. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 30, 259–263 (2007)
Lara M., Palacián J.F., Yanguas P. et al.: Analytical theory for spacecraft motion about Mercury. Acta Astron. 66, 1022–1038 (2010)
Laskar J.: Secular evolution of the solar system over 10 million years. Astron. Astrophys. 198, 341–362 (1988)
Laskar, J.: Frequency map analysis and quasiperiodic decomposition, in Hamiltonian systems and fourier analysis: new prospects for gravitational dynamics. In: Benest et al. (ed.) Cambridge Sci. Publ., pp. 99–129 (2005)
Lemaître A., Delsate N., Valk S.: A web of secondary resonances for large A/m geostationary debris. Cel. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 104, 383–402 (2009)
Lidov, M.L.: Evolution of the orbits of artificial satellites of planets as affected by gravitational perturbation from external bodies, 9, pp. 719–759, Planet. Space Sci. (1962)
Lucchesi D.M., Iafolla V.: The non-gravitational perturbations impact on the BepiColombo Radio Science Experiment and the key rôle of the ISA accelerometer: direct solar radiation and albedo effects. Cel. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 96, 99–127 (2006)
Paskowitz, M., Scheeres, D.: Orbit mechanics about planetary satellites. Am. Astron. Soc. 244, (2004)
Paskowitz M., Scheeres D.: Design of science orbits about planetary satellites: application to Europa. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 29, 1147–1158 (2006)
Russell R.P., Brinckerhoff A.T.: Circulating eccentric orbits around planetary moons. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 32, 424–436 (2009)
Russell R.P., Lara M.: Long-lifetime lunar repeat ground track orbits. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 30, 982–993 (2007)
Saleh L.A., Rasio F.A.: The stability and dynamics of planets in tight binary systems. Astrophys. J. 694, 1566–1576 (2009)
San-Juan J., Lara M., Ferrer S.: Phase space structure around oblate planetary satellites. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 29, 113–120 (2006)
Scheeres D., Guman M., Villac B.: Stabillity analysis of planetary satellite orbiters: application to the europa orbiter. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 24, 778–787 (2001)
Seidelmann P.K. et al.: Report of the IAU/IAG working group on cartographic coordinates and rotational elements: 2006. Cel. Mech. Dyn. Astr. 98, 155–180 (2007)
Standish, E.M.: JPL planetary and lunar ephemeris, de405/le405, JPL Interoffice Memorandum IOM 312. D-98-048 (1998)
Stoer J., Bulirsch R.: Introduction to Numerical Analysis. Springer-Verlag, New York (1980)
Sturm, C.: Mémoires présentés par divers savants àé1 l’Académie royale des Sciences de l’Institut de France, Vol.6, chap. Mémoire sur la résolution des équations numériques, (1835)
Tremaine S., Touma J., Namouni F.: Satellite dynamics on the Laplace surface. Astron. J. 1137, 3706–3717 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delsate, N., Robutel, P., Lemaître, A. et al. Frozen orbits at high eccentricity and inclination: application to Mercury orbiter. Celest Mech Dyn Astr 108, 275–300 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-010-9306-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-010-9306-2