Abstract
Background
Youth psychosocial and school adjustment results from complex developmental transactions between their individual characteristics and diverse environmental influences, which appear as risk or protective factors throughout one’s development.
Objective
From an ecosystemic and developmental perspective, this study aims to: (1) identify risk profiles among 13-year-old adolescents, and (2) associate these specific profiles with school dropout risk and substance abuse at age 15 years.
Method
Data comes from a large Canadian study, the Quebec Longitudinal Study of Development through which adolescents (n = 1312) answered questionnaires at 13 and 15 years old.
Results
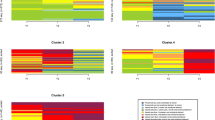
First, through latent profile analyses, five profiles were identified based on individual, family, social, and school-based risk factors. Some profiles present higher levels of risk factors, while others comprise risk factors that are under the sample average level. Higher-risk profiles show stronger longitudinal associations with later adjustment difficulties.
Conclusions
The findings help provide a deeper understanding of how the co-occurrence of various risk factors in adolescence is associated with later adjustment. The combination of the developmental psychopathology and ecosystemic frameworks, as well as the person-centered approach allowed by the latent profile analyses, helps shed new light on individual and developmental risk.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achenbach, T. M., & Rescorla, L. A. (2001). Manual for the ASEBA school-age forms and profiles. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth, and Families.
Achenbach, T. A., & Rescorla, L. A. (2016). Developmental issues in assessment, taxonomy and diagnosis of psychopathology: Life span and multicultural perspectives. In D. Cicchetti (Ed.), Developmental psychopathology: Theory and method (3rd ed., Vol. 1, pp. 47–93). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
Alexander, K. L., Entwisle, D. R., & Horsey, C. S. (1997). From first grade forward: Early foundations of high school dropout. Sociology of Education, 70(2), 87–107. https://doi.org/10.2307/2673158.
Alexander, K. L., Entwisle, D. R., & Kabbani, N. S. (2001). The dropout process in life course perspective: Early risk factors at home and school. Teachers College Record, 103(5), 760–822. https://doi.org/10.1111/0161-4681.00134.
Archambault, I., & Janosz, M. (2009). Fidélité, validité discriminante et prédictive de l’indice de prédiction du décrochage. [Fidelity, discriminant and predictive validity of the Dropout Prediction Index.]. Canadian Journal of Behavioural Science/Revue canadienne des sciences du comportement, 41(3), 187–191. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0015261.
Archambault, I., Janosz, M., Fallu, J.-S., & Pagani, L. S. (2009). Student engagement and its relationship with early high school dropout. Journal of Adolescence, 32(3), 651–670. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2008.06.007.
Bailey, D., Duncan, G. J., Odgers, C. L., & Yu, W. (2017). Persistence and fadeout in the impacts of child and adolescent interventions. Journal of research on educational effectiveness, 10(1), 7–39.
Bernard, M., Bolognini, M., Plancherel, B., Chinet, L., Laget, J., Stephan, P., et al. (2009). French validity of two substance-use screening tests among adolescents: A comparison of the CRAFFT and DEP-ADO. Journal of Substance Use, 10(6), 385–395. https://doi.org/10.1080/14659890412331333050.
Berndt, T. J., & Murphy, L. M. (2002). Influences of friends and friendships: Myths, truths, and research recommendations. Advances in Child Development and Behavior (Vol. 30, pp. 275–310). San Diego, CA: Academic Press.
Brière, F. N., Rohde, P., Seeley, J. R., Klein, D., & Lewinsohn, P. M. (2014). Comorbidity between major depression and alcohol use disorder from adolescence to adulthood. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 55(3), 526–533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2013.10.007.
Bronfenbrenner, U. (1979). The ecology of human development: Experiments by nature and design. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Brownell, M. D., Roos, N., MacWilliam, L., Leclair, L., Ekuma, O., & Fransoo, R. (2010). Academic and social outcomes for high-risk youths in Manitoba. Canadian Journal of Education, 33(4), 804–836.
Bukowski, W. M., Velasquez, A. M., & Brendgen, M. (2008). Variation in patterns of peer influence: Considerations of self and other. In M. J. Prinstein & K. A. Dodge (Eds.), Understanding peer influence in children and adolescents (pp. 125–140). New York, NY: Guilford Press US.
Chassin, L., Flora, D. B., & King, K. M. (2004). Trajectories of alcohol and drug use and dependence from adolescence to adulthood: The effects of familial alcoholism and personality. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 113(4), 483–498. https://doi.org/10.1037/0021-843X.113.4.483.
Christenson, S. L., & Thurlow, M. L. (2004). School dropouts: Prevention considerations, interventions, and challenges. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 13(1), 36–39. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0963-7214.2004.01301010.x.
Chung, T., Smith, G. T., Donovan, J. E., Windle, M., Faden, V. B., Chen, C. M., et al. (2012). Drinking frequency as a brief screen for adolescent alcohol problems. Pediatrics. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2011-1828.
Cloutier, R., Bissonnette, C., Ouellet-Laberge, J., & Plourde, M. (2004). Monoparentalité et développement de l’enfant. In M.-C. Saint-Jacques, R. Cloutier, S. Drapeau, & D. Turcotte (Eds.), Familles en transformation: Bilan d’une réalité complexe et pistes d’action (pp. 33–63). Québec: Presses de l’Université Laval.
Coohey, C., Renner, L. M., Hua, L., Zhang, Y. J., & Whitney, S. D. (2011). Academic achievement despite child maltreatment: A longitudinal study. Child Abuse and Neglect, 35(9), 688–699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2011.05.009.
Coughlin, L., Esposito, T., Milne, L., & Trocmé, N. (2010). Retard scolaire. Branché. Retrieved from https://www.mcgill.ca/crcf/files/crcf/Branche_Vol_1_Ed_5.pdf
Cummings, E. M., & Davies, P. T. (1994). Maternal depression and child development. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 35(1), 73–122.
Cummings, E. M., Davies, P. T., & Campbell, S. B. (2000). Developmental psychopathology and family process: Theory, research, and clinical implications. New York: Guilford Press.
Dahl, R. E., Allen, N. B., Wilbrecht, L., & Suleiman, A. B. (2018). Importance of investing in adolescence from a developmental science perspective. Nature, 554(7693), 441.
Debowska, A., Willmott, D., Boduszek, D., & Jones, A. D. (2017). What do we know about child abuse and neglect patterns of co-occurrence? A systematic review of profiling studies and recommendations for future research. Child Abuse & Neglect, 70(Supplement C), 100–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chiabu.2017.06.014.
Dion, K., & Fontaine, C. (2016). Étude de la non-réponse partielle au volet 2015. Québec Retrieved from http://www.jesuisjeserai.stat.gouv.qc.ca/doc_tech.htm
Dupéré, V., Leventhal, T., Dion, E., Crosnoe, R., Archambault, I., & Janosz, M. (2015). Stressors and turning points in high school and dropout: A stress process, life course framework. Review of Educational Research, 85(4), 591–629. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654314559845.
Eccles, J. S., Midgley, C., Wigfield, A., Buchanan, C. M., Reuman, D., Flanagan, C., et al. (1993). Development during adolescence: The impact of stage-environment fit on young adolescents’ experiences in schools and in families. American Psychologist, 48(2), 90–101. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.48.2.90.
Ennett, S. T., Bauman, K. E., Hussong, A., Faris, R., Foshee, V. A., Li, C., et al. (2006). The peer context of adolescent substance use: Findings from social network analysis. Journal of Research on Adolescence (Wiley-Blackwell), 16(2), 159–186. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-7795.2006.00127.x.
Fallu, J.-S., Brière, F. N., Vitaro, F., Cantin, S., & Borge, A. I. H. (2011). The influence of close friends on adolescent substance use: Does popularity matter? In A. Ittel, H. Merkens, & L. Stecher (Eds.), Jahrbuch Jugendforschung (Vol. 10, pp. 235–262). Wiesbaden: VS Verlag.
Fergusson, D. M., & Horwood, J. L. (1998). Early conduct problems and later life opportunities. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 39(8), 1097–1108.
Fergusson, D. M., Horwood, J. L., & Ridder, E. M. (2007). Conduct and attentional problems in childhood and adolescence and later substance use, abuse and dependence: Results of a 25-year longitudinal study. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 88(Supplement 1), S14–S26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2006.12.011.
Fortin, L., Marcotte, D., Potvin, P., Royer, É., & Joly, J. (2006). Typology of students at risk of dropping out of school: Description by personal, family and school factors. European Journal of Psychology of Education, 21(4), 363–383. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03173508.
Fredricks, J. A., Blumenfeld, P. C., & Paris, A. H. (2004). School engagement: Potential of the concept, state of the evidence. Review of Educational Research, 74(1), 59–109. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543074001059.
Freeman, J., & Simonsen, B. (2015). Examining the impact of policy and practice interventions on high school dropout and school completion rates: A systematic review of the literature. Review of Educational Research, 85(2), 205–248.
Gerard, J. M., & Booth, M. Z. (2015). Family and school influences on adolescents’ adjustment: The moderating role of youth hopefulness and aspirations for the future. Journal of Adolescence, 44, 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2015.06.003.
Germain, M., Guyon, L., Landry, M., Tremblay, J., Brunelle, N., & Bergeron, J. (2016). DEP-ADO: Grille de dépistage de consommation problématique d’alcool et de drogues chez les adolescents et les adolescentes (33rd ed.). Trois-Rivières, QC: RISQ - Centre universitaire de Québec.
Gershoff, E. T., & Grogan-Kaylor, A. (2016). Spanking and child outcomes: Old controversies and new meta-analyses. Journal of Family Psychology, 30(4), 453–469. https://doi.org/10.1037/fam0000191.
Goulet, M., Cantin, S., Archambault, I., & Vitaro, F. (2015). L’influence des amis sur l’engagement scolaire au secondaire: La popularité des élèves comme variable modératrice? [The influence of friends on school engagement in high school: The popularity of students as moderator?]. Canadian Journal of Behavioural Science/Revue Canadienne des Sciences du Comportement, 47(2), 141–152. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0038104.
Gutman, L. M., Sameroff, A. J., & Cole, R. (2003). Academic growth curve trajectories from 1st grade to 12th grade: Effects of multiple social risk factors and preschool child factors. Developmental Psychology, 39(4), 777–790.
Hawkins, J. D., Catalano, R. F., & Miller, J. Y. (1992). Risk and protective factors for alcohol and other drug problems in adolescence and early adulthood: Implications for substance abuse prevention. Psychological Bulletin, 112(1), 64–105. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-2909.112.1.64.
Hay, D. F. (1994). Prosocial development. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 35(1), 29–71.
Hay, D. F., & Pawlby, S. (2003). Prosocial development in relation to children’s and mothers’ psychological problems. Child Development, 74(5), 1314–1327. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-8624.00609.
Haziza, D., & Beaumont, J.-F. (2007). On the construction of imputation classes in surveys. International Statistical Review, 75, 25–43.
Howard-Jones, P. A. (2014). Neuroscience and education: Myths and messages. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 15(12), 817.
Hussong, A. M., Jones, D. J., Stein, G. L., Baucom, D. H., & Boeding, S. (2011). An internalizing pathway to alcohol use and disorder. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 25(3), 390–404. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0024519.
Institut de la Statistique du Québec. (2014). Étude longitudinale du développement des enfants du Québec 1998–2011. Montréal: Direction des Enquêtes Longitudinales et Sociales, Institut de la Statistique du Québec.
Janosz, M., Le Blanc, M., Boulerice, B., & Tremblay, R. E. (2000). Predicting different types of school dropouts: A typological approach with two longitudinal samples. Journal of Educational Psychology, 92(1), 171–190. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.92.1.171.
Janosz, M., Pascal, S., Belleau, L., Archambault, I., Parent, S., & Pagani, L. (2013). Les élèves du primaire à risque de décrocher au secondaire: caractéristiques à 12 ans et prédicteurs à 7 ans. Étude longitudinale du développement des enfants du Québec (ÉLDEQ 1998–2010)
Jimerson, S. R., Anderson, G. E., & Whipple, A. D. (2002). Winning the battle and losing the war: Examining the relation between grade retention and dropping out of high school. Psychology in the Schools, 39(4), 441–457. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.10046.
Kim, B. K. E., Oesterle, S., Catalano, R. F., & Hawkins, J. D. (2015). Change in protective factors across adolescent development. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 40, 26–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appdev.2015.04.006.
Kirisci, L., Reynolds, M., Carver, D., & Tarter, R. (2013). Quick screen to detect current substance use disorder in adolescents and the likelihood of future disorder. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 128(1–2), 116–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2012.08.017.
Kovacs, M. (1985). The children’s depression, inventory (CDI). Psychopharmacology Bulletin, 21(4), 995.
Kraemer, H. C., Stice, E., Kazdin, A., Offord, D., & Kupfer, D. (2001). How do risk factors work together? Mediators, moderators, and independent, overlapping, and proxy risk factors. American Journal of Psychiatry, 158(6), 848–856. https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.ajp.158.6.848.
Ladd, G. W., Kochenderfer, B. J., & Coleman, C. C. (1997). Classroom peer acceptance, friendship, and victimization: Distinct relation systems that contribute uniquely to children’s school adjustment? Child Development, 68(6), 1181–1197.
Lambert, G., Haley, N., Tremblay, G., Frappier, J.-Y., Roy, E., & Otis, J. (2015). Consommation problématique de substances psychoactives et comportements sexuels à risque chez les adolescents admis en centre jeunesse. Drogues, Santé et Société, 14(1), 132–151.
Larson, R. W., Wilson, S., Brown, B. B., Furstenberg, J. F. F., & Verma, S. (2002). Changes in adolescents’ interpersonal experiences: Are they being prepared for adult relationships in the twenty-first century? Journal of Research on Adolescence, 12(1), 31–68. https://doi.org/10.1111/1532-7795.00024.
Laursen, B., Hafen, C. A., Kerr, M., & Stattin, H. (2012). Friend influence over adolescent problem behaviors as a function of relative peer acceptance: To be liked is to be emulated. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 121(1), 88–94. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0024707.
Laursen, B., & Hoff, E. (2006). Person-centered and variable-centered approaches to longitudinal data. Merrill-Palmer Quarterly, 52(3), 377–389.
Laventure, M. (2008). Profils de consommation d’adolescents, garçons et filles, desservis par des centres jeunesse. Drogues, Santé et Société, 7(2), 9–45.
Lécallier, D., Hadj-Slimane, F., Landry, M., Bristol-Gauzy, P., Cordoliani, C., Grélois, M., et al. (2012). Repérer, orienter, conseiller les adolescents consommateurs de substances psycho-actives. Étude prospective randomisée contrôlée auprès de 2120 adolescents. La Presse Médicale, 41(9), 411–419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lpm.2011.10.032.
Levin, H., Belfield, C., Muennig, P., & Rouse, C. (2007). The costs and benefits of an excellent education for all of America’s children. New York, NY: Columbia University.
Levy, S., Weiss, R., Sherritt, L., Ziemnik, R., Spalding, A., Van Hook, S., et al. (2014). An electronic screen for triaging adolescent substance use by risk levels. JAMA Pediatrics, 168(9), 822–828. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamapediatrics.2014.774.
Lewis, M. (2013). Beyond the dyad. In L. Mayes & M. Lewis (Eds.), The Cambridge handbook of environment in human development (pp. 103–116). New York: Cambridge University Press.
Li, Y., & Lerner, R. (2013). Interrelations of behavioral, emotional, and cognitive school engagement in high school students. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 42(1), 20–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-012-9857-5.
Lo, Y., Mendell, N. R., & Rubin, D. B. (2001). Testing the number of components in a normal mixture. Biometrika, 88(3), 767–778. https://doi.org/10.1093/biomet/88.3.767.
Luiselli, J. K., Putnam, R. F., Handler, M. W., & Feinberg, A. B. (2005). Whole-school positive behaviour support: Effects on student discipline problems and academic performance. Educational Psychology, 25(2–3), 183–198. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144341042000301265.
Maltais, C., & Normandeau, S. (2015). Le parcours scolaire des enfants victimes de maltraitance parentale: Recension d’études entre 2007 et 2014. Revue de psychoéducation, 44(2), 317–350.
Marcotte, D., Fortin, L., Royer, É., Potvin, P., & Leclerc, D. (2001). L’influence du style parental, de la dépression et des troubles du comportement sur le risque d’abandon scolaire. Revue des sciences de l’éducation, 27(3), 687–712.
Masten, A. S., & Coatsworth, J. D. (1998). The development of competence in favorable and unfavorable environments: Lessons from research on successful children. American Psychologist, 53(2), 205–220. https://doi.org/10.1037/0003-066X.53.2.205.
Masten, A. S., Morison, P., & Pellegrini, D. S. (1985). A revised class play method of peer assessment. Developmental Psychology, 21(3), 523.
Meier, M. H., Hall, W., Caspi, A., Belsky, D. W., Cerdá, M., Harrington, H. L., et al. (2015). Which adolescents develop persistent substance dependence in adulthood? Using population-representative longitudinal data to inform universal risk assessment. Psychological Medicine, 46(4), 877–889. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291715002482.
Muthén, L. K., & Muthén, B. O. (2017). Mplus user’s guide (8th ed.). Los Angeles, CA: Muthén & Muthén.
Nation, M., & Heflinger, C. A. (2006). Risk factors for serious alcohol and drug use: The role of psychosocial variables in predicting the frequency of substance use among adolescents. The American Journal of Drug and Alcohol Abuse, 32(3), 415–433.
Norman, R. E., Byambaa, M., De, R., Butchart, A., Scott, J., & Vos, T. (2012). The long-term health consequences of child physical abuse, emotional abuse, and neglect: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Medicine, 9(11), e1001349.
Nylund, K. L., Asparouhov, T., & Muthén, B. O. (2007). Deciding on the number of classes in latent class analysis and growth mixture modeling: A monte carlo simulation study. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 14(4), 535–569. https://doi.org/10.1080/10705510701575396.
Oberski, D. (2016). Mixture models: Latent profile and latent class analysis. In J. Robertson & M. Kaptein (Eds.), Modern statistical methods for HCI (pp. 275–287). Switzerland: Springer International Publishing.
Piché, G., Huỳnh, C., Clément, M.-È., & Durrant, J. E. (2016). Predicting externalizing and prosocial behaviors in children from parental use of corporal punishment. Infant and Child Development. https://doi.org/10.1002/icd.2006.
Quiroga, C., Janosz, M., Bisset, S., & Morin, A. J. S. (2013). Early adolescent depression symptoms and school dropout: Mediating processes involving self-reported academic competence and achievement. Journal of Educational Psychology, 105(2), 552–560. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0031524.
Quiroga, C., Janosz, M., & Marcotte, D. (2006). Les sentiments dépressifs à l’adolescence: un facteur de risque différentiel du décrochage scolaire chez les filles et les garçons de milieu défavorisé. Revue de psychoéducation, 35(2), 277–300.
Ramaswamy, V., Desarbo, W. S., Reibstein, D. J., & Robinson, W. T. (1993). An empirical pooling approach for estimating marketing mix elasticities with PIMS data. Marketing Science, 12(1), 103–124. https://doi.org/10.1287/mksc.12.1.103.
Resnick, M. D., Bearman, P. S., & Blum, R. M. (1997). Protecting adolescents from harm: Findings from the national longitudinal study on adolescent health. JAMA, 278(10), 823–832. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1997.03550100049038.
Robins, L. N., & Helzer, J. E. (1985). Diagnostic interview schedule (DIS), version III-A. Washington, DC: Department of Psychiatry, Washington University School of Medicine.
Romano, E., Tremblay, R. E., Boulerice, B., & Swisher, R. (2005). Multilevel correlates of childhood physical aggression and prosocial behavior. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 33(5), 565–578. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-005-6738-3.
Rumberger, R. W. (2011). High school dropouts in the United States. In S. Lamb, E. Markussen, R. Teese, J. Polesel, & N. Sandberg (Eds.), School dropout and completion: International comparative studies in theory and policy (pp. 275–294). Oslo: Springer.
Rumberger, R. W., & Lamb, S. P. (2003). The early employment and further education experiences of high school dropouts: A comparative study of the United States and Australia. Economics of Education Review, 22(4), 353–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0272-7757(02)00038-9.
Rumberger, R. W., & Lim, S. A. (2008). Why students drop out of school: A review of 25 years of research. Santa Barbara, CA: UC Santa Barbara Retrieved from http://www.spokanecounty.org/data/juvenile/modelsforchange/School%20dropouts%20-%20Why%20sudents%20dropout%20of%20school.pdf
Rumberger, R. W., & Rotermund, S. (2012). The relationship between engagement and high school dropout. In S. Christenson, A. L. Reschly, & C. Wylie (Eds.), Handbook of research on student engagement (pp. 491–513). New York: Springer.
Russell, D. W., & Cutrona, C. E. (1984). Social provisions scale. Iowa: Iowa State University.
Sameroff, A. J., & Fiese, B. H. (2000). Models of development and ecological risk. In C. H. Zeanah (Ed.), Handbook of infant mental health (2nd ed., pp. 3–19). New York: Guilford Press.
Schwarz, G. (1978). Estimating the dimension of a model. Annals of Statistics. https://doi.org/10.1214/aos/1176344136.
Sclove, S. L. (1987). Application of model-selection criteria to some problems in multivariate analysis. Psychometrika, 52(3), 333–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02294360.
Shulman, S., & Scharf, M. (2018). Adolescent psychopathology in times of change: The need for intergrating a developmental psychopathology perspective. Journal of Adolescence, 65, 95–100.
Smith, S. R. (2007). Making sense of multiple informants in child and adolescent psychopathology: A guide for clinicians. Journal of Psychoeducational Assessment, 25(2), 139–149. https://doi.org/10.1177/0734282906296233.
Sroufe, L. A. (2013). The promise of developmental psychopathology: Past and present. Development and Psychopathology, 25(4 pt 2), 1215–1224. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0954579413000576.
Steinberg, L. (2005). Cognitive and affective development in adolescence. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 9(2), 69–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2004.12.005.
Steinberg, L. D. (2014). Age of opportunity: Lessons from the new science of adolescence. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt.
Steinberg, L. D. (2017). Adolescence (11th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Education.
Sterba, S. K. (2014). Modeling strategies in developmental psychopathology research: Prediction of individual change. In M. Lewis & K. D. Rudolph (Eds.), Handbook of developmental psychopathology (3rd ed., pp. 109–124). New York: Springer.
Stone, S. (2007). Child maltreatment, out-of-home placement and academic vulnerability: A fifteen-year review of evidence and future directions. Children and Youth Services Review, 29(2), 139–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2006.05.001.
Stone, A. L., Becker, L. G., Huber, A. M., & Catalano, R. F. (2012). Review of risk and protective factors of substance use and problem use in emerging adulthood. Addictive Behaviors, 37(7), 747–775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2012.02.014.
Stone, S., & Zibulsky, J. (2015). Maltreatment, academic difficulty and systems-involved youth: current evidence and oppotunities. Psychology in the Schools, 52(1), 22–39. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.21812.
Tremblay, R. E., Loeber, R., Gagnon, C., Charlebois, P., Larivée, S., & LeBlanc, M. (1991). Disruptive boys with stable and unstable high fighting behavior patterns during junior elementary school. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 19(3), 285–300. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00911232.
Trickett, P. K., Negriff, S., Ji, J., & Peckins, M. (2011). Child maltreatment and adolescent development. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 21(1), 3–20. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-7795.2010.00711.x.
Trout, A. L., Hagaman, J., Casey, K., Reid, R., & Epstein, M. H. (2008). The academic status of children and youth in out-of-home care: A review of the literature. Children and Youth Services Review, 30(9), 979–994. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.childyouth.2007.11.019.
Veronneau, M.-H., & Vitaro, F. (2007). Social experiences with peers and high school graduation: A review of theoretical and empirical research. Educational Psychology, 27(3), 419–445. https://doi.org/10.1080/01443410601104320.
Veronneau, M.-H., Vitaro, F., Brendgen, M., Dishion, T. J., & Tremblay, R. E. (2010). Transactional analysis of the reciprocal links between peer experiences and academic achievement from middle childhood to early adolescence. Developmental Psychology, 46(4), 773–790. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0019816.
Vitaro, F., Brendgen, M., & Tremblay, R. E. (1999). Prevention of school dropout through the reduction of disruptive behaviors and school failure in elementary school. Journal of School Psychology, 37(2), 205–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-4405(99)00006-0.
Wang, M.-T., & Fredricks, J. A. (2014). The reciprocal links between school engagement, youth problem behaviors, and school dropout during adolescence. Child Development, 85(2), 722–737. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.12138.
Yeager, D. S., Dahl, R. E., & Dweck, C. S. (2018). Why interventions to influence adolescent behavior often fail but could succeed. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 13(1), 101–122.
Zahn-Waxler, C., Kochanska, G., Krupnick, J., & McKnew, D. (1990). Patterns of guilt in children of depressed and well mothers. Developmental Psychology, 26(1), 51.
Funding
Funding was provided by Canada Excellence Research Chairs, Government of Canada (Grant No. 950-230848).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
The treatment of our study’s human participants complies with APA ethical standards and with the home university of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the original study from which the analyses are based.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Goulet, M., Clément, ME., Helie, S. et al. Longitudinal Association Between Risk Profiles, School Dropout Risk, and Substance Abuse in Adolescence. Child Youth Care Forum 49, 687–706 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10566-020-09550-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10566-020-09550-9