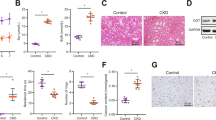
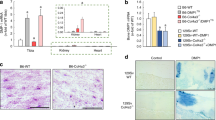
Abstract
Hypercalcemia is a common complication in chronic kidney disease (CKD) and unfortunately contributes to nerve injury. This study aims to investigate the potential role and underlying mechanisms of Cinacalcet (CIN) in hypercalcemia-driven nerve injury in CKD. A CKD mouse model was first established by adenine feeding to identify the therapeutic effects of CIN. Molecules related to CIN and CKD were predicted by bioinformatics analysis and their expression in the kidney tissues of CKD mice was measured by immunochemistry. Gain- and loss-of-functions assays were performed both in vitro and in vivo to evaluate their effects on nerve injury in CKD, as reflected by Scr and BUN, and brain calcium content as well as behavior tests. CIN ameliorated hypercalcemia-driven nerve injury in CKD mice. Interactions among TRAF2, an E3-ubiquitin ligase, KLF2, and SERPINA3 were bioinformatically predicted on CIN effect. CIN restricted the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of KLF2 by downregulating TRAF2. KLF2 targeted and inversely regulated SERPINA3 to repress hypercalcemia-driven nerve injury in CKD. CIN was substantiated in vivo to ameliorate hypercalcemia-driven nerve injury in CKD mice through the TRAF2/KLF2/SERPINA3 regulatory axis. Together, CIN suppresses SERPINA3 expression via TRAF2-mediated inhibition of the ubiquitin-dependent degradation of KLF2, thus repressing hypercalcemia-induced nerve injury in CKD mice.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Alhoshani AR, Hafez MM, Husain S, Al-Sheikh AM, Alotaibi MR, Al Rejaie SS, et al. Protective effect of rutin supplementation against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. BMC Nephrol. 2017;18(1):194. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12882-017-0601-y.
Asonitis N, Kassi E, Kokkinos M, Giovanopoulos I, Petychaki F, Gogas H. 2017 Hypercalcemia of malignancy treated with cinacalcet. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. https://doi.org/10.1530/EDM-17-0118.
Boer K, Crino PB, Gorter JA, Nellist M, Jansen FE, Spliet WG, et al. Gene expression analysis of tuberous sclerosis complex cortical tubers reveals increased expression of adhesion and inflammatory factors. Brain Pathol. 2010;20(4):704–19. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3639.2009.00341.x.
Borghi A, Verstrepen L, Beyaert R. TRAF2 multitasking in TNF receptor-induced signaling to NF-kappaB, MAP kinases and cell death. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016;116:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2016.03.009.
Brown EM. Anti-parathyroid and anti-calcium sensing receptor antibodies in autoimmune hypoparathyroidism. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2009;38(2):437–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecl.2009.01.001.
Chen H, Lu S, Guan J, Zhu X, Sun F, Huang J, et al. Identification of prognostic immune-related genes in rhabdoid tumor of kidney based on TARGET database analysis. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(4):5461–74. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.202475.
Chen PH, Smith TJ, Wu J, Siesser PF, Bisnett BJ, Khan F, et al. Glycosylation of KEAP1 links nutrient sensing to redox stress signaling. EMBO J. 2017;36(15):2233–50. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201696113.
Cruzado JM, Moreno P, Torregrosa JV, Taco O, Mast R, Gomez-Vaquero C, et al. A randomized study comparing parathyroidectomy with Cinacalcet for treating hypercalcemia in kidney allograft recipients with hyperparathyroidism. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2016;27(8):2487–94. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2015060622.
Eidman KE, Wetmore JB. Treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism: how do cinacalcet and etelcalcetide differ? Semin Dial. 2018;31(5):440–4. https://doi.org/10.1111/sdi.12734.
Guixe-Muntet S, de Mesquita FC, Vila S, Hernandez-Gea V, Peralta C, Garcia-Pagan JC, et al. Cross-talk between autophagy and KLF2 determines endothelial cell phenotype and microvascular function in acute liver injury. J Hepatol. 2017;66(1):86–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2016.07.051.
Hammerland LG, Garrett JE, Hung BC, Levinthal C, Nemeth EF. Allosteric activation of the Ca2+ receptor expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes by NPS 467 or NPS 568. Mol Pharmacol. 1998;53(6):1083–8.
Hannan FM, Stevenson M, Bayliss AL, Stokes VJ, Stewart M, Kooblall KG, et al. Ap2s1 mutation causes hypercalcaemia in mice and impairs interaction between calcium-sensing receptor and adaptor protein-2. Hum Mol Genet. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddab076.
Hashem RM, Mohamed RH, Abo-El-matty DM. Effect of curcumin on TNFR2 and TRAF2 in unilateral ureteral obstruction in rats. Nutrition. 2016;32(4):478–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2015.10.005.
Howles SA, Hannan FM, Gorvin CM, Piret SE, Paudyal A, Stewart M, et al. 2017 Cinacalcet corrects hypercalcemia in mice with an inactivating Galpha11 mutation. JCI Insight 2(20) https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.96540.
Jean G, Souberbielle JC, Chazot C. 2017 Vitamin D in chronic kidney disease and dialysis patients. Nutrients. 9(4):https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9040328.
Kannan-Thulasiraman P, Seachrist DD, Mahabeleshwar GH, Jain MK, Noy N. Fatty acid-binding protein 5 and PPARbeta/delta are critical mediators of epidermal growth factor receptor-induced carcinoma cell growth. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(25):19106–15. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.099770.
Lau WL, Obi Y, Kalantar-Zadeh K. Parathyroidectomy in the management of secondary hyperparathyroidism. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2018;13(6):952–61. https://doi.org/10.2215/CJN.10390917.
Li L, Liao J, Yuan Q, Hong X, Li J, Peng Y, et al. 2021 Fibrillin-1-enriched microenvironment drives endothelial injury and vascular rarefaction in chronic kidney disease. Sci Adv. 7(5):https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abc7170.
Liu Y. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011;7(12):684–96. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2011.149.
Manaka K, Sato J, Kinoshita Y, Ito N, Fujita M, Iiri T, et al. Effectiveness and safety of cinacalcet for primary hyperparathyroidism: a single center experience. Endocr J. 2019;66(8):683–9. https://doi.org/10.1507/endocrj.EJ19-0034.
Murphy CE, Kondo Y, Walker AK, Rothmond DA, Matsumoto M, Shannon WC. Regional, cellular and species difference of two key neuroinflammatory genes implicated in schizophrenia. Brain Behav Immun. 2020;88:826–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2020.05.055.
Nguyen S, Gosmanova EO, Gosmanov AR. Cinacalcet-associated resolution of primary hyperparathyroidism in a patient with normal kidney function. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2020;8:2324709620936836. https://doi.org/10.1177/2324709620936836.
O’Callaghan S, Yau H. Treatment of malignancy-associated hypercalcemia with cinacalcet: a paradigm shift. Endocr Connect. 2021;10(1):R13–24. https://doi.org/10.1530/EC-20-0487.
Palmer SC, Nistor I, Craig JC, Pellegrini F, Messa P, Tonelli M, et al. Cinacalcet in patients with chronic kidney disease: a cumulative meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS Med. 2013;10(4): e1001436. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1001436.
Pulskens WP, Verkaik M, Sheedfar F, van Loon EP, van de Sluis B, Vervloet MG, et al. Deregulated renal calcium and phosphate transport during experimental kidney failure. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(11): e0142510. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0142510.
Rane MJ, Zhao Y, Cai L. Krupsilonppel-like factors (KLFs) in renal physiology and disease. EBioMedicine. 2019;40:743–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.01.021.
Saidak Z, Brazier M, Kamel S, Mentaverri R. Agonists and allosteric modulators of the calcium-sensing receptor and their therapeutic applications. Mol Pharmacol. 2009;76(6):1131–44. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.109.058784.
Sanchez-Navarro A, Gonzalez-Soria I, Caldino-Bohn R, Bobadilla NA. An integrative view of serpins in health and disease: the contribution of SerpinA3. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2021;320(1):C106–18. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00366.2020.
Sanchez-Navarro A, Mejia-Vilet JM, Perez-Villalva R, Carrillo-Perez DL, Marquina-Castillo B, Gamba G, et al. SerpinA3 in the early recognition of acute kidney injury to chronic kidney disease (CKD) transition in the rat and its potentiality in the recognition of patients with CKD. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):10350. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-46601-1.
Sanfilippo C, Longo A, Lazzara F, Cambria D, Distefano G, Palumbo M, et al. CHI3L1 and CHI3L2 overexpression in motor cortex and spinal cord of sALS patients. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2017;85:162–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcn.2017.10.001.
Sangwung P, Zhou G, Nayak L, Chan ER, Kumar S, Kang DW, et al. KLF2 and KLF4 control endothelial identity and vascular integrity. JCI Insight. 2017;2(4): e91700. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.91700.
Saum K, Campos B, Celdran-Bonafonte D, Nayak L, Sangwung P, Thakar C, et al. 2018 Uremic advanced glycation end products and protein-bound solutes induce endothelial dysfunction through Suppression of Kruppel-like factor 2. J Am Heart Assoc. 7(1):https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.117.007566.
Sheehan MT, Wermers RA, Jatoi A, Loprinzi CL, Onitilo AA. Oral cinacalcet responsiveness in non-parathyroid hormone mediated hypercalcemia of malignancy. Med Hypotheses. 2020;143:110149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110149.
Tan Z, Shi Y, Yan Y, Liu W, Li G, Li R. Impact of endogenous hydrogen sulfide on toll-like receptor pathway in renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Ren Fail. 2015;37(4):727–33. https://doi.org/10.3109/0886022X.2015.1012983.
Tanaka S, Okusa MD. Crosstalk between the nervous system and the kidney. Kidney Int. 2020;97(3):466–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2019.10.032.
Turner JJO. Hypercalcaemia - presentation and management. Clin Med (lond). 2017;17(3):270–3. https://doi.org/10.7861/clinmedicine.17-3-270.
Turnier JL, Brunner HI, Bennett M, Aleed A, Gulati G, Haffey WD, et al. Discovery of SERPINA3 as a candidate urinary biomarker of lupus nephritis activity. Rheumatology (oxford). 2019;58(2):321–30. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/key301.
Wang F, Yang C, Long J, Zhao X, Tang W, Zhang D, et al. Executive summary for the 2015 Annual Data Report of the China Kidney Disease Network (CK-NET). Kidney Int. 2019;95(3):501–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2019.05.004.
Wazna-Jablonska E, Galazka Z, Durlik M. Treatment of persistent hypercalcemia and hyperparathyroidism with Cinacalcet after successful kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc. 2016;48(5):1623–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2016.01.044.
Ye P, Liu J, Xu W, Liu D, Ding X, Le S, et al. Dual-specificity phosphatase 26 protects against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice through transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1 suppression. Hepatology. 2019;69(5):1946–64. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.30485.
Yin Q, Lamothe B, Darnay BG, Wu H. Structural basis for the lack of E2 interaction in the RING domain of TRAF2. Biochemistry. 2009;48(44):10558–67. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi901462e.
Zhang C, Miller CL, Gorkhali R, Zou J, Huang K, Brown EM, et al. molecular basis of the extracellular ligands mediated signaling by the calcium sensing receptor. Front Physiol. 2016;7:441. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2016.00441.
Zhong F, Mallipattu SK, Estrada C, Menon M, Salem F, Jain MK, et al. Reduced Kruppel-like factor 2 aggravates glomerular endothelial cell injury and kidney disease in mice with unilateral nephrectomy. Am J Pathol. 2016;186(8):2021–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.03.018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yaochen Cao and Yingquan Xiong conceived and designed research. Hongming Sun performed experiments. Yaochen Cao interpreted results of experiments. Hongming Sun analyzed data and prepared Figures. Yingquan Xiong drafted paper. Yaochen Cao and Hongming Sun edited and revised manuscript. Ziqiang Wang contributed to the revision. All authors read and approved final version of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Animal experiments were approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Fourth Hospital of Daqing and performed in accordance with Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the National Institutes of Health.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Yaochen Cao and Yingquan Xiong are regarded as co-first authors.
Yaochen Cao is sponsored by China Scholarship Council.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

10565_2022_9717_Fig8_ESM.png
Supplementary Fig. 1 Effect of TRAF2 and cIAP1 on the KLF2 ubiquitination. A: KLF2 ubiquitination in TCMK-1 cells treated with oe-TRAF2 or combined with sh-cIAP1 determined by Co-IP and Western blot; B: KLF2 ubiquitination in TCMK-1 cells treated with sh-TRAF2 or combined with oe-cIAP1 determined by Co-IP and Western blot. All cell experiments were repeated 3 times independently. (PNG 444 KB)

Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, Y., Xiong, Y., Sun, H. et al. Neurorescuing effect of Cinacalcet against hypercalcemia-induced nerve injury in chronic kidney disease via TRAF2/cIAP1/KLF2/SERPINA3 signal axis. Cell Biol Toxicol 39, 1–17 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-022-09717-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-022-09717-1