Abstract
Purpose
LINC01089 is a newly identified lncRNA and rarely reported in human cancers. Our study aimed to investigate its role in lung cancer.
Methods
YY1, LINC01089, and miR-301b-3p levels in lung cancer tissues and cells were assessed using qRT-PCR. Bioinformatics analysis and luciferase reporter, ChIP, and RIP assays were carried out for determining the relationships among YY1, LINC01089, miR-301b-3p, and HPGD. Gain- and loss-of-function assays were carried out to confirm the impacts of LINC01089 and HPDG in lung cancer cells. CCK-8 assay was used to assess cell proliferation rate, and Transwell assay was applied to measure cell invasion and migration. An in vivo tumor model was applied for validating the role of LINC01089.
Results
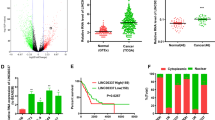
LINC01089 was decreased in lung cancer tissues and cells, and low LINC01089 level predicted a poor clinical outcome. YY1 directly bound to LINC01089 promoter region and inhibited its transcription. LINC01089 knockdown thwarted the proliferation, invasion, and migration capacity of H1299 and A549 cells and aggravated tumor growth. Specifically, LINC01089 functioned as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-301b-3p to modulate HPGD and thereby affected lung cancer progression.
Conclusion
Our data revealed that LINC01089, directly suppressed by YY1, inhibited lung cancer progression by targeting the miR-301b-3p/HPGD axis.

1. LINC01089 expression was downregulated in lung cancer tisuues and cell lines, and low LINC01089 levels predicted a poor clinical outcome. 2. LINC01089 knockdown enhanced proliferation, invasion, and migration of H1299 and A549 cells in vitro and promoted lung cancer cell tumorigenesis and metastasis in vivo. 3. LINC01089, directly suppressed by YY1, functioned as a competing endogenous RNA against miR-301b-3p to increase HPGD expression.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barta JA, Powell CA, Wisnivesky JP. Global epidemiology of lung cancer. Ann Glob Health. 2019;85(1). https://doi.org/10.5334/aogh.2419.
Bhan A, Soleimani M, Mandal SS. Long noncoding RNA and cancer: a new paradigm. Cancer Res. 2017;77(15):3965–81. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-16-2634.
Chan JJ, Tay Y. Noncoding RNA:RNA regulatory networks in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051310.
Chen L, Tian G, Shao C, Cobos E, Gao W. Curcumin modulates eukaryotic initiation factors in human lung adenocarcinoma epithelial cells. Mol Biol Rep. 2010;37(7):3105–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-009-9888-5.
Chen S, Xu Z, Shao J, Fu P, Wu H. MicroRNA-218 promotes early chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells and inhibits later chondrocyte maturation. BMC Biotechnol. 2019a;19(1):6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12896-018-0496-0.
Chen Y, Zhang R, Wang L, Correa AM, Pataer A. Tumor characteristics associated with engraftment of patient-derived non-small cell lung cancer xenografts in immunocompromised mice. 2019b;125(21):3738–48. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.32366.
Chi Y, Wang H, Wang F, Ding M. PHTF2 regulates lipids metabolism in gastric cancer. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(8):6600–10. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102995.
Chow PH, Bowen J, Yool AJ. Combined systematic review and transcriptomic analyses of mammalian aquaporin classes 1 to 10 as biomarkers and prognostic indicators in diverse cancers. 2020;12(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071911.
Coleman JE, Huentelman MJ, Kasparov S, Metcalfe BL, Paton JF, Katovich MJ, et al. Efficient large-scale production and concentration of HIV-1-based lentiviral vectors for use in vivo. Physiol Genomics. 2003;12(3):221–8. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00135.2002.
Donner I, Katainen R, Sipilä LJ, Aavikko M, Pukkala E, Aaltonen LA. Germline mutations in young non-smoking women with lung adenocarcinoma. Lung Cancer. 2018;122:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2018.05.027.
Duveau DY, Yasgar A, Wang Y, Hu X, Kouznetsova J, Brimacombe KR, Jadhav A, Simeonov A, Thomas CJ, Maloney DJ. Structure-activity relationship studies and biological characterization of human NAD(+)-dependent 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2014;24(2):630–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.11.081.
Feng X, Yang S. Long non-coding RNA LINC00243 promotes proliferation and glycolysis in non-small cell lung cancer cells by positively regulating PDK4 through sponging miR-507. Mol Cell Biochem. 2020;463(1-2):127–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-019-03635-3.
Fink SP, Yamauchi M, Nishihara R, Jung S, Kuchiba A, Wu K, Cho E, Giovannucci E, Fuchs CS, Ogino S, Markowitz SD, Chan AT. Aspirin and the risk of colorectal cancer in relation to the expression of 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (HPGD). Sci Transl Med. 2014;6(233):233re232. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3008481.
Grigorieva EV, Prudnikova TY, Domanitskaya NV, Mostovich LA, Pavlova TV, Kashuba VI, Zabarovsky ER. D-glucuronyl C5-epimerase suppresses small-cell lung cancer cell proliferation in vitro and tumour growth in vivo. Br J Cancer. 2011;105(1):74–82. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2011.170.
Huang T, Wang G, Yang L, Peng B, Wen Y, Ding G, Wang Z. Transcription factor YY1 modulates lung cancer progression by activating lncRNA-PVT1. DNA Cell Biol. 2017;36(11):947–58. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2017.3857.
Jin S, He J, Zhou Y, Wu D, Li J, Gao W. LncRNA FTX activates FOXA2 expression to inhibit non-small-cell lung cancer proliferation and metastasis. 2020;24(8):4839–49. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15163.
Kawahara K, Hohjoh H, Inazumi T, Tsuchiya S, Sugimoto Y. Prostaglandin E2-induced inflammation: relevance of prostaglandin E receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1851(4):414–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.07.008.
Lei W, Liu HB, Wang SB, Zhou XM, Zheng SD, Guo KN, Ma BY, Xia YL, Tan WS, Liu XY, Wang YG. Tumor suppressor in lung cancer-1(TSLC1) mediated by dual-regulated oncolytic adenovirus exerts specific antitumor actions in a mouse model. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2013;34(4):531–40. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2012.196.
Lemjabbar-Alaoui H, Hassan OU, Yang YW, Buchanan P. Lung cancer: biology and treatment options. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1856(2):189–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2015.08.002.
Leung K. (89)Zr-Desferrioxamine B-Transferrin. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD). Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004.
Li M, Guo X. LINC01089 blocks the proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells via regulating miR-27b-3p/HOXA10 axis. 2020;13:8251–60. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s256148.
Li P, Xing W, Xu J, Yuan D, Liang G, Liu B, Ma H. microRNA-301b-3p downregulation underlies a novel inhibitory role of long non-coding RNA MBNL1-AS1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):144. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-019-1235-8.
Li S, Han Y, Liang X, Zhao M. LINC01089 inhibits the progression of cervical cancer via inhibiting miR-27a-3p and increasing BTG2. 2020a;23:e3280. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgm.3280.
Li D, Wang J, Zhang M, Hu X, She J, Qiu X, Zhang X, Xu L, Liu Y, Qin S. LncRNA MAGI2-AS3 is regulated by brd4 and promotes gastric cancer progression via maintaining ZEB1 overexpression by sponging miR-141/200a. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020b;19:109–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2019.11.003.
Li X, Yu M, Yang C. YY1-mediated overexpression of long noncoding RNA MCM3AP-AS1 accelerates angiogenesis and progression in lung cancer by targeting miR-340-5p/KPNA4 axis. J Cell Biochem. 2020c;121(3):2258–67. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29448.
Liang Y, Song X, Li Y, Chen B, Zhao W, Wang L, Zhang H, Liu Y, Han D, Zhang N, Ma T, Wang Y, Ye F, Luo D, Li X, Yang Q. LncRNA BCRT1 promotes breast cancer progression by targeting miR-1303/PTBP3 axis. 2020;19(1):85. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01206-5.
Lu X, Wang F, Fu M, Li Y, Wang L. Long noncoding RNA KCNQ1OT1 accelerates the progression of ovarian cancer via MicroRNA-212-3/LCN2 axis. Oncol Res. 2020;28(2):135–46. https://doi.org/10.3727/096504019x15719983040135.
Mao Y, Yang D, He J, Krasna MJ. Epidemiology of lung cancer. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2016;25(3):439–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soc.2016.02.001.
Monteleone NJ, Moore AE, Iacona JR, Lutz CS, Dixon DA. miR-21-mediated regulation of 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase in colon cancer. 2019;9(1):5405. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-41862-2.
Nasim F, Sabath BF, Eapen GA. Lung cancer. Med Clin North Am. 2019;103(3):463–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2018.12.006.
Peng WX, Koirala P, Mo YY. LncRNA-mediated regulation of cell signaling in cancer. Oncogene. 2017;36(41):5661–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.184.
Qi X, Wang Y, Hou J, Huang Y. A single nucleotide polymorphism in HPGD gene is associated with prostate cancer risk. J Cancer. 2017;8(19):4083–6. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.22025.
Qian X, Zhao J, Yeung PY, Zhang QC, Kwok CK. Revealing lncRNA structures and interactions by sequencing-based approaches. Trends Biochem Sci. 2019;44(1):33–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2018.09.012.
Sas-Chen A, Aure MR, Leibovich L, Carvalho S, Enuka Y. LIMT is a novel metastasis inhibiting lncRNA suppressed by EGF and downregulated in aggressive breast cancer. 2016;8(9):1052–64. https://doi.org/10.15252/emmm.201606198.
Schmitt AM, Chang HY. Long noncoding RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell. 2016;29(4):452–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2016.03.010.
Tang XJ, Wang W, Hann SS. Interactions among lncRNAs, miRNAs and mRNA in colorectal cancer. Biochimie. 2019;163:58–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2019.05.010.
Tay Y, Rinn J, Pandolfi PP. The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature. 2014;505(7483):344–52. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12986.
Vainio P, Gupta S, Ketola K, Mirtti T, Mpindi JP, Kohonen P, Fey V, Perälä M, Smit F, Verhaegh G, Schalken J, Alanen KA, Kallioniemi O, Iljin K. Arachidonic acid pathway members PLA2G7, HPGD, EPHX2, and CYP4F8 identified as putative novel therapeutic targets in prostate cancer. Am J Pathol. 2011;178(2):525–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2010.10.002.
Wang F, Yang Q. Long non-coding RNA LINC01089 enhances the development of gastric cancer by sponging miR-145-5p to mediate SOX9 expression. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:9213–24. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s249392.
Wang L, Cho KB, Li Y, Tao G, Xie Z, Guo B. Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA)-mediated competing endogenous RNA networks provide novel potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for colorectal cancer. 2019;20(22). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225758.
Wang L, Lin C, Sun N, Wang Q, Ding X, Sun Y. Long non-coding RNA CASC19 facilitates non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by targeting the miR-301b-3p/LDLR axis. e3254. 2020;22:e3254. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgm.3254.
Wu XS, Wang F, Li HF, Hu YP, Jiang L, Zhang F, et al. LncRNA-PAGBC acts as a microRNA sponge and promotes gallbladder tumorigenesis. 2017;18(10):1837–53. https://doi.org/10.15252/embr.201744147.
Yan Z, Yang Q, Xue M, Wang S, Hong W. YY1-induced lncRNA ZFPM2-AS1 facilitates cell proliferation and invasion in small cell lung cancer via upregulating of TRAF4. 2020;20:108. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-1157-7.
Yao S, Xu J, Zhao K, Song P, Yan Q, Fan W, Li W, Lu C. Down-regulation of HPGD by miR-146b-3p promotes cervical cancer cell proliferation, migration and anchorage-independent growth through activation of STAT3 and AKT pathways. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(11):1055. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-1059-y.
Ye Y, Gu B, Wang Y, Shen S, Huang W. YY1-induced upregulation of long noncoding RNA ARAP1-AS1 promotes cell migration and invasion in colorectal cancer through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2019;34(8):519–28. https://doi.org/10.1089/cbr.2018.2745.
Yuan H, Qin Y, Zeng B, Feng Y, Li Y, Xiang T, Ren G. Long noncoding RNA LINC01089 predicts clinical prognosis and inhibits cell proliferation and invasion through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in breast cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2019;12:4883–95. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.s208830.
Zheng X, Weigert A (2020) Spatial density and distribution of tumor-associated macrophages predict survival in non-small cell lung carcinoma. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-20-0069
Data Availability of data and material
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RSY and ZCL: study concepts, literature research, experimental studies, manuscript writing; HC: study concepts, study design, literature research, manuscript preparation and editing; YS: data acquisition, statistical analysis and manuscript preparation. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of The Second Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University. Written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, R., Liu, Z., Cao, H. et al. LINC01089, suppressed by YY1, inhibits lung cancer progression by targeting miR-301b-3p/HPDG axis. Cell Biol Toxicol 38, 1063–1077 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09643-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09643-8