Abstract
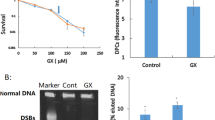
We investigated the effect of C-reactive protein (CRP) and sodium azide (NaN3) on endothelial Cx43 gap junctions. Human aortic endothelial cells (HAEC) were treated with (a) detoxified CRP, (b) detoxified dialyzed CRP, (c) detoxified dialyzed CRP plus NaN3, (d) NaN3, or (e) dialyzed NaN3. The concentration of CRP in all preparations was fixed to 25 μg/ml and that of NaN3 in the preparations of (c) to (e) was equivalent to that contained in the 25 μg/ml CRP purchased commercially. The results showed that both the expression of Cx43 protein and gap junctional communication function post-48-h incubation were reduced and inhibited by the detoxified CRP, NaN3, or detoxified dialyzed CRP plus NaN3, but not by the detoxified dialyzed CRP or dialyzed NaN3. Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis of cells treated for 72 h also showed a pattern of transcriptional regulation essentially the same as that for the proteins. We concluded that CRP does not have a significant effect on Cx43 gap junctions of HAEC, but NaN3 inhibited the viability of cells and downregulate their junctions.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Cx43:
-
Connexin43
- HAEC:
-
Human aortic endothelial cells
- NaN3 :
-
Sodium azide
References
Abraham J, Campbell CY, Cheema A, Gluckman TJ, Blumenthal RS, Danyi P. C-reactive protein in cardiovascular risk assessment: a review of the evidence. J Cardiometab Syndr. 2007;2:119–23. doi:10.1111/j.1559-4564.2007.05950.x.
Banach K, Ramanan SV, Brink PR. The influence of surface charges on the conductance of the human connexin37 gap junction channel. Biophys J. 2000;78:752–60. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(00)76633-1.
Chung S, Yoon IY, Shin YK, Lee CH, Kim JW, Lee T, et al. Endothelial dysfunction and C-reactive protein in relation with the severity of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Sleep. 2007;30:997–1001.
Clapp BR, Hirschfield GM, Storry C, Gallimore JR, Stidwill RP, Singer M, et al. Inflammation and endothelial function: direct vascular effects of human C-reactive protein on nitric oxide bioavailability. Circulation. 2005;111:1530–6. doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000159336.31613.31.
Davignon J, Ganz P. Role of endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2004;109:III27–32.
Devaraj S, Xu DY, Jialal I. C-reactive protein increases plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression and activity in human aortic endothelial cells: implications for the metabolic syndrome and atherothrombosis. Circulation. 2003;107:398–404. doi10.1161/01.CIR.0000052617.91920.FD.
Devaraj S, Kumaresan PR, Jialal I. Effect of C-reactive protein on chemokine expression in human aortic endothelial cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2004;36:405–10. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2003.12.005.
Devaraj S, Venugopal S, Jialal I. Native pentameric C-reactive protein displays more potent pro-atherogenic activities in human aortic endothelial cells than modified C-reactive protein. Atherosclerosis. 2006;184:48–52. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2005.03.031.
el-Fouly MH, Trosko JE, Chang CC. Scrape-loading and dye transfer. A rapid and simple technique to study gap junctional intercellular communication. Exp Cell Res. 1987;168:422–30.
Hu J, Cotgreave IA. Differential regulation of gap junctions by proinflammatory mediators in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1997;99:2312–6.
Jialal I, Devaraj S, Venugopal SK. C-reactive protein: risk marker or mediator in atherothrombosis? Hypertension. 2004;44:6–11.
Kawanami D, Maemura K, Takeda N, Harada T, Nojiri T, Saito T, et al. C-reactive protein induces VCAM-1 gene expression through NF-kappaB activation in vascular endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis. 2006;185:39–46.
Khreiss T, Jozsef L, Potempa LA, Filep JG. Conformational rearrangement in C-reactive protein is required for proinflammatory actions on human endothelial cells. Circulation. 2004;109:2016–22.
Liu C, Wang S, Deb A, Nath KA, Katusic ZS, McConnell JP, et al. Proapoptotic, antimigratory, antiproliferative, and antiangiogenic effects of commercial C-reactive protein on various human endothelial cell types in vitro: implications of contaminating presence of sodium azide in commercial preparation. Circ Res. 2005;97:135–43.
Macintyre S, Samols D, Dailey P. Two carboxylesterases bind C-reactive protein within the endoplasmic reticulum and regulate its secretion during the acute phase response. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:24496–503.
Mensink A, de Haan LH, Lakemond CM, Koelman CA, Koeman JH. Inhibition of gap junctional intercellular communication between primary human smooth muscle cells by tumor necrosis factor alpha. Carcinogenesis. 1995;16:2063–7.
Nakakuki T, Ito M, Iwasaki H, Kureishi Y, Okamoto R, Moriki N, et al. Rho/Rho-kinase pathway contributes to C-reactive protein-induced plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 expression in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:2088–93.
Nystrom T, Nygren A, Sjoholm A. Persistent endothelial dysfunction is related to elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) levels in type II diabetic patients after acute myocardial infarction. Clin Sci (Lond). 2005;108:121–8.
Pasceri V, Willerson JT, Yeh ET. Direct proinflammatory effect of C-reactive protein on human endothelial cells. Circulation. 2000;102:2165–8.
Ridker PM, Cushman M, Stampfer MJ, Tracy RP, Hennekens CH. Plasma concentration of C-reactive protein and risk of developing peripheral vascular disease. Circulation. 1998;97:425–8.
Ridker PM, Rifai N, Rose L, Buring JE, Cook NR. Comparison of C-reactive protein and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in the prediction of first cardiovascular events. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1557–65.
Simon AM, McWhorter AR. Vascular abnormalities in mice lacking the endothelial gap junction proteins connexin37 and connexin40. Dev Biol. 2002;251:206–20.
Singh U, Devaraj S, Jialal I. C-reactive protein decreases tissue plasminogen activator activity in human aortic endothelial cells: evidence that C-reactive protein is a procoagulant. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:2216–21.
Taylor KE, Giddings JC, van den Berg CW. C-reactive protein-induced in vitro endothelial cell activation is an artefact caused by azide and lipopolysaccharide. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25:1225–30.
Venugopal SK, Devaraj S, Yang T, Jialal I. Alpha-tocopherol decreases superoxide anion release in human monocytes under hyperglycemic conditions via inhibition of protein kinase C-alpha. Diabetes. 2002;51:3049–54.
Venugopal SK, Devaraj S, Jialal I. C-reactive protein decreases prostacyclin release from human aortic endothelial cells. Circulation. 2003;108:1676–8.
Verma S, Szmitko PE, Yeh ET. C-reactive protein: structure affects function. Circulation. 2004;109:1914–7.
Volanakis JE. Human C-reactive protein: expression, structure, and function. Mol Immunol. 2001;38:189–97.
Wang Q, Zhu X, Xu Q, Ding X, Chen YE, Song Q. Effect of C-reactive protein on gene expression in vascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;288:H1539–45.
Wang HH, Kung CI, Tseng YY, Lin YC, Chen CH, Tsai CH, et al. Activation of endothelial cells to pathological status by down-regulation of connexin43. Cardiovasc Res. 2008;79:509–18.
Yaron G, Brill A, Dashevsky O, Yosef-Levi IM, Grad E, Danenberg HD, et al. C-reactive protein promotes platelet adhesion to endothelial cells: a potential pathway in atherothrombosis. Br J Haematol. 2006;134:426–31.
Yeh HI, Rothery S, Dupont E, Coppen SR, Severs NJ. Individual gap junction plaques contain multiple connexins in arterial endothelium. Circ Res. 1998;83:1248–63.
Yeh HI, Lu SK, Tian TY, Hong RC, Lee WH, Tsai CH. Comparison of endothelial cells grown on different stent materials. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2006;76:835–41.
Funding
Supported by grants NSC 94-2314-B-195-026 from the National Science Council, Taiwan and MMH-E-97003 from the Medical Research Department of the Mackay Memorial Hospital, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, HH., Yeh, HI., Wang, CY. et al. C-reactive protein, sodium azide, and endothelial connexin43 gap junctions. Cell Biol Toxicol 26, 153–163 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-009-9125-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-009-9125-y