Abstract
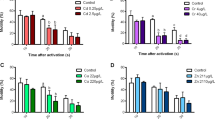
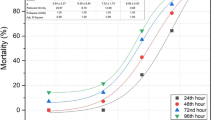
Sea urchin embryos and larvae represent suitable model systems on where to investigate the effects of heavy metals on development and cell viability. Here, we tested the toxic effects of low (10−12 M), medium (10−9 M), and high (10−6 M) cadmium chloride concentrations, mimicking unpolluted, moderately and highly polluted seawaters, respectively, on Paracentrotus lividus sea urchins offspring. Larvae were continuously treated from fertilization and inspected at time intervals comprised between 10 and 30 days of development. Delays and/or morphological abnormalities were firstly evident in larvae treated for 15 days with high cadmium (10−6 M) and for 25 days with medium cadmium (10−9 M). Major defects consisted in the reduction and lack of arms and skeleton elongation. No obvious differences with respect to controls were observed in embryos/larvae exposed to low cadmium (10−12 M), even after 30 days of exposure. Using in situ terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling assay (TUNEL) assay on larvae whole mounts, we detected apoptosis after 10 days of treatment with 10−6 and 10−9 M CdCl2, when no morphological abnormalities were recognizable yet. Supernumerary apoptotic cells were found in arm buds, ciliary bands, and apex. In conclusion, echinoderm embryos and larvae represent candidates of choice for the study of stress and defense mechanisms activated by cadmium exposure.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnello M, Filosto S, Scudiero R, Rinaldi AM, Roccheri MC. Cadmium accumulation induces apoptosis in P. lividus embryos. Caryologia 2006;59:403–8.
Agnello M, Filosto S, Scudiero R, Rinaldi AM, Roccheri MC. Cadmium induces apoptotic response in sea urchin embryos. Cell Stress Chaperones 2007;12:44–50.
Beiras R, Bellas J, Fernández N, Lorenzo JI, Cobelo-García A. Assessment of coastal marine pollution in Galicia (NW Iberian Peninsula); metal concentrations in seawater, sediments and mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) versus embryo–larval bioassays using Paracentrotus lividus and Ciona intestinalis. Mar Environ Res 2003;56:531–53.
Bertin G, Averbeck D. Cadmium: cellular effects, modifications of biomolecules, modulation of DNA repair and genotoxic consequences. Biochimie 2006;88(11):1549–59.
Bonaventura R, Poma V, Costa C, Matranga V. UVB radiation prevents skeleton growth and stimulates the expression of stress markers in sea urchin embryos. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2005;328(1):150–7.
Bridges CC, Zalups RK. Molecular and ionic mimicry and the transport of toxic metals. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2005;204(3):274–308.
Casano C, Roccheri MC, Maenza L, Migliore S, Gianguzza F. Sea urchin deciliation induces thermoresistance and activates the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Cell Stress Chaperones 2003;8(1):70–5.
Censi P, Mazzola S, Alonzo G, Saiano F, Patti B, Sprovieri M, Bonanno A, Spoto S. Trace element distributions in the Strait of Sicily (central Mediterranean sea). I. Evidence of rock-water interactions and pollution. Period Mineral 2002;71(3):255–72.
Chalmers AT, Van Metre PC, Callender E. The chemical response of particle-associated contaminants in aquatic sediments to urbanization in New England, U.S.A.. J Contam Hydrol 2007;91(1–2):4–25.
Chan PK, Cheng SH. Cadmium-induced ectopic apoptosis in zebrafish embryos. Arch Toxicol 2003;77(2):69–79.
Cheng SH, Chan KW, Chan PK, So CH, Lam PK, Wu RS. Whole-mount in situ TUNEL method revealed ectopic pattern of apoptosis in cadmium treated naupliar larvae of barnacle (Balanus amphitrite Darwin). Chemosphere 2004;55(10):1387–94.
Ercal N, Gurer-Orhan H, Aykin-Burns N. Toxic metals and oxidative stress part I: mechanisms involved in metal-induced oxidative damage. Curr Top Med Chem 2001;1(6):529–39, Review.
Foulkes EC. Transport of toxic heavy metals across cell membranes. Review Article. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 2000;223:234–40.
Goldstone JV, Hamdoun A, Cole BJ, Howard-Ashby M, Nebert DW, Scally M, Dean M, Epel D, Hahn ME, Stegeman JJ. The chemical defensome: environmental sensing and response genes in the Strongylocentrotus purpuratus genome. Dev Biol 2006;300(1):366–84.
Habeebu SS, Liu J, Klaassen CD. Cadmium-induced apoptosis in mouse liver. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1998;149(2):203–9.
Hamada T, Tanimoto A, Sasaguri Y. Apoptosis induced by cadmium. Apoptosis 1997;2(4):359–67.
Hamdoun A, Epel D. Embryo stability and vulnerability in an always changing world. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007;104(6):1745–50, Review.
Haouem S, Hmad N, Najjar MF, El Hani A, Sakly R. Accumulation of cadmium and its effects on liver and kidney functions in rats given diet containing cadmium-polluted radish bulb. Exp Toxicol Pathol 2007;59(Issue 1):77–80.
Hart MW. The functional and evolutionary significance of variation in feeding larval forms of echinoderms. Invertebr Biol 1996;115:30–45.
Hays GC, Richardson AJ, Robinson C. Climate change and marine plankton. Trends Ecol Evol 2005;20(6):337–44.
Ishido M, Tohyama C, Suzuki T. Cadmium-bound metallothionein induces apoptosis in rat kidneys, but not in cultured kidney LLC-PK1 cells. Life Sci 1999;64(9):797–804.
Kesseler A, Brand MD. Localisation of the sites of action of cadmium on oxidative phosphorylation in potato tuber mitochondria using top–down elasticity analysis. Eur J Biochem 1994;225(3):897–906.
Kim BJ, Kim MS, Kim KB, Kim KW, Hong YM, Kim IK, Lee HW, Jung YK. Sensitizing effects of cadmium on TNF-alpha- and TRAIL-mediated apoptosis of NIH3T3 cells with distinct expression patterns of p53. Carcinogenesis 2002;23(9):1411–7.
Kobayashi N, Okamura H. Effects of heavy metals on sea urchin embryo development. 1. Tracing the cause by the effects. Chemosphere 2004;55(10):1403–12.
Kobayashi N, Okamura H. Effects of heavy metals on sea urchin embryo development. Part 2. Interactive toxic effects of heavy metals in synthetic mine effluents. Chemosphere 2005;61:1198–203.
Kremling K, Streu P. Behaviour of dissolved Cd, Co, Zn, and Pb in North Atlantic near-surface waters (30° N/60° W to 60° N/2° W). Deep Sea Res I 2001;48/12:2541–67.
Lesser MP, Kruse VA, Barry TM. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation causes apoptosis in developing sea urchin embryos. J Exp Biol 2003;206(Pt 22):4097–103.
Lin AJ, Zhang XH, Chen MM, Cao Q. Oxidative stress and DNA damages induced by cadmium accumulation. J Environ Sci (China) 2007;19(5):596–602.
Mouchet F, Baudrimont M, Gonzalez P, Cuenot Y, Bourdineaud JP, Boudou A, Gauthier L. Genotoxic and stress inductive potential of cadmium in Xenopus laevis larvae. Aquat Toxicol 2006;78(2):157–66.
Mouchet F, Gauthier L, Baudrimont M, Gonzalez P, Mailhes C, Ferrier V, Devaux A. Comparative evaluation of the toxicity and genotoxicity of cadmium in amphibian larvae (Xenopus laevis and Pleurodeles waltl) using the comet assay and the micronucleus test. Environ Toxicol 2007;22(4):422–35.
Pellerito C, D’Agati P, Fiore T, Mansueto C, Mansueto V, Stocco G, Nagy L, Pellerito L. Synthesis, structural investigations on organotin(IV) chlorin-e6 complexes, their effect on sea urchin embryonic development and induced apoptosis. J Inorg Biochem 2005;99(6):1294–305.
Pohl C, Hennings U. The coupling of long-term trace metal trends to seasonal diffusive trace metal fluxes at the oxic–anoxic interface in the Gotland Basin; (57°19.20′ N; 20°03.00′ E) Baltic Sea. J Mar Sys 2005;56:207–25.
Radakovitch O, Roussiez V, Ollivier P, Ludwig W, Grenz C, Probst J. Input of particulate heavy metals from rivers and associated sedimentary deposits on the Gulf of Lion continental shelf. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science. 2008;(in press).
Rainbow PS, Black WH. Cadmium, zinc and the uptake of calcium by two crabs, Carcinus maenas and Eriocheir sinensis. Aquat Toxicol 2005;72(1–2):45–65.
Risso-de Faverney C, Devaux A, Lafaurie M, Girard JP, Bailly B, Rahmani R. Cadmium induces apoptosis and genotoxicity in rainbow trout hepatocytes through generation of reactive oxygene species. Aquat Toxicol 2001;53(1):65–76.
Roccheri MC, Tipa C, Bonaventura R, Matranga V. Physiological and induced apoptosis in sea urchin larvae undergoing metamorphosis. Int J Dev Biol 2002;46(6):801–6.
Roccheri MC, Agnello M, Bonaventura R, Matranga V. Cadmium induces the expression of specific stress proteins in sea urchin embryos. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004;321:80–7.
Roesijadi G, Hansen KM, Unger ME. Cadmium-induced metallothionein expression during embryonic and early larval development of the mollusc Crassostrea virginica. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1996;140(2):356–63.
Rule KL, Comber SD, Ross D, Thornton A, Makropoulos CK, Rautiu R. Diffuse sources of heavy metals entering an urban wastewater catchment. Chemosphere 2006;63(1):64–72.
Russo R, Bonaventura R, Zito F, Schröder HC, Müller I, Müller WE, Matranga V. Stress to cadmium monitored by metallothionein gene induction in Paracentrotus lividus embryos. Cell Stress Chaperones 2003;8(3):232–41.
Sato Y, Kaneko H, Negishi S, Yazaki I. Larval arm resorption proceeds concomitantly with programmed cell death during metamorphosis of the sea urchin Hemicentrotus pulcherrimus. Cell Tissue Res 2006;326(3):851–60.
Schröder HC, Hassanein HMA, Lauenroth S, Koziol C, Mohamed TAA, Lacorn M, Steinhart H, Batel R, Müller WEG. Induction of DNA strand breaks and expression of HSP70 and GRP78 homolog by cadmium in the marine sponge Suberites domuncula. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 1999;36:47–55.
Schröder HC, Di Bella G, Janipour N, Bonaventura R, Russo R, Müller WEG, Matranga V. DNA damage and developmental defects after exposure to UV and heavy metals in sea urchin cells and embryos compared to other invertebrates. Prog Mol Subcell Biol 2005;39:111–37.
Shimizu M, Hochadel JF, Waalkes MP. Effects of glutathione depletion on cadmium-induced metallothionein synthesis, cytotoxicity, and proto-oncogene expression in cultured rat myoblasts. J Toxicol Environ Health 1997;51:609–21.
Sunda WG, Huntsman S. Processes regulating cellular metal accumulation and physiological effects: Phytoplankton as model systems. Total Environ 1998;219:165–81.
Tankere SPC, Statham PJ. Distribution of dissolved Cd, Cu, Ni and Zn in the Adriatic Sea. Mar Pollut Bull 1996;32:623–30.
Tsangaris GT, Tzortzatou-Stathopoulou F. Cadmium induces apoptosis differentially on immune system cell lines. Toxicology 1998;128(2):143–50.
Vega RL, Epel D. Stress-induced apoptosis in sea urchin embryogenesis. Mar Environ Res 2004;58(2–5):799–802.
Vega Thurber R, Epel D. Apoptosis in early development of the sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. Dev Biol 2007;303(1):336–46.
Viarengo A, Nicotera P. Possible role of Ca2+ in heavy metal cytotoxicity. Comp Biochem Physiol 1991;100C:81–4.
Waalkes MP, Rehm S. Lack of cacinogenicity of cadmium chloride in female Syrian hamsters. Toxicology 1998;126(3):173–8.
Yazaki I. Mechanisms of sea urchin metamorphosis: stimuli and responses. In: Yokota Y, Matranga V, Smolenicka Z, editors. The sea urchin: from basic biology to aquaculture. The Netherlands: Balkema, Lisse; 2002. p. 51–71.
Yokota Y, Matranga V, Smolenicka Z. The sea urchin: from basic biology to aquaculture. The Netherlands: Balkema, Lisse; 2002. p. 1–231.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from MIUR (ex 60%) and partially by the ASI MoMa project (contract 1/014/06/0).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Filosto, S., Roccheri, M.C., Bonaventura, R. et al. Environmentally relevant cadmium concentrations affect development and induce apoptosis of Paracentrotus lividus larvae cultured in vitro. Cell Biol Toxicol 24, 603–610 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-008-9066-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-008-9066-x