Abstract
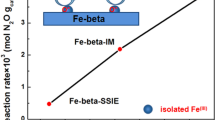
To reveal the effect of zeolite topology on the status of iron species, a series of Fe-zeolite catalysts (Fe-Beta, Fe-ZSM-5, Fe-Y, Fe-ZSM-35, Fe-MCM-22, Fe-SSZ-13) were synthesized using the wet ion-exchange technique. The catalytic reduction of N2O by NH3 with Fe-zeolites was carried out, and the corresponding activities followed the order Fe-Beta > Fe-ZSM-5 > Fe-Y > Fe-ZSM-35 > Fe-MCM-22 > Fe-SSZ-13. The Fe-Beta catalyst shows the best activity, which achieving more than 98% N2O conversion at 350 ℃. The prepared catalysts were subjected to physicochemical characterization. It shows that the structure of Fe-Beta and Fe-ZSM-5 zeolite facilitated the loading of Fe ions upon the framework of zeolites through the pores and the sequent formation of active centers (Fe3+) on the ion exchange sites. In addition, the larger pore sizes in Fe-zeolites are more favorable for the diffusion of N2O within the pores and channels of the zeolite, so the catalytic reduction of N2O by ammonia is promoted.
Graphical Abstract






Similar content being viewed by others

References
Coq B, Mauvezin M, Delahay G, Butet JB, Kieger S (2000) The simultaneous catalytic reduction of NO and N2O by NH3 using an Fe-zeolite-beta catalyst. Appl Catal B: Environ 27:193–198. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-3373(00)00148-X
Pieterse J (2004) Evaluation of Fe-zeolite catalysts prepared by different methods for the decomposition of N2O. Appl Catal B: Environ 51:215–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2004.02.013
Guzmanvargas A (2003) Catalytic decomposition of N2O and catalytic reduction of N2O and N2O + NO by NH3 in the presence of O2 over Fe-zeolite. Appl Catal B: Environ 42:369–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0926-3373(02)00268-0
Christoforou SC, Efthimiadis EA, Vasalos IA (2002) Catalytic reduction of NO and N2O to N2 in the presence of O2, C3H6, SO2, and H2O. Ind Eng Chem Res 41:2090–2095. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie010862o
Xue LI, Hong HE, Liu C, Zhang C, Zhang B (2009) Promotion effects and mechanism of alkali metals and alkaline earth metals on Cobalt-Cerium composite oxide catalysts for N2O decomposition. Environ Sci Technol 43:890–895. https://doi.org/10.1021/es801867y
Sugawara K, Nobukawa T, Yoshida M, Sato Y, Okumura K, Tomishige K, Kunimori K (2007) The importance of Fe loading on the N2O reduction with NH3 over Fe-MFI: effect of acid site formation on Fe species. Appl Catal B: Environ 69:154–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2006.06.027
Zhang X, Shen Q, He C, Ma C, Cheng J, Hao Z (2012) N2O catalytic reduction by NH3 over Fe-zeolites: effective removal and active site. Catal Commun 18:151–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2011.11.029
Lu R, Zhang X, Ma C, Wang Z, Wang Y, Hao Z (2013) Fe-Beta catalysts prepared by heating wet ion exchange and their catalytic performances on N2O catalytic decomposition and reduction. Asia-Pac J Chem Eng 9:159–166. https://doi.org/10.1002/apj.1754
Abu-Zied BM (2011) Cu2+-acetate exchanged X zeolites: preparation, characterization and N2O decomposition activity. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 139:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2010.10.017
Gao F, Walter ED, Karp EM, Luo J, Tonkyn RG, Kwak JH, Szanyi J, Peden CHF (2013) Structure–activity relationships in NH3-SCR over Cu-SSZ-13 as probed by reaction kinetics and EPR studies. J Catal 300:20–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2012.12.020
Hajjar R, Millot Y, Man PP, Che M, Dzwigaj S (2008) Two kinds of framework Al sites studied in BEA zeolite by X-ray diffraction, fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, NMR techniques, and V probe. J Phys Chem C 112:20167–20175. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp808356q
Mentzen BF (2007) Crystallographic determination of the positions of the monovalent H, Li, Na, K, Rb, and Tl cations in fully dehydrated MFI typezeolites. J Phys Chem C 111:18932–18941. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp077356i
Zeng J, Chen SY, Fan ZH, Wang CZ, Chang HZ, Li JH (2020) Simultaneous selective catalytic reduction of NO and N2O by NH3 over Fe-zeolite catalysts. Ind Eng Chem Res 59:19500–19509. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c02909
Abu-Zied BM (2011) Cu2+-acetate exchanged X zeolites: preparation, characterization and N2O decomposition activity. Micropor Mesopor Mat 139:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2010.10.017
You Y, Chen S, Li J, Zeng J, Chang H, Ma L, Li J (2020) Low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of N2O by CO over Fe-ZSM-5 catalysts in the presence of O2. J Hazard Mater 383:121117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121117
BorońP CL, Gurgul J, Łątka K, Shishido T, Krafft JM, Dzwigaj S (2013) BEA zeolite modified with iron as effective catalyst for N2O decomposition and selective reduction of NO with ammonia. Appl Catal B: Environ 138–139:434–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.03.022
Delahay G, Mauvezin M, Coq B, Kieger S (2001) Selective catalytic reduction of nitrous oxide by ammonia on iron zeolite Beta catalysts in an oxygen rich atmosphere: effect of iron contents. J Catal 202:156–162. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcat.2001.3279
Shahami M, Dooley KM, Shantz DF (2018) Steam-assisted crystallized Fe-ZSM-5 materials and their unprecedented activity in benzene hydroxylation to phenol using hydrogen peroxide. J Catal 368:354–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2018.10.011
Rutkowska M, Chmielarz L, Macina D, Piwowarska Z, Dudek B, Adamski A, Witkowski S, Sojka Z, ObalováL VO, CJ, Cool P, (2014) Catalytic decomposition and reduction of N2O over micro-mesoporous materials containing Beta zeolite nanoparticles. Appl Catal B: Environ 146:112–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.05.005
Lim JB, Cha SH, Hong SB (2019) Direct N2O decomposition over iron-substituted small-pore zeolites with different pore topologies. Appl Catal B: Environ 243:750–759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.10.068
Marturano P, DrozdováL PGD, Kogelbauer A, Prins R (2001) The mechanism of formation of the Fe species in Fe/ZSM-5 prepared by CVD. Phys Chem 3:5585–5595. https://doi.org/10.1039/b107266h
Chen L, Wang X, Cong Q, Ma H, Li S, Li W (2019) Design of a hierarchical Fe-ZSM-5@CeO2 catalyst and the enhanced performances for the selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3. Chem Eng J 369:957–967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.055
Mauvezin M, Delahay G, Coq B, Kieger S, Jumas JC, Olivier-Fourcade J (2001) Identification of iron species in Fe−BEA: influence of the exchange level. J Phys Chem B 105:928–935. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0021906
Long RQ, Yang RT (2000) Characterization of Fe-ZSM-5 catalyst for selective catalytic reduction of nitric oxide by ammonia. J Catal 194:80–90. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcat.2000.2935
Guo QH, Li J, Li YX (2013) Fe-Modified ZSM-5 and β Zeolites for direct N2O decomposition. Adv Mater Research 610:94–99. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.610-613.94
Boroń P, Chmielarz L, Gurgul J, Łątka K, Gil B, Marszałek B, Dzwigaj S (2015) Influence of iron state and acidity of zeolites on the catalytic activity of FeHBEA, FeHZSM-5 and FeHMOR in SCR of NO with NH3 and N2O decomposition. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 203:73–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2014.10.023
Cao Y, Fan D, Tian P, Cao L, Sun T, Xu S, Yang M, Liu Z (2018) The influence of low-temperature hydration methods on the stability of Cu-SAPO-34 SCR catalyst. Chem Eng J 354:85–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.07.195
Ma L, Chang H, Yang S, Chen L, Fu L, Li J (2012) Relations between iron sites and performance of Fe/HBEA catalysts prepared by two different methods for NH3-SCR. Chem Eng J 209:652–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.08.042
Koller H, Meijer EL, van Santen RA (1997) 27Al quadrupole interaction in zeolites loaded with probe molecules–a quantum-chemical study of trends in electric field gradients and chemical bonds in clusters. Solid State Nucl Magn Reson 9:165–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0926-2040(97)00056-8
Bulánek R, Kolářová M, Chlubná P, Čejka J (2013) Coordination of extraframework Li+ cation in the MCM-22 and MCM-36 zeolite: FTIR study of CO adsorbed. Adsorption 19:455–463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-012-9467-2
Martinovic F, Ballauri S, Blangetti N, Bensaid S, Pirone R, Bonelli B, Armandi M, Deorsola FA (2023) Solid-state ion exchange of Fe in small pore SSZ-13 zeolite: characterization of the exchanged species and their relevance for the NOx SCR reaction. Appl Catal A: Gen 658:119160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2023.119160
Funding
This work was funded by Innovation Fund of SINOPEC Catalyst Co. Ltd-State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering (Grant no. 36100000-22-ZC0607-0041); National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos. 21976012 and 22176010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Du, S., Kang, B., Guo, X. et al. Catalytic Reduction of N2O by NH3 over Fe-zeolite Catalysts with Different Topologies. Catal Lett (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-024-04637-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-024-04637-7