Abstract
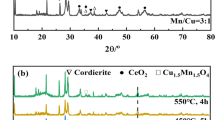
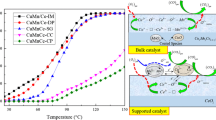
Cu–Mn–Ce ternary mixed oxides, prepared via the citric acid complex method and supported on cordierite, were investigated for their catalytic activity in the oxidation of chlorobenzene. The impact of various reaction conditions, including chlorobenzene concentration, GHSV, water vapor and HCl, was thoroughly investigated to analyze oxidative activity, stability, and anti-poisoning ability. Among the catalysts tested, those with 20 wt% CuMnOx and 10 wt% CeO2, calcined at 450 °C for 4 h with one step, exhibited the highest apparent activity with T90 < 300 °C in the feed containing 500ppm chlorobenzene at a space velocity of 10,000 h−1. Notably, Cu–Mn–Ce–O exhibited a stable and effective catalyst performance for the oxidation of chlorinated aromatics under low water vapor (< 5%) and HCl (2%) concentrations. Further insights into the oxidation process were gained via in-situ FTIR spectroscopy and GC–MS analysis. The exceptional performance of Cu–Mn–Ce–O was attributed to the incorporation of CeO2, resulting in a lower H2 reduction peak, smaller particle size, abundant surface active oxygen, and a higher specific surface area. To understand the reaction mechanism, the relationship between inlet and outlet gas compounds and the reaction temperature over Cu–Mn–Ce–O was studied, revealing the presence of NO/NOx during the reaction at temperature up to 300 °C.
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gu YF, Cai T, Gao XH, Xia HQ, Sun W, Zhao J, Dai QG, Wang XY (2019) Catalytic combustion of chlorinated aromatics over WOX/CeO2 catalysts at low temperature. Appl Catal B 248:264–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.12.055
Liu XL, Chen L, Zhu TY, Ning RL (2019) Catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene over noble metals (Pd, Pt, Ru, Rh) and the distributions of polychlorinated by-products. J Hazard Mater 363:90–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.09.074
Li J, Hu M, Zuo S, Wang X (2018) Catalytic combustion of volatile organic compounds on pillared interlayered clay (PILC)-based catalysts. Curr Opin Chem Eng 20:93–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coche.2018.02.001
Meng J, Fu YX, Chen SH, Zhang HY, Li Z, Wang XR, Luo J, Zhou Y, Luo SP, Qin HF (2023) Hollow zeolite-based V-Cu bimetallic oxide catalyst for remarkable catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene. Sep Purif Technol 326:124775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2023.124775
Wang Y, Wu J, Wang G, Yang DY, Ishihara T, Guo LM (2021) Oxygen vacancy engineering in Fe doped akhtenskite-type MnO2 for low-temperature toluene oxidation. Appl Catal B 285:119873–119889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119873
Qin LB, Zhao B, Chen WS, Han YX, Wan Y, Liu L, Lu HJ, Han J (2022) Simultaneous removal of toluene and chlorobenzene in a nonthermal plasma-catalysis reactor packed with Fe1-Mn1/γ-Al2O3. J Clean Prod 363:132611–212626. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132611
Tian J, Wei JY, Liang YP, Guo RX, Li BB, Qu RJ, Zhou DM, Wang ZY, Sun P (2022) Catalytic ozonation of an imidazole ionic liquid via Fe3O4/ZnO nanocomposites: performance, products and reaction mechanism. J Clean Prod 10:108726–108737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2022.108726
He C, Xu BT, Shi JW, Qiao NL, Hao ZP, Zhao JL (2015) Catalytic destruction of chlorobenzene over mesoporous ACeOX (A = Co, Cu, Fe, Mn, or Zr) composites prepared by inorganic metal precursor spontaneous precipitation. Fuel Process Technol 130:179–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2014.10.008
Wang XW, Jiang WY, Yin RQ, Sun PF, Lu YH, Wu ZB, Weng XL (2020) The role of surface sulfation in mediating the acidity and oxidation ability of nickel modified ceria catalyst for the catalytic elimination of chlorinated organics. J Colloid Interface Sci 574:251–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.04.047
Xiang Y, Zhu Y, Lu J, Zhu CZ, Zhu MG, Xie QQ, Chen TH (2019) Co3O4/α-Fe2O3 catalyzed oxidative degradation of gaseous benzene: preparation, characterization and its catalytic properties. Solid State Sci 93:76–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2019.05.008
Zhou ZW, Li QQ, Su GJ, Pang JX, Sun BH, Meng J, Shi B (2024) Catalytic degradation of chlorinated volatile organic compounds (CVOCs) over Ce-Mn-Ti composite oxide catalysts. J Environ Sci 138:326–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2023.03.019
Chen T, Wang R, Sun C, Kong DB, Lu SY, Li XD (2022) Metal-organic frameworks templated micropore-enriched defective MnCeOX for low temperature chlorobenzene oxidation. Appl Catal A 645:118845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2022.118845
Li L, Shi JW, Tian MJ, Chen CW, Wang BR, Ma MD, He C (2021) In situ fabrication of robust three dimensional ordered macroporous γ-MnO2/LaMnO3.15 catalyst for chlorobenzene efficient destruction. Appl Catal B 282:119565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2020.119565
Dai QG, Yin LL, Bai SX, Wang W, Wang XY, Gong XQ, Lu GZ (2016) Catalytic total oxidation of 1,2-dichloroethane over VOX/CeO2 catalysts: further insights via isotopic tracer techniques. Appl Catal B 182:598–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.10.016
Huang H, Gu Y, Zhao J, Wang XY (2015) Catalytic combustion of chlorobenzene over VOX/CeO2 catalysts. J Catal 326:54–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2015.02.016
Zhou H, Wu QW, Cheng FZ (2019) Catalytic oxidation of CO by La0.8Sr0.2Mn1-xCuXO3 by flame spray synthesis. J Chem Eng 72(10):5159–5171. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/detail.aspx?FileName=HGSZ202110018&DbName=CJFQ2021
Kang N, Lin J, Lu SX, Zhao ZQ, Yu XY (2023) Inhibition of CO oxidation over Cu-Mn-Ce-O composite catalyst in the presence of dry powder fire extinguishing agent: mechanism investigation and mitigation strategy. Appl Catal A 664:119343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2023.119343
Zhang HY, Sui SH, Zheng XM, Cao RR, Zhang PY (2019) One-pot synthesis of atomically dispersed Pt on MnO2 for efficient catalytic decomposition of toluene at low temperatures. Appl Catal B 257:117878–117879. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.117878
Wang Y, Wang G, Deng W, Han J, Qin LB, Zhao B, Guo LM, Xing FT (2020) Study on the structure-activity relationship of Fe-Mn oxide catalysts for chlorobenzene catalytic combustion. Chem Eng J 395:125172–125185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.125172
Wang Y, Deng W, Wang YF, Guo LM, Ishihara T (2018) A comparative study of the catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene and toluene over Ce-Mn oxides. Mol Catal 459:61–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2018.08.022
Yang WH, Su ZA, Xu ZH, Yang WN, Peng Y, Li JH (2020) Comparative study of α-, β-, γ- and δ-MnO2 on toluene oxidation: oxygen vacancies and reaction intermediates. Appl Catal B 260:118150–118184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118150
Lu SH, Li KL, Huang FL, Chen CC, Sun B (2017) Efficient MnOX-Co3O4-CeO2 catalysts for formaldehyde elimination. Appl Surf Sci 400:277–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.12.207
Yang S, Zhao HJ, Dong F, Zha F, Tang ZC (2019) Highly efficient catalytic combustion of o-dichlorobenzene over three-dimensional ordered mesoporous cerium manganese bimetallic oxides: a new concept of chlorine removal mechanism. Mol Catal 463:119–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcat.2018.12.006
He C, Yu YK, Shen Q, Chen JS, Qiao NL (2014) Catalytic behavior and synergistic effect of nanostructured mesoporous CuO-MnOX-CeO2 catalysts for chlorobenzene destruction. Appl Surf Sci 297:59–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.01.076
Wang XY, Ran L, Dai Y, Lu YJ, Dai QG (2014) Removal of Cl adsorbed on Mn–Ce–La solid solution catalysts during CVOC combustion. J Colloid Interface Sci 426:324–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.10.007
Dai QG, Wu JY, Deng W, Hu JS, Wu QQ, Guo LM, Sun W, Zhan WC, Wang XY (2019) Comparative studies of P/CeO2 and Ru/CeO2 catalysts for catalytic combustion of dichloromethane: from effects of H2O to distribution of chlorinated by-products. Appl Catal B 249:9–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.02.065
Yu XH, Dai LY, Deng JG, Liu YX, Jing L, Zhang X, Gao RY, Hou ZQ, Wei L, Dai HX (2022) An isotopic strategy to investigate the role of water vapor in the oxidation of 1,2-dichloroethane over the Ru/WO3 or Ru/TiO2 catalyst. Appl Catal B 305:121037. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.121037
Chen L, Si ZC, Wu XD, Weng D, Wu ZW (2015) Effect of water vapor on NH3–NO/NO2 SCR performance of fresh and aged MnOX–NbOX–CeO2 catalysts. J Environ Sci 31:240–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2014.07.037
Song ZJ, Yu SX, Liu H, Wang Y, Gao CY, Wang ZS, Qin YM, Peng Y, Li JH (2022) Carbon/chlorinate deposition on MnOX-CeO2 catalyst in chlorobenzene combustion: the effect of SCR flue gas. Chem Eng J 433:133552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.133552
Jin QJ, Xu MT, Lu Y, Yang B, Ji WY, Xue ZW, Dai Y, Wang Y, Shen YS, Xu HT (2022) Simultaneous catalytic removal of NO, mercury and chlorobenzene over WCeMnOX/TiO2–ZrO2: performance study of microscopic morphology and phase composition. Chemosphere 295:133794–133812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.133794
Sun PF, Wang WL, Dai XX, Weng XL, Wu ZB (2016) Mechanism study on catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene over MnXCe1-xO2/H-ZSM5 catalysts under dry and humid conditions. Appl Catal B 198:389–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.05.076
He C, Yu YK, Shi JW, Shen Q, Chen JS, Liu HX (2015) Mesostructured Cu-Mn-Ce-O composites with homogeneous bulk composition for chlorobenzene removal: catalytic performance and microactivation course. Mater Chem Phys 157:87–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2015.03.020
Yan X, Zhao LK, Huang Y, Zhang JF, Jiang S (2023) Three-dimensional porous CuO-modified CeO2-Al2O3 catalysts with chlorine resistance for simultaneous catalytic oxidation of chlorobenzene and mercury: Cu-Ce interaction and structure. J Hazard Mater 455:131585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.131585
Wu SX, Wu SL, Dong F, Xi YT, Wang P, Chu YH, Tang ZC, Zhang JY (2024) Elucidating the nature role of acid etching on the CoMnOX catalyst with outstanding performance for the catalytic combustion of o-dichlorobenzene. Appl Catal B 342:123390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2023.123390
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (No. BK20170954, BK20150890 and BK20190786), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21501097, 51902166), the Qing Lan Project of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD), and NUIST-Reading Research Institute Pump-Priming Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Gu, My., An, Gf. et al. Enhanced Catalytic Performance and Poison Resistance of Cu–Mn–Ce Ternary Mixed Oxide for Chlorobenzene Oxidation. Catal Lett 154, 2866–2877 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-023-04511-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-023-04511-y