Abstract
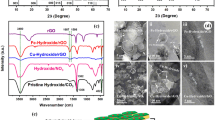
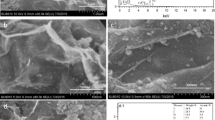
Using the mental-organic frameworks (MOFs) as a promising precursor to derive the Fe–N-C catalyst (FexCN@GN) with Fe-Nx moieties for sulfate radical (SO4·−) based advanced oxidation process (SR-AOP) for Trichlorophenol degradation. The catalyst exhibited high activity in activation of PS to generate free radicals and achieved 92% degradation of TCP within 60 min. Through the characterization of the catalyst and EPR detection, we found that the sp2-hybridized carbon structure on GO can adsorb TCP strongly and fix free radicals on the surface of the catalyst at the same time, so that free radicals can react with TCP rapidly and avoid long-distance mass transfer loss in solution. We also found that N atom plays an important role in the catalyst, and the Fe-Nx active center formed by pyridine N and Fe atoms is the active center of the catalytic reaction. Based on this, the degradation mechanism is deduced. In conclusion, this work provided new Fe–N-C-based nanocatalysts for the generation of surface radicals, providing a new pathway for the removal of emerging contaminants.
Graphical Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul MKN, Kwame KP, Wang C, Zhang W, Luo R, Zhang M et al (2019) Metal-organic framework-derived hollow Co3O4/carbon as efficient catalyst for peroxymonosulfate activation. Chem Eng J 363:234–246
Adewuyi YG, Khan MA, Sakyi NY (2013) Kinetics and modeling of the removal of nitric oxide by aqueous sodium persulfate simultaneously activated by temperature and Fe2+. Ind Eng Chem Res 53:828–839
Andrew Lin K-Y, Hsu F-K, Lee W-D (2015) Magnetic cobalt–graphene nanocomposite derived from self-assembly of MOFs with graphene oxide as an activator for peroxymonosulfate. J Mater Chem A 3:9480–9490
Bukola S, Merzougui B, Akinpelu A, Laoui T, Hedhili MN, Swain GM et al (2014) Fe-N-C electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction synthesized by using aniline salt and Fe3+ /H2 O2 catalytic system. Electrochim Acta 146:809–818
Cao J, Sun S, Li X, Yang Z, Xiong W, Wu Y et al (2020) Efficient charge transfer in aluminum-cobalt layered double hydroxide derived from Co-ZIF for enhanced catalytic degradation of tetracycline through peroxymonosulfate activation. Chem Eng J 382:122082
Chen X, Oh W-D, Lim T-T (2018) Graphene- and CNTs-based carbocatalysts in persulfates activation: Material design and catalytic mechanisms. Chem Eng J 354:941–976
Chen X, Wang N, Shen K, Xie Y, Tan Y, Li Y (2019) MOF-derived isolated Fe atoms implanted in N -Doped 3D hierarchical carbon as an efficient ORR electrocatalyst in both alkaline and acidic media. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:25976–25985
Du W, Zhang Q, Shang Y, Wang W, Li Q, Yue Q, et al. Sulfate saturated biosorbent-derived Co-S@NC nanoarchitecture as an efficient catalyst for peroxymonosulfate activation. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental 2020; 262.
Duan X, Ao Z, Sun H, Indrawirawan S, Wang Y, Kang J et al (2015) Nitrogen-doped graphene for generation and evolution of reactive radicals by metal-free catalysis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:4169–4178
Duan X, Sun H, Kang J, Wang Y, Indrawirawan S, Wang S (2015) Insights into heterogeneous catalysis of persulfate activation on dimensional-structured nanocarbons. ACS Catal 5:4629–4636
Farisabadi A, Moradi M, Hajati S, Kiani MA, Espinos JP (2019) Controlled thermolysis of MIL-101(Fe, Cr) for synthesis of FexOy/porous carbon as negative electrode and Cr2O3/porous carbon as positive electrode of supercapacitor. Appl Surf Sci 469:192–203
Guo T, Jiang L, Wang K, Li Y, Huang H, Wu X, Zhang G (2021) Efficient persulfate activation by hematite nanocrystals for degradation of organic pollutants under visible light irradiation: Facet-dependent catalytic performance and degradation mechanism. Appl Catal B Environ 286:119883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.119883
Hao X, Jin Z, Yang H, Lu G, Bi Y (2017) Peculiar synergetic effect of MoS 2 quantum dots and graphene on Metal-Organic Frameworks for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Appl Catal B 210:45–56
Hu J, Chen D, Li N, Xu Q, Li H, He J et al (2017) In situ fabrication of Bi2O2CO3/MoS2 on carbon nanofibers for efficient photocatalytic removal of NO under visible-light irradiation. Appl Catal B 217:224–231
Huang YH, Huang YF, Huang CI, Chen CY (2009) Efficient decolorization of azo dye Reactive Black B involving aromatic fragment degradation in buffered Co2+/PMS oxidative processes with a ppb level dosage of Co2+-catalyst. J Hazard Mater 170:1110–1118
Hummers SW, Offeman RE (1958) Preparation of graphitic oxide. Am Chem Soc 80:1339
Hussain I, Zhang Y, Huang S, Du X (2012) Degradation of p-chloroaniline by persulfate activated with zero-valent iron. Chem Eng J 203:269–276
Jeong B, Shin D, Jeon H, Ocon JD, Mun BS, Baik J et al (2014) Excavated Fe-N-C sites for enhanced electrocatalytic activity in the oxygen reduction reaction. Chemsuschem 7:1289–1294
Li H, Tian J, Zhu Z, Cui F, Zhu Y-A, Duan X et al (2018) Magnetic nitrogen-doped nanocarbons for enhanced metal-free catalytic oxidation: Integrated experimental and theoretical investigations for mechanism and application. Chem Eng J 354:507–516
Li W, Wu X, Li S, Tang W, Chen Y (2018) Magnetic porous Fe3O4/carbon octahedra derived from iron-based metal-organic framework as heterogeneous Fenton-like catalyst. Appl Surf Sci 436:252–262
Li X, Guo W, Liu Z, Wang R, Liu H (2016) Fe-based MOFs for efficient adsorption and degradation of acid orange 7 in aqueous solution via persulfate activation. Appl Surf Sci 369:130–136
Liu C, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Li R, Meng W, Song Z et al (2018) Enhancement of Fe@porous carbon to be an efficient mediator for peroxymonosulfate activation for oxidation of organic contaminants: Incorporation NH2-group into structure of its MOF precursor. Chem Eng J 354:835–848
Liu X, Zhou Y, Zhang J, Tang L, Luo L, Zeng G (2017) Iron containing metal-organic frameworks: structure, synthesis, and applications in environmental remediation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:20255–20275
Lu J-Y, Yuan Y-R, Hu X, Liu W-J, Li C-X, Liu H-Q et al (2020) MOF-derived Fe2O3/nitrogen/carbon composite as a stable heterogeneous electro-fenton catalyst. Ind Eng Chem Res 59:1800–1808
Ma J, Yang Q, Wen Y, Liu W (2017) Fe-g-C3N4/graphitized mesoporous carbon composite as an effective Fenton-like catalyst in a wide pH range. Appl Catal B 201:232–240
Ma W, Wang N, Tong T, Zhang L, Lin K-YA, Han X et al (2018) Nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur tri-doped hollow carbon shells derived from ZIF-67@poly (cyclotriphosphazene-co-4, 4′-sulfonyldiphenol) as a robust catalyst of peroxymonosulfate activation for degradation of bisphenol A. Carbon 137:291–303
Matzek LW, Carter KE (2016) Activated persulfate for organic chemical degradation: A review. Chemosphere 151:178–188
Oh SY, Kim HW, Park JM, Park HS, Yoon C (2009) Oxidation of polyvinyl alcohol by persulfate activated with heat, Fe2+, and zero-valent iron. J Hazard Mater 168:346–351
Pu M, Ma Y, Wan J, Wang Y, Wang J, Brusseau ML (2017) Activation performance and mechanism of a novel heterogeneous persulfate catalyst: Metal Organic Framework MIL-53(Fe) with Fe(II)/Fe(III) mixed-valence coordinative unsaturated iron center. Catal Sci Technol 7:1129–1140
Ren J, Jiang L, Li Y, Zhang G (2021) Cobalt doped bismuth oxysulfide with abundant oxygen vacancies towards tetracycline degradation through peroxymonosulfate activation. Sep Purif Technol 275:119100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119100
Tang J, Wang J (2018) Metal organic framework with coordinatively unsaturated sites as efficient fenton-like catalyst for enhanced degradation of sulfamethazine. Environ Sci Technol 52:5367–5377
Vu TA, Le GH, Vu HT, Nguyen KT, Quan TTT, Nguyen QK et al (2017) Highly photocatalytic activity of novel Fe-MIL-88B/GO nanocomposite in the degradation of reactive dye from aqueous solution. Mater Res Exp 4:035038
Wang J, Wang S (2018) Activation of persulfate (PS) and peroxymonosulfate (PMS) and application for the degradation of emerging contaminants. Chem Eng J 334:1502–1517
Wang X, Qin Y, Zhu L, Tang H (2015) Nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide as a bifunctional material for removing bisphenols: synergistic effect between adsorption and catalysis. Environ Sci Technol 49:6855–6864
Wang Y, Wang J, Wei D, Li M (2019) A “MOF-protective-Pyrolysis” strategy for the preparation of Fe-N-C catalysts and the Role of Fe, N, and C in the oxygen reduction reaction in acidic medium. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:35755–35763
Xian G, Niu L, Zhang G, Zhou N, Long Z, Zhi R (2020) An efficient CuO-gammaFe2O3 composite activates persulfate for organic pollutants removal: Performance, advantages and mechanism. Chemosphere 242:125191
Xiao T, Wang Y, Wan JN, Ma YW, Yan ZC, Huang SH, Zeng C (2022) Fe-N-C catalyst with Fe-N-X sites anchored nano carboncubes derived from Fe-Zn-MOFs activate peroxymonosulfate for high-effective degradation of ciprofloxacin: thermal activation and catalytic mechanism. J Hazard Mater 424:127380. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127380
Xu Y, Wang Y, Wan J, Ma Y (2020) Reduced graphene oxide-supported metal organic framework as a synergistic catalyst for enhanced performance on persulfate induced degradation of trichlorophenol. Chemosphere 240:124849
Yang S, Yang X, Shao X, Niu R, Wang L (2011) Activated carbon catalyzed persulfate oxidation of Azo dye acid orange 7 at ambient temperature. J Hazard Mater 186:659–666
Yue X, Guo W, Li X, Zhou H, Wang R (2016) Core-shell Fe3O4@MIL-101(Fe) composites as heterogeneous catalysts of persulfate activation for the removal of Acid Orange 7. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23:15218–15226
Zeng T, Yu M, Zhang H, He Z, Chen J, Song S (2017) Fe/Fe3C@N-doped porous carbon hybrids derived from nano-scale MOFs: robust and enhanced heterogeneous catalyst for peroxymonosulfate activation. Catal Sci Technol 7:396–404
Zeng T, Zhang X, Wang S, Niu H, Cai Y (2015) Spatial confinement of a Co3O4 catalyst in hollow metal-organic frameworks as a nanoreactor for improved degradation of organic pollutants. Environ Sci Technol 49:2350–2357
Zhu C, Liu F, Ling C, Jiang H, Wu H, Li A (2019) Growth of graphene-supported hollow cobalt sulfide nanocrystals via MOF-templated ligand exchange as surface-bound radical sinks for highly efficient bisphenol A degradation. Appl Catal B 242:238–248
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by National Key Research and Development Project (No. 2018YFE0110400), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21978102, 31670585) and Science and Technology Commissioner project of Guangdong province (No. GDKTP2020066400).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, C., Huang, S., Wang, Y. et al. Graphene-Supported Fe–N Catalysts for Activation of Persulfate for Trichlorophenol Degradation by Surface Radicals. Catal Lett 153, 3122–3135 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-022-04198-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-022-04198-7