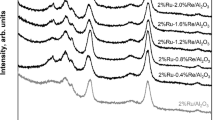
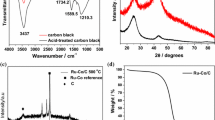
Abstract
Catalytic combustion of hazardous particulate matter (soot) generated by automobile engines is a primary method of their elimination. Ruthenium-based catalysts are a promising alternative for traditional noble metal (Pt, Pd) based systems; however, their relatively poor thermal stability hinders wide applications. In this study, we synthesized a novel, highly active, and stable catalyst for soot oxidation containing bimetallic RuRe nanoparticles supported on TiO2. The RuRe NPs were synthesized by colloidal, microwave-assisted polyol method and deposited on rutile or anatase TiO2. The effect of rhenium content and the nature of TiO2 support on the performance of RuRe nanoparticles (NPs) in the soot oxidation under air atmosphere was investigated. Bimetallic RuRe/TiO2 nanocatalysts exhibited higher activity in the soot oxidation than Ru/TiO2 systems, and the rutile supported 2 wt% Ru–0.4 wt% Re nanocatalyst (Ru/Re atomic ratio of 9:1) showed the best catalytic performance (T50 = 340 °C and T90 < 400 °C). All studied nanocatalysts were stable under reaction conditions in the consecutive catalytic tests. The exceptional catalytic performance of bimetallic RuRe NPs is explained by the synergy effect between ruthenium, rhenium, and TiO2.
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frank B, Schlogl R, Su DS (2013) Diesel soot toxification. Environ Sci Technol 47:3026–3027. https://doi.org/10.1021/es4003873
Prasad R, Bella VR (2010) A review on diesel soot emission, its effect and control. Bull Chem React Eng Catal 5:69–86. https://doi.org/10.9767/bcrec.5.2.794.69-86
Fino D, Bensaid S, Piumetti M, Russo N (2016) A review on the catalytic combustion of soot in Diesel particulate filters for automotive applications: from powder catalysts to structured reactors. Appl Catal A 509:75–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2015.10.016
Neyertz CA, Banus ED, Miro E, Querini CA (2014) Potassium-promoted Ce0.65Zr03.5O2 monolithic catalysts for diesel soot combustion. Chem Eng J 248:394–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.03.048
Bueno-López A (2014) Diesel soot combustion ceria catalysts. Appl Catal B 146:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.02.033
Stelmachowski P, Legutko P, Kopacz A, Jakubek T, Indyka P, Pietrzyk P, Wojtasik M, Markowski J, Krasodomski W, Ziemiański L, Żak G, Sojka Z, Kotarba A (2016) Role of chain length of the capping agents of iron oxide based fuel borne catalysts in the enhancement of soot combustion activity. Appl Catal B 199:485–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.06.056
Gandhi HS, Graham GW, McCabe RW (2003) Automotive exhaust catalysis. J Catal 216:433–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9517(02)00067-2
Legutko P, Jakubek T, Kaspera W, Stelmachowski P, Sojka Z, Kotarba A (2017) Strong enhancement of desoot activity of transition metal oxides by alkali doping, additive effects of potassium and nitric oxide. Top Catal 60:162–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-016-0727-3
Totton TS, Misquitta AJ, Kraft M (2012) A quantitative study of the clustering of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons at high temperatures. Phys Chem Chem Phys 14:4081–4094. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2CP23008A
Ramdas R, Nowicka E, Jenkins R, Sellick D, Davies C, Golunski S (2015) Using real particulate matter to evaluate combustion catalysts for direct regeneration of diesel soot filters. Appl Catal B 176–177:436–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2015.04.031
Castoldi L, Aneggi E, Matarrese R, Bonzi R, Trovarelli A, Lietti L (2017) Simultaneous removal of soot and NOx over silver and ruthenium-based catalysts. Top Catal 60:29–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-016-0599-6
Matarrese R, Aneggi E, Castoldi L, Llorca J, Trovarelli A, Lietti L (2016) Simultaneous removal of soot and NOx over K- and Ba-doped ruthenium supported catalysts. Catal Today 267:119–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2015.12.016
Aouad S, Saab E, Abi-Aad E, Aboukaïs A (2007) Reactivity of Ru-based catalysts in the oxidation of propene and carbon black. Catal Today 119:273–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2006.08.030
Aouad S, Abi-Aad E, Aboukaïs A (2009) Simultaneous oxidation of carbon black and volatile organic compounds over Ru/CeO2 catalysts. Appl Catal B 88:249–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.10.002
Ledwa KA, Pawlyta M, Kępiński L (2018) RuxCe1-xO2-y nanoparticles deposited on functionalized gamma-Al2O3 as a thermally stable oxidation catalyst. Appl Catal B 230:135–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.02.037
Homsi D, Aouad S, El Nakat J, El Khoury B, Obeid P, Abi-Aad E, Aboukaïs A (2011) Carbon black and propylene oxidation over Ru/CexZr1-xO2 catalysts. Catal Commun 12:776–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2011.01.014
Tschamber V, Jeguirim M, Villani K, Martens J, Ehrburger P (2007) Comparison of the activity of Ru and Pt catalysts for the oxidation of carbon by NO2. Appl Catal B 77:299–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2006.10.016
Villani K, Kirschhock CEA, Liang D, Van Tendeloo G, Martens JA (2006) Catalytic carbon oxidation over ruthenium-based catalysts. Angew Chem Int Ed 45:3106–3109. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200503799
Jeguirim M, Villani K, Brilhac JF, Martens JA (2010) Ruthenium and platinum catalyzed carbon oxidation: a comparative kinetic study. Appl Catal B 96:34–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.01.031
Okal J, Zawadzki M (2009) Catalytic combustion of butane on Ru/γ-Al2O3 catalysts. Appl Catal B 89:22–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2008.11.024
Okal J, Zawadzki M, Tylus W (2011) Microstructure characterization and propane oxidation over supported Ru nanoparticles synthesized by the microwave-polyol method. Appl Catal B 101:548–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2010.10.028
Okal J, Zawadzki M, Kraszkiewicz P, Adamska K (2018) Ru/CeO2 catalysts for combustion of mixture of light hydrocarbons: Effect of preparation method and metal salt precursors. Appl Catal A 549:161–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2017.09.036
Mondelli C, Amrute AP, Krumeich F, Schmidt T, Pérez-Ramírez J (2011) Shaped RuO2/SnO2–Al2O3 catalyst for large-scale stable Cl2 production by HCl oxidation. Chem Cat Chem 3:657–663. https://doi.org/10.1002/cctc.201000424
Kondratenko EV, Amrute AP, Pohl MM, Steinfeldt N, Mondelli C, Pérez-Ramírez J (2013) Superior activity of rutile-supported ruthenium nanoparticles for HCl oxidation. Catal Sci Technol 3:2555–2558. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CY00372H
Wang X, Liu Y, Xu Ch, Lu X, Ma R, Fu Y, Wang S, Zhu W (2021) Effects of the support-crystal size on the catalytic performance of RuO2/TiO2 in the deacon process. Catal Lett 151:2346–2354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-020-03493-5]
Perkas N, Zhong Z, Chen L, Besson M, Gedanken A (2005) Sonochemically prepared high dispersed Ru/TiO2 mesoporous catalyst for partial oxidation of methane to syngas. Catal Lett 103:9–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-005-6496-4
Baranowska K, Okal J, Tylus W (2016) Microwave-assisted polyol synthesis of bimetallic RuRe nanoparticles stabilized by PVP or oxide supports (γ-alumina and silica). Appl Catal A 511:117–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2015.11.045
Baranowska K, Okal J (2015) Bimetallic Ru–Re/γ-Al2O3 catalysts for the catalytic combustion of propane: effect of the Re addition. Appl Catal A 499:158–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2015.04.023
Okal J, Zawadzki M, Baranowska K (2016) Methane combustion over bimetallic Ru–Re/γ-Al2O3 catalysts: effect of Re and pretreatments. Appl Catal B 194:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.04.038
Ayvali T, Fazzini PF, Lecante P, Mayoral A, Philippot K, Chaudret B (2017) Control of reactivity through chemical order in very small RuRe nanoparticles. Dalton Trans 46:15070–15079. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7DT02287E
Lee Y, Kim YT, Kwon EE, Lee J (2020) Biochar as a catalytic material for the production of 1,4-butanediol and tetrahydrofuran from furan. Environ Res 184:109325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109325
Di X, Li C, Zhang B, Qi J, Li W, Su D, Liang C (2017) Role of Re and Ru in Re-Ru/C bimetallic catalysts for the aqueous hydrogenation of succinic acid. Ind Eng Chem Res 56:4672–4683. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b04875
Jung KB, Lee J, Ha JM, Lee H, Suh DJ, Jun CH, Jae J (2018) Effective hydrodeoxygenation of lignin-derived phenols using bimetallic RuRe catalysts: effect of carbon supports. Catal Today 303:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2017.07.027
Jin X, Thapa PS, Subramaniam B, Chaudhari RV (2016) Kinetic modeling of sorbitol hydrogenolysis over bimetallic RuRe/C catalyst. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 4:6037–6047. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.6b01346
Adamska K, Smykała SZ, Zieliński S, Szymański D, Hojeńska A, Stelmachowski P, Kotarba A, Okal J (2021) Oxidation of soot over supported RuRe nanoparticles prepared by the microwave-polyol method. React Kinet Mech Cat 134:221–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11144-021-02048-y
Liu L, Zhao H, Andino JM, Li Y (2012) Photocatalytic CO2 reduction with H2O on TiO2 nanocrystals: comparison of anatase, rutile and brookite polymorphs and exploration of surface chemistry. ACS Catal 2:1817–1828. https://doi.org/10.1021/cs300273q
Debecker DP, Farin B, Gaigneaux EM, Sanchez C, Sassoye C (2014) Total oxidation of propane with a nano-RuO2/TiO2 catalyst. Appl Catal A 481:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2014.04.043
Zhou G, Dou R, Bi H, Xie S, Pei Y, Fan K, Qiao M, Sun B, Zong B (2015) Ru nanoparticles on rutile/anatase junction of P25 TiO2: controlled deposition and synergy in partial hydrogenation of benzene to cyclohexene. J Catal 332:119–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2015.09.016
Brzezinska M, Niemeier J, Louven Y, Keller N, Palkovits R, Ruppert A (2020) TiO2 supported Ru catalysts for the hydrogenation of succinic acid: influence of the support. Catal Sci Technol 10:6860–6869. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0CY01446J
Martynova SA, Yusenko KV, Korolkov IV, Baidina IA, Korenev SV (2009) X-ray diffraction study of [Ru(NH3)5Cl][ReCl6] and [Ru(NH3)5Cl]2[ReCl6]Cl2 and their thermolysis products: crystal-chemical analysis of the Ru–Re system. J Struct Chem 50:120–126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10947-009-0016-0
Wang DX, Huang J, Liu F, Xu XL, Fang XZ, Liu JJ, Xie YC, Wang X (2020) Rutile RuO2 dispersion on rutile and anatase TiO2 supports: The effects of support crystalline phase structure on the dispersion behaviors of the supported metal oxides. Catal Today 339:220–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2019.02.038
Kim A, Debecker DP, Devred F, Dubois V, Sanchez C, Sassoye C (2018) CO2 methanation on Ru/TiO2 catalysts: On the effect of mixing anatase and rutile TiO2 supports. Appl Catal B 220:615–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.08.058
Xiang G, Shi X, Wu Y, Zhuang J, Wang X (2012) Size effects in atomic-level epitaxial redistribution process of RuO2 over TiO2. Sci Rep 2:801. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep00801
Dunn JP, Stenger HG Jr, Wachs IE (1999) Oxidation of SO2 over supported metal oxide catalysts. J Catal 181:233–243. https://doi.org/10.1006/jcat.1998.2305
Seitsonen AP, Over H (2010) Oxidation of HCl over TiO2-supported RuO2: a density functional theory study. J Phys Chem C 114:22624–22629. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp108603a
Secordel X, Berrier E, Capron M, Cristol S, Paul JF, Fournier M, Payen E (2010) TiO2-supported rhenium oxide catalysts for methanol oxidation: effect of support texture on the structure and reactivity evidenced by an operando Raman study. Catal Today 155:177–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2010.01.003
Ro I, Xu M, Graham GW, Pan X, Christopher P (2019) Synthesis of heteroatom Rh−ReOx atomically dispersed species on Al2O3 and their tunable catalytic reactivity in ethylene hydroformylation. ACS Catal 9:10899–10912. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscatal.9b02111
Okal J, Tylus W, Kępiński L (2004) XPS study of oxidation of rhenium metal on γ-Al2O3 support. J Catal 225:489–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcat.2004.05.004
Sato Y, Soma Y, Miyao T, Naito S (2006) The water-gas-shift reaction over Ir/TiO2 and Ir-Re/TiO2 catalysts. Appl Catal A 304:78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2006.02.022
Zhou L, Lin W, Liu K, Wang Z, Liu Q, Cheng H, Zhang Ch, Arai M, Zhao F (2020) Hydrodeoxygenation of ethyl stearate over Re-promoted Ru/TiO2 catalysts: rate enhancement and selectivity control by the addition of Re. Catal Sci Technol 10:222–230. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9CY01909J
Moulder JF, Stickle WF, Sobol PE, Bomben KD (1992) Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (Perkin Elmer Corp., Eden Prairie/USA)
Ma L, He D (2009) Hydrogenolysis of glycerol to propanediols over highly active Ru–Re bimetallic catalysts. Top Catal 52:834–844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11244-009-9231-3
Kaspera W, Zieliński S, Kotarba A (2017) Alkali tungsten bronzes as soot oxidation catalysts: the key role of electrodonor properties of catalytic surface. Catal Commun 98:76–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catcom.2017.05.009
Zhu R, Yan Q, He J, Cao G, Ouyang F (2017) Simultaneous removal of soot and NOx with Ru-Ir/TiO2 catalyst under oxygen-rich condition. Appl Catal A 541:42–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcata.2017.04.014
Mukherjee D, Venkataswamy P, Devaiah D, Rangaswamy A, Reddy BM (2017) Crucial role of titanium dioxide support in soot oxidation catalysis of manganese doped ceria. Catal Sci Technol 7:3045–3055. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CY01029J
Małecka MA, Kępiński L, Miśta W (2007) Structure evolution of nanocrystalline CeO2 and CeLnOx mixed oxides (Ln = Pr, Tb, Lu) in O2 and H2 atmosphere and their catalytic activity in soot combustion. Appl Catal B 74:290–298. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2007.02.021
Aneggi E, de Leitenburg C, Trovarelli A (2012) On the role of lattice/surface oxygen in ceria–zirconia catalysts for diesel soot combustion. Catal Today 181:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cattod.2011.05.034
Querini CA, Ulla RF, Soria J, Sedrán UA, Miró EE (1998) Catalytic combustion of diesel soot particles. Activity and characterization of Co/MgO and Co K/MgO catalysts. Appl Catal B 15:5–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-3373(97)00032-5
Svintsitskiy DA, Slavinskaya EM, Kibis LS, Stadnichenko AI, Fedorova EA, Stonkus OA, Korneeva EV, Romanenko AV, Boronin AI (2021) Effect of the support nature on the physicochemical properties of platinum catalysts for ammonia oxidation. J Struct Chem 62:598–612. https://doi.org/10.1134/S0022476621040120
Perkas N, Teo J, Shen S, Wang Z, Highfield J, Zhong Z, Gedanken A (2011) Supported Ru catalysts prepared by two sonication-assisted methods for preferential oxidation of CO in H2. Phys Chem Chem Phys 13:15690–15698. https://doi.org/10.1039/C1CP21870K
Hebenstreit ELD, Hebenstreit W, Geisler H, Ventrice CA Jr, Hite DA, Sprunger PT, Diebold U (2002) The adsorption of chlorine on TiO2(110) studied with scanning tunneling microscopy and photoemission spectroscopy. Surf Sci 505:336–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0039-6028(02)01385-7
Hanaor DAH, Sorrell CC (2011) Review of the anatase to rutile phase transformation. J Mater Sci 46:855–874. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-5113-0
Matarrese R, Morandi S, Castoldi L, Villa P, Lietti L (2017) Removal of NOx and soot over Ce/Zr/K/Me (Me = Fe, Pt, Ru, Au) oxide catalysts. Appl Catal B 201:318–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.07.013
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank: Mrs. Ewa Bukowska for the XRD measurements, Mrs. Agnieszka Hojeńska for ICP-AES analysis, Dr. Marcin Kuśnierz for XPS study, Mrs. Dagmara Białowieska, Mrs. Patrycja Kokot vel Kokocińska and Agnieszka Siomra for technical assistance. This work was carried out within the Reintegration program of the Foundation for Polish Science, co-financed by the European Union under the European Regional Development Fund, Project No. POIR.04.04.00-00-5F33/18-00.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KA: Methodology, Visualization, Investigation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Writing—original draft, SS: Investigation, Methodology, Formal analysis, Writing, SZ: Methodology, Investigation, DS: Methodology, Investigation, PS: Methodology, Writing—review & editing, AK: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing—review, JO: Conceptualization, Writing—review & editing, LK: Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adamska, K., Smykała, S., Zieliński, S. et al. TiO2 Supported RuRe Nanocatalysts for Soot Oxidation: Effect of Re and the Support Nature. Catal Lett 153, 1372–1389 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-022-04066-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-022-04066-4