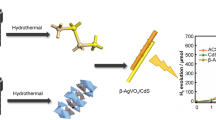
Abstract
Due to the poor photocatalytic hydrogen evolution ability of pure CdS, we need to develop a photocatalytic hydrogen evolution catalyst with high activity and no precious metal doping. Therefore, in this article, we used a simple hydrothermal synthesis of CdS nanoparticles, using water as a carrier, loading a small amount of amorphous CoS, by changing the loading ratio of amorphous CoS, synthesized TYPE–II type heterojunction composite catalyst CCS. The successful synthesis of the composite catalyst CCS was verified by XRD, SEM and other characterization methods. UV–vis, PL and other characterization showed that the supported amorphous CoS could significantly improve the photocatalytic activity of CdS, and the photochemical detection also showed that the performance of composite catalyst CCS was better than that of pure CdS. Using Na2S and Na2SO3 mixed solution as electron sacrificial agent, the hydrogen production performance of CCS composite catalyst was determined through hydrogen evolution experiment and cyclic stability experiment. It was found that the sacrificial agent had a great promotion effect on the hydrogen production performance of photocatalyst. It was found that the hydrogen production rate of the composite catalyst could reach 2.01 mmol·g−1·h−1, which was 6.3 times of the pure CdS. This study offers a novel approach for the design of amorphous–based nanostructures as efficient hydrogen evolution cocatalysts.
Graphic Abstract
First, CdS are excited by light, consuming S2− and SO32− ions in the sacrificial agent, generating a large number of electrons and holes. Due to the energy difference between the conducting band (CB) of CdS and amorphous CoS, the electrons are transferred from the surface of CdS to the conducting band (CB) of amorphous CoS, while the electrons obtained from water and H+ in the sacrificial agent are reduced to H2. The amorphous CoS is used as the transfer medium of electron acceptor, and the synergistic effect between heterojunctions is used to improve the charge separation efficiency and electron transfer rate. Therefore, the photocatalytic hydrogen production effect of the composite catalyst CCS–7 has been greatly improved.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jin Z, Li Y, Hao X (2020) Ni, Co-based selenide anchored g-C3N4 for boosting photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Acta Phys Chim Sin 36:1912033
Yang Q, Peng P, Xiang Z (2017) Covalent organic polymer modified TiO2 nanosheets as highly efficient photocatalysts for hydrogen generation. Chem Eng Sci 162:33–40
Shen R, Zhang L, Chen X, Jaroniec M, Li N, Li X (2020) Integrating 2D/2D CdS/α-Fe2O3 ultrathin bilayer Z-scheme heterojunction with metallic β-NiS nanosheet-based ohmic-junction for efficient photocatalytic H2 evolution. Appl Catal B 266:118619
Peng J, Shen J, Yu X, Tang H, Liu Q (2021) Construction of LSPR-enhanced 0D/2D CdS/MoO3-x S-scheme heterojunctions for visible-light-driven photocatalytic H2 evolution. Chin J Catal 42(1):87–96
Xu J, Huo F, Zhao Y, Liu Y, Yang Q, Cheng Y, Min S, Jin Z, Xiang Z (2018) In-situ La doped Co3O4 as highly efficient photocatalyst for solar hydrogen generation. Int J Hydrog Energ 43(18):8674–8682
Zhou Z, Peng P, Xiang Z (2018) N-rich covalent organic polymer in situ modified TiO2 for highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Sci Bull 63(6):369–375
Zhang L, Hao X, Li J, Wang Y, Jin Z (2020) Unique synergistic effects of ZIF-9(Co)-derived cobalt phosphide and CeVO4 heterojunction for efficient hydrogen evolution. Chin J Catal 41(1):82–94
Zhang L, Hao X, Li Y, Jin Z (2020) Performance of WO3/g-C3N4 heterojunction composite boosting with NiS for photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Appl Surf Sci 499:143862
Shen R, Xie J, Xiang Q, Chen X, Jiang J, Li X (2019) Ni-based photocatalytic H2-production cocatalysts2. Chin J Catal 40(3):240–288
Zhang Z-W, Li Q-H, Qiao X-Q, Hou D, Li D-S (2019) One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of willow branch-shaped MoS2/CdS heterojunctions for photocatalytic H2 production under visible light irradiation. Chin J Catal 40(3):371–379
Chong B, Chen L, Han D, Wang L, Feng L, Li Q, Li C, Wang W (2019) CdS-modified one-dimensional g-C3N4 porous nanotubes for efficient visible-light photocatalytic conversion. Chin J Catal 40(6):959–968
Jian Q, Hao X, Jin Z, Ma Q (2020a) Amorphous tungsten phosphosulphide-modified CdS nanorods as a highly efficient electron-cocatalyst for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production. Phys Chem Chem Phys 22:1932–1943
Jian Q, Hao X, Jin Z, Ma Q (2020b) Amorphous tungsten phosphosulphide-modified CdS nanorods as a highly efficient electron-cocatalyst for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production. Phys Chem Chem Phys 22:1932–1943
Dai K, Hu T, Zhang J, Lu L (2019) Carbon nanotube exfoliated porous reduced graphene oxide/CdS-diethylenetriamine heterojunction for efficient photocatalytic H2 production. Appl Surf Sci 512:144783
Li L-L, Yin X-L, Pang D-H, Du X-X, Xue H, Zhou H-W, Yao Q-X, Wang H-W, Qian J-C, Yang J, Li D-C, Dou J-M (2019) One-pot synthesis of MoS2/CdS nanosphere heterostructures for efficient H2 evolution under visible light irradiation. Int J Hydrog Energ 44(60):31930–31939
Gai Q, Zheng X, Liu W, Dong Q, Wang Y, Gao R, Ren S (2019) 2D–2D heterostructured CdS–CoP photocatalysts for efficient H2 evolution under visible light irradiation. Int J Hydrog Energ 44(50):27412–27420
Bao N, Shen L, Takata T, Domen K (2007) Self-templated synthesis of nanoporous CdS nanostructures for highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production under visible light. Chem Mater 20:110–117
Xiang Q, Cheng B, Yu J (2013) Hierarchical porous CdS nanosheet-assembled flowers with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic H2-production performance. Appl Catal B Environ 138:299–303
Yu J, Yu Y, Zhou P, Xiao W, Cheng B (2014) Morphology-dependent photocatalytic H2-production activity of CdS. Appl Catal B Environ 156:184–191
Jin J, Yu J, Liu G, Wong PK (2013) Single crystal CdS nanowires with high visible-light photocatalytic H2-production performance. J Mater Chem A 1:10927–10934
Li C, Yuan J, Han B, Shangguan W (2011) Synthesis and photochemical performance of morphology-controlled CdS photocatalysts for hydrogen evolution under visible light. Int J Hydrog Energ 36:4271–4279
Zhang Y, Han L, Wang C, Wang W, Ling T, Yang J, Dong C, Lin F, Du X (2017) Zincblende CdS nanocubes with coordinated facets for photocatalytic water splitting. ACS Catal 7:1470–1477
Lu Y, Cheng X, Tian G, Zhao H, He L, Hu J, Wu S, Dong Y, Chang G, Lenaerts S, Siffert S, Tendeloo GV, Li Z, Xu L, Yang X, Su B (2018) HierarchicalCdS/m-TiO2/G ternary photocatalyst for highly active visible light-induced hydrogen production from water splitting with high stability. Nano Energ 47:8–17
Hu Y, Gao X, Yu L, Wang Y, Ning J, Xu S, Lou XW (2013) Carbon-coated CdS petalous nanostructures with enhanced photostability and photocatalytic activity. Angew Chem Int Ed 52:5636–5639
Ma BJ, Xu HJ, Lin KY, Li J, Zhan HJ, Liu WY, Li C (2016) Mo2C as non-noble metal co-catalyst in Mo2C/CdS composite for enhanced photocatalytic H2 evolution under visible light irradiation. Chem SusChem 9:820–824
Ma BJ, Liu YH, Li J, Lin KY, Liu WY, Zhan HJ (2016) Mo2N: an efficient non-noblemetal cocatalyst on CdS for enhanced photocatalytic H2 evolution under visible light irradiation. Int J Hydrog Energ 41:22009–22016
Ma BJ, Wang XY, Lin KY, Li J, Liu YH, Zhan HJ, Liu WY (2017) A novel ultra efficient non-noble metal composite cocatalyst Mo2N/Mo2C/graphene for enhanced photocatalytic H2 evolution. Int J Hydrog Energ 42:18977–18984
Chao YG, Zheng JF, Zhang HX, Li F, Yan F, Tan YS, Zhua ZP (2018) Oxygen-in corporation in Co2P as a non-noble metal cocatalyst to enhance photocatalysis for reducing water to H2 under visible light. Chem Eng J 346:281–288
Shen Q, Wang Yi, Xue J, Gao G, Liu X, Jia H, Li Qi, Xu B (2019) The dual effects of RGO films in TiO2/CdSe heterojunction: enhancing photocatalytic activity and improving photocorrosion resistance. Appl Surf Sci 481:1515–1523
Wang X, Xiang Y, Zhou B, Zhang Y, Wu J, Hu R, Liu L, Song J, Qu J (2019) Enhanced photocatalytic performance of Ag/TiO2 nanohybrid sensitized by black phosphorus nanosheets in visible and near-infrared light. J Colloid Interface Sci 534:1–11
Bahruji H, Bowker M, Davies PR, Pedrono F (2011) New insights into the mechanism of photocatalytic reforming on Pd/TiO2[J]. Appl Catal B 107(1):205–209
Vamvasakis I, Liu B, Armatas GS (2016) Size effects of platinum nanoparticles in the photocatalytic hydrogen production over 3D mesoporous networks of CdS and Pt nanojunctions. Adv Func Mater 26(44):8062–8071
Iwashina K, Kudo A (2011) Rh-Doped SrTiO3 photocatalyst electrode showing cathodic photocurrent for water splitting under visible-light irradiation. J Am Chem Soc 133(34):13272–13275
Yu H, Yuan R, Gao D, Xu Y, Yu J (2019) Ethyl acetate-induced formation of amorphous MoSx nanoclusters for improved H2-evolution activity of TiO2 photocatalyst. Chem Eng J 375:121934
Xue Y, Min S, Meng J, Liu X, Lei Y, Tian L, Wang F (2019) Light-induced confined growth of amorphous Co doped MoSx nanodots on TiO2 nanoparticles for efficient and stable in situ photocatalytic H2 evolution. Int J Hydrog Energ 44(16):8133–8143
Liu X, Min S, Xue Y, Lei Y, Chen Y, Wang F, Zhang Z (2019) Accelerating photosensitized H2 evolution over in situ grown amorphous MoSx catalyst employing TiO2 as an efficient catalyst loading matrix and electron transfer relay. Renew Energ 138:562–572
Li Y, Shen Q, Guan R, Xue J, Liu X, Jia H, Xua B, Wu Y (2020) A C@TiO2 yolk–shell heterostructure for synchronous photothermal–photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants. J Mater Chem C 8:1025–1040
Gao J, Shen Q, Guan R, Xue J, Liu X, Jia H, Li Q, Wu Y (2020) Oxygen vacancy self-doped black TiO2 nanotube arrays by aluminothermic reduction for photocatalytic CO2 reduction under visible light illumination. J CO2 Util 35:205–215
Sun Z-G, Li X-S, Liu J-L, Li Y-C, Zhu B, Zhu A-M (2019) A promising visible-light photocatalyst: H2 plasma-activated amorphous-TiO2-supported Au nanoparticles. J Catal 375:380–388
Chen F, Luo W, Mo Y, Yu H, Cheng B (2018) In situ photodeposition of amorphous CoSx on the TiO2 towards hydrogen evolution. Appl Surf Sci 430:448–456
Hao X, Hu Y, Cui Z, Zhou J, Wang Y, Zou Z (2019) Self-constructed facet junctions on hexagonal CdS single crystals with high photoactivity and photostability for water splitting. Appl Catal B 244:694–703
Yu H, Xu J, Yin C, Liu Z, Li Y (2019) Significant improvement of photocatalytic hydrogen evolution rate over g-C3N4 with loading CeO2@Ni4S3. J Solid State Chem 272:102–112
Xu J, Yu H, Guo H (2018) Synthesis and behaviors of g-C3N4 coupled with LaxCo3-xO4 nanocomposite for improved photocatalytic activeity and stability under visible light. Mater Res Bull 105:342–348
Mao M, Xu J, Li L, Zhao S, Li X, Li Y, Liu Z (2019) High performance hydrogen production of MoS2-modified perovskite LaNiO3 under visible light. Ionics 10:1–14
Han J-F, Liao C, Cha L-M, Jiang T, Xie H-M, Zhao K, Besland M-P (2014) TEM and XPS studies on CdS/CIGS interfaces. J Phys Chem Solids 75(12):1279–1283
Hao X, Wang Y, Zhou J, Cui Z, Wang Y, Zou Z (2018) Zinc vacancy-promoted photocatalytic activity and photostability of ZnS for effiffifficient visible-light-driven hydrogen evolution. Appl Catal B Environ 221:302–311
Guo J, Liang Y, Liu Li, Hu J, Wang H, An W, Cui W (2020) Noble-metal-free CdS/Ni-MOF composites with highly efficient charge separation for photocatalytic H2 evolution. Appl Surf Sci 522:146356
Sun K, Shen J, Yang Y, Tang H, Lei C (2020) Highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution from 0D/2D heterojunction of FeP nanoparticles/ CdS nanosheets. Appl Surf Sci 505:144042
Luo X, Ke Y, Yu L, Wang Y, Homewood KP, Chen X, Gao Y (2020) Tandem CdS/TiO2(B) nanosheet photocatalysts for enhanced H2 evolution. Appl Surf Sci 515:145970
Yin X-L, Li L-L, Li D-C, Wei D-H, Hu C-C, Dou J-M (2019) Room temperature synthesis of CdS/SrTiO3 nanodots-on-nanocubes for efficient photocatalytic H2 evolution from water. J Colloid Interface Sci 536:694–700
Ren D, Shen R, Jiang Z, Xinyong Lu, Li X (2020) Highly efficient visible-light photocatalytic H2 evolution over 2D–2D CdS/Cu7S4 layered heterojunctions. Chin J Catal 41(1):31–40
Ren D, Liang Z, Ng YH, Zhang P, Xiang Q, Li X (2020) Strongly coupled 2D–2D nanojunctions between P-doped Ni2S (Ni2SP) cocatalysts and CdS nanosheets for efficient photocatalytic H2 evolution. Chem Eng J 390:124496
Huang C, Chen C, Zhang M, Lin L, Ye X, Lin S, Antonietti M, Wang X (2015) Carbon-doped BN nanosheets for metal-free photoredox catalysis. Nat Commun 6:7698
Zhang G, Zang S, Lan ZA, Huang C, Li G, Wang X (2015) Cobalt selenide: a versatile cocatalyst for photocatalytic water oxidation with visible light. J Mater Chem A 3(35):17946–17950
Zhang G, Huang C, Wang X (2015) Dispersing molecular cobalt in graphitic carbon nitride frameworks for photocatalytic water oxidation. Small 11(9–10):1215–1221
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Ningxia Province (NZ17262).
Funding
This work was financially supported by the Open Project of State Key Laboratory of High–efficiency Utilization of Coal and Green Chemical Engineering, Ningxia University (2019-KF-36).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All authors have no conflict of interest with respect to this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Xu, J., Li, L. et al. Construction of Amorphous CoS/CdS Nanoparticles Heterojunctions for Visible–Light–Driven Photocatalytic H2 Evolution. Catal Lett 151, 2408–2419 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-020-03468-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-020-03468-6