Abstract
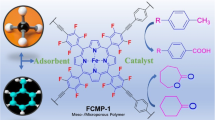
Metalporphyrin-based porous polymers supporting high dispersed Pd nanoparticle (NP) catalysts (HUST-1-Pd) were prepared with a novel solvent-knitting hyper-crosslinked polymer method using 5-, 10-, 15-, and 20-tetraphenylporphyrin (TPP) as building blocks. The N2 sorption isotherms of the catalysts show that the HUST-1-Pd possesses many ultra-micropores and continuous mesopores. The NPs are assembled on tetraphenylporphyrin structures and show Pd-N4 composition-dependent catalysis for methanolysis of ammonia borane (AB) and hydrogenation of aromatic nitro compounds to primary amines in methanol solutions at room temperature. The nano-palladium reduced by NaBH4 has efficient catalytic activity for AB methanolysis. A variety of R-NO2 derivatives were reduced selectively into R-NH2 via palladium catalyzed tandem reactions with 5–30 min of reaction time with conversion yields reaching up to 90%. The derivatives also give excellent recycling performance (more than 10 times). Furthermore, the turnover frequency (TOF) can reach 87,209 h−1. The HUST-1-Pd compounds represent a unique metal catalyst for hydrogenation reactions in a green environment without using pure hydrogen.
Graphic Abstract
A monodisperse Pd NPs embed in porphyrin-based microporous organic polymer was reported to catalyse the tandem dehydrogenation of ammonia borane and hydrogenation of R-NO2 to R-NH2 at room temperature. The catalyst is efficient and reusable in an environment-friendly process with short reaction times and high yields.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang F, Wang M, Liu W, Yang B, Wang Y, Luo J, Tang Y, Hou L, Li Y, Li Z, Zhang B, Yang W, Li Y (2019) Atomically dispersed Ni as the active site towards selective hydrogenation of nitroarenes. Green Chem 21:704
Yang Q, Chen YZ, Wang ZU, Xu Q, Jiang HL (2015) One-pot tandem catalysis over Pd@MIL-101: boosting the efficiency of nitro compound hydrogenation by coupling with ammonia borane dehydrogenation. Chem Commun (Camb) 51:10419
Westerhaus FA, Jagadeesh RV, Wienhöfer G, Pohl M-M, Radnik J, Surkus A-E, Rabeah J, Junge K, Junge H, Nielsen M (2013) Heterogenized cobalt oxide catalysts for nitroarene reduction by pyrolysis of molecularly defined complexes. Nat Chem 5:537
Yang X, Song K, Tan L, Hussain I, Li T, Tan B (2014) Hollow microporous organic capsules loaded with highly dispersed pt nanoparticles for catalytic applications. Macromol Chem Phys 215:1257
Luo L, Duan Z, Li H, Kim J, Henkelman G, Crooks RM (2017) Tunability of the adsorbate binding on bimetallic alloy nanoparticles for the optimization of catalytic hydrogenation. J Am Chem Soc 139:5538
Hartmann CE, Jurcik V, Songis O, Cazin CS (2013) Tandem ammonia borane dehydrogenation/alkene hydrogenation mediated by [Pd(NHC)(PR3)] (NHC = N-heterocyclic carbene) catalysts. Chem Commun (Camb) 49:1005
Rossin A, Peruzzini M (2016) Ammonia-borane and amine-borane dehydrogenation mediated by complex metal hydrides. Chem Rev 116:8848
Yao Q, Lu Z-H, Yang Y, Chen Y, Chen X, Jiang H-L (2018) Facile synthesis of graphene-supported Ni-CeOx nanocomposites as highly efficient catalysts for hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. Nano Res 11:4412
Yang K, Zhou L, Yu G, Xiong X, Ye M, Li Y, Lu D, Pan Y, Chen M, Zhang L, Gao D, Wang Z, Liu H, Xia Q (2016) Ru nanoparticles supported on MIL-53(Cr, Al) as efficient catalysts for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Int J Hydrog Energy 41:6300
Richard J, Cid SL, Rouquette J, Van Der Lee A, Bernard S, Haines J (2016) Pressure-induced insertion of ammonia borane in the siliceous zeolite, silicalite-1F. J Phys Chem C 120:9334
Shang N, Zhou X, Feng C, Gao S, Wu Q, Wang C (2017) Synergetic catalysis of NiPd nanoparticles supported on biomass-derived carbon spheres for hydrogen production from ammonia borane at room temperature. Int J Hydrog Energy 42:5733
Wen M, Cui Y, Kuwahara Y, Mori K, Yamashita H (2016) Non-noble-metal nanoparticle supported on metal-organic framework as an efficient and durable catalyst for promoting H2 production from ammonia borane under visible light irradiation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:21278
Ma X, Zhou YX, Liu H, Li Y, Jiang HL (2016) A MOF-derived Co-CoO@N-doped porous carbon for efficient tandem catalysis: dehydrogenation of ammonia borane and hydrogenation of nitro compounds. Chem Commun (Camb) 52:7719
Zhou Y-H, Yang Q, Chen Y-Z, Jiang H-L (2017) Low-cost CuNi@MIL-101 as an excellent catalyst toward cascade reaction: integration of ammonia borane dehydrogenation with nitroarene hydrogenation. Chem Commun 53:12361
Altintas C, Erucar I, Keskin S (2018) High-throughput computational screening of the metal organic framework database for CH4/H2 separations. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:3668
Luo S, Zhang Q, Zhang Y, Weaver KP, Phillip WA, Guo R (2018) Facile synthesis of a pentiptycene-based highly microporous organic polymer for gas storage and water treatment. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:15174
Gu S, Guo J, Huang Q, He J, Fu Y, Kuang G, Pan C, Yu G (2017) 1,3,5-Triazine-based microporous polymers with tunable porosities for CO2 capture and fluorescent sensing. Macromolecules 50:8512
Bai Y, Chen BWJ, Peng G, Mavrikakis M (2018) Density functional theory study of thermodynamic and kinetic isotope effects of H2/D2 dissociative adsorption on transition metals. Catal Sci Technol 8:3321
Tang C, Zou Z, Fu Y, Song K (2018) Highly dispersed DPPF locked in knitting hyper-crosslinked polymers as efficient and recyclable catalyst. ChemistrySelect 3:5987
Su J, Chen J-S (2017) Synthetic porous materials applied in hydrogenation reactions. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 237:246
Chen X, Shen K, Ding D, Chen J, Fan T, Wu R, Li Y (2018) Solvent-driven selectivity control to either anilines or dicyclohexylamines in hydrogenation of nitroarenes over a bifunctional Pd/MIL-101 catalyst. ACS Catal 8:10641
Bera R, Mondal S, Das N (2018) Triptycene based microporous polymers (TMPs): efficient small gas (H2 and CO2) storage and high CO2/N2 selectivity. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 257:253
Wang M, Ye C, Xu M, Bao S (2018) MoP nanoparticles with a P-rich outermost atomic layer embedded in N-doped porous carbon nanofibers: self-supported electrodes for efficient hydrogen generation. Nano Res 11:4728
Eghbali P, Nişancı B, Metin Ö (2018) Graphene hydrogel supported palladium nanoparticles as an efficient and reusable heterogeneous catalysts in the transfer hydrogenation of nitroarenes using ammonia borane as a hydrogen source. Pure Appl Chem 90:327
Zhu W, Wang X, Li T, Shen R, Hao SJ, Li Y, Wang Q, Li Z, Gu ZG (2018) Porphyrin-based porous polyimide polymer/Pd nanoparticle composites as efficient catalysts for Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reactions. Polym Chem 9:1430
Kumar S, Thorat KG, Lee WZ, Ravikanth M (2018) Synthesis, structural, spectral, and electrochemical studies of selenabenziporphyrin and its Pd(II) complex. Inorg Chem 57:8956
Fu Y-F, Song K-P, Zou Z-J, Li M-Q (2018) External cross-linked sulfonate-functionalized N-heterocyclic carbenes: an efficient and recyclable catalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura reactions in water. Transit Met Chem 43:665
Wang S, Song K, Zhang C, Yu S, Tao L, Tan B (2017) A novel metalporphyrin-based microporous organic polymer with high CO2 uptake and efficient chemical conversion of CO2 under ambient conditions. J Mater Chem A 5:1509
Karataş Y, Gülcan M, Celebi M, Zahmakiran M (2017) Pd(0) nanoparticles decorated on graphene nanosheets (GNS): synthesis, definition and testing of the catalytic performance in the methanolysis of ammonia borane at room conditions. ChemistrySelect 2:9628
Sheng X, Guo H, Qin Y, Wang X, Wang F (2015) A novel metalloporphyrin-based conjugated microporous polymer for capture and conversion of CO2. RSC Adv 5:31664
Gulcan M, Zahmakiran M, Özkar S (2014) Palladium(0) nanoparticles supported on metal organic framework as highly active and reusable nanocatalyst in dehydrogenation of dimethylamine-borane. Appl Catal B 147:394
Veisi H, Najafi S, Hemmati S (2018) Pd(II)/Pd(0) anchored to magnetic nanoparticles (Fe3O4) modified with biguanidine-chitosan polymer as a novel nanocatalyst for Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reactions. Int J Biol Macromol 113:186
Chandra S, Kundu T, Dey K, Addicoat M, Heine T, Banerjee R (2016) Interplaying intrinsic and extrinsic proton conductivities in covalent organic frameworks. Chem Mater 28:1489
Ding ZD, Zhu W, Li T, Shen R, Li Y, Li Z, Ren X, Gu ZG (2017) A metalloporphyrin-based porous organic polymer as an efficient catalyst for the catalytic oxidation of olefins and arylalkanes. Dalton Trans 46:11372
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province (2017B030314092), the Fundamental Research Funds of CWNU (17C038) and Meritocracy Research Funds of CWNU (17Y031), Science and Technology Foundation of Sichuan Province (2017JY0015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, Z., Jiang, Y. & Song, K. Pd Nanoparticles Assembled on Metalporphyrin-Based Microporous Organic Polymer as Efficient Catalyst for Tandem Dehydrogenation of Ammonia Borane and Hydrogenation of Nitro Compounds. Catal Lett 150, 1277–1286 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-019-03028-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-019-03028-7