Abstract
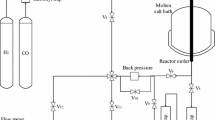
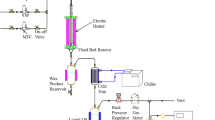
The catalytic performance of Co/γ-Al2O3, Co/SiO2 and Co/TiO2 catalysts has been investigated in a slurry-phase Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis (FTS). Although Co/SiO2 catalyst shows higher CO conversion than the other catalysts, the intrinsic activity is much higher on Co/TiO2 due to large pore size and low deactivation of large cobalt particles by reoxidation mechanism. Co/γ-Al2O3 catalyst confirms low formation rate of oxygenates and C5+ selectivity because of deactivation of catalyst due to catalyst aggregation and reoxidation by the in situ generated water during the FTS reaction. Long-chain hydrocarbons such as wax formed during FTS reaction generally contains water and trace amount of oxygenate which are conducive to the formation of a macro-emulsion of wax products. Formation of such macro-emulsion on the catalyst suggests that the presence of proper amount of alcohol content derived FTS reaction on large pore of catalyst inhibits the catalyst aggregation. The intrinsic activity (turn-over frequency; TOF) of cobalt-based catalysts, in a slurry-phase FTS reaction, is affected by the average pore size of catalyst, cobalt particle size, degree of reduction of cobalt species and possible reoxidation by in situ generated water.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang Y, Liu Y, Yang G, Sun S, Tsubaki N (2007) Appl Catal A 321:79
Storsæter S, Tøtda B, Walmsley JC, Tanem BS (2005) J Catal 236:139
Iglesia E (1997) Appl Catal A 161:59
Reuel RC, Bartholomew CH (1984) J Catal 85:78
Riva R, Miessner H, Vitali R, Del Piero G (2000) Appl Catal A 196:111
Jacobs G, Das TK, Zhang Y, Li J, Racoillet G, Davis BH (2002) Appl Catal A 233:263
Panpranot J, Goodwin J G Jr, Sayari A (2002) J Catal 211:530
Bae JW, Lee YJ, Park JY, Jun KW (2008) Energy Fuels 22:2885
Khodakov AY, Chu W, Fongarland P (2007) Chem Rev 107:1692
Oukaci R, Singleton AH, Goodwin J G Jr (1999) Appl Catal A 186:129
Khodakov AY, Girardon JS, Griboval-Constant A, Lermontov AS, Chernavskii PA (2004) Stud Surf Sci Catal 147:295
Zhang Y, Wei D, Hammache S, Goodwin JG Jr (1999) J Catal 188:281
Xiong J, Borg O, Blekkan EA, Holmen A (2008) Catal Commun 9:2327
Moradi GR, Basir MM, Taeb A, Kiennemann A (2003) Catal Comm 4:27
Chu W, Chernavskii PA, Gengembre L, Pankina GA, Fongarland P, Khodakov AY (2007) J Catal 252:215
Park SJ, Bae JW, Oh JH, Chary KVR, Sai Prasad PS, Jun KW, Rhee YW (2009) J Mol Catal A 298:81
Schulz H, Nie Z, Ousmanov F (2002) Catal Today 71:351
Bae JW, Kim SM, Lee YJ, Lee MJ, Jun KW Catal Commun doi:10.1016/j.catcom.2009.02.023
Okabe K, Li XH, Wei MD, Arakawa H (2004) Catal Today 89:431
Dalai AK, Davis BH (2008) Appl Catal A 348:1
Chakrabarty T Wittenbrink RJ Berlowitz PJ Ansell LL USP 6677388 B2
Bezemer GL, Bitter JH, Kuipers HPCE, Oosterbeek H, Holewijn JE, Xu X, Kapteijn F, van Dillen AJ, de Jong KP (2006) J Am Chem Soc 128:3956
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the financial support of KEMCO and GTL Technology Development Consortium (Korea National Oil Corp., Daelim Industrial Co., Ltd, Doosan Mecatec Co., Ltd, Hyundai Engineering Co. Ltd and SK Energy Co. Ltd) under “Energy & Resources Technology Development Programs” of the Ministry of Knowledge Economy, Republic of Korea. P. K. Khanna thanks KOSEF for a Brain Pool fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oh, JH., Bae, J.W., Park, SJ. et al. Slurry-Phase Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis Using Co/γ-Al2O3, Co/SiO2 and Co/TiO2: Effect of Support on Catalyst Aggregation. Catal Lett 130, 403–409 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-009-0021-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-009-0021-0