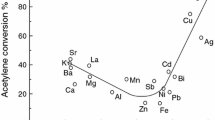
Abstract
Acetylene hydrochlorination using a carbon-supported gold catalyst is studied. Reactivation of the catalyst is demonstrated using a brief treatment of the spent catalyst with boiling aqua regia and the process of reactivation and deactivation is characterised using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Deactivation is considered to be due to loss of Au3+ which is restored by the aqua regia treatment.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hutchings GJ, Grady DT (1985) Appl Catal 16:411
Hutchings GJ, Grady DT (1985) Appl Catal 17:155
Hutchings GJ (1985) J Catal 96:292
Nkosi B, Coville NJ, Hutchings GJ (1988) J Chem Soc, Chem Comm 71
Nkosi B, Coville NJ, Hutchings GJ (1988) Appl Catal 43:33
Nkosi B, Coville NJ, Hutchings GJ, Adams MD, Friedl J, Wagner FE (1991) J Catal 128:366
Nkosi B, Coville NJ, Hutchings GJ, Adams MD, Friedl J, Wagner FE (1991) J Catal 128:378
Popov VE, Lazukin VI, Skaya T, Novikov IN, Yakumova MN, Yu A (1979) Kinet Katal 17:60
Hutchings GJ (1996) Gold Bull 29:123
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the support of the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) of the UK and Johnson Matthey plc (project ATHENA) and the European Union (project AURICAT; Contract HPRN-CT-2002-00174). In addition we thank the World Gold Council who have provided sponsorship for the studentship of MC under the GROW scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Conte, M., Carley, A.F. & Hutchings, G.J. Reactivation of a Carbon-supported Gold Catalyst for the Hydrochlorination of Acetylene. Catal Lett 124, 165–167 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-008-9583-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-008-9583-5