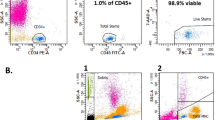
Abstract
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) can be isolated through umbilical cord blood (UCB), which can be used for HSC transplantation. Despite many advantages, the low number of UCB CD34+ cells lead to delayed engraftment. Ex-vivo CD34+HSC expansion is a potentially safe approach to increasing CD34+ cell numbers. The NLR family of pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) is an intracellular protein that plays an essential role in the innate immune response. Several blood cell types, HSCs and progenitor cells (HSPCs) express the NLRP3 inflammasome complex genes and participate in the development and proliferation of HSPCs. In this study, magnetic-activated cell sorting (MACS) beads isolated CD34+HSCs. The cell purity was evaluated by flow cytometry. CD34+ cells, under the influence of different doses of glucose, MCC950 were cultured for seven days. The qRT-PCR was used to evaluate gene expression. The results showed that in the culture medium treated with glucose concentrations, the expression of the NLRP3 inflammasome complex genes and the amount of CD34+ cells increased by more than 50%. In contrast, genes expression and the number of CD34+ cells in the culture medium treated with MCC950 decreased. UCB is a source of new therapeutic methods. This study demonstrates the relationship between glucose and the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. Based on these results, glucose causes the expansion of CD34+HSCs through its effect on HSCs in simultaneous culture.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
References
Adamiak M, Abdel-Latif A, Bujko K et al (2020) Nlrp3 inflammasome signaling regulates the homing and engraftment of hematopoietic stem cells (HSPCs) by enhancing incorporation of CXCR4 receptor into membrane lipid rafts. Stem Cell Rev Rep 16:954–967. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12015-020-10005-W/FIGURES/8
Al-Sweedan SA, Musalam L, Obeidat B (2013) Factors predicting the hematopoietic stem cells content of the umbilical cord blood. Transfus Apher Sci 48:247–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TRANSCI.2013.01.003
Bijou F, Ivanovic Z, Fizet D et al (2015) Neonatal sex and weight influence CD34+ cell concentration in umbilical cord blood but not stromal cell–derived factor 1–3′A polymorphism. Cytotherapy 17:68–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCYT.2014.09.002
Chou S, Chu P, Hwang W, Lodish H (2010) Expansion of human cord blood hematopoietic stem cells for transplantation. Cell Stem Cell 7:427–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.STEM.2010.09.001
Cooney J (2018) Expansion of cord blood stem cells and enhancing their mobilization and homing potential using mesenchymal stromal cells. Blood 132:3344. https://doi.org/10.1182/BLOOD-2018-99-117779
Espinoza JL, Kamio K, Lam VQ, Takami A (2021) The impact of NLRP3 activation on hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJMS222111845
Espin-Palazon R, Weijts B, Mulero V, Traver D (2018) Proinflammatory signals as fuel for the fire of hematopoietic stem cell emergence. Trends Cell Biol 28:58–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.TCB.2017.08.003
Fei XM, Wu YJ, Chang Z et al (2007) Co-culture of cord blood CD34+ cells with human BM mesenchymal stromal cells enhances short-term engraftment of cord blood cells in NOD/SCID mice. Cytotherapy 9:338–347. https://doi.org/10.1080/14653240701291638
Frame JM, Long T, Schuster-Kubaczka C et al (2018) Inflammasome-mediated regulation of hematopoiesis in the vertebrate embryo. Blood 132:330. https://doi.org/10.1182/BLOOD-2018-99-117076
Frame J, Long T, Schuster-Kubaczka C, Inflammasome-mediated expansion of the hematopoietic system in the vertebrate embryoInflammasome-mediated expansion of the hematopoietic system in the vertebrate embryo (2019) Exp Hematol 76:S66. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EXPHEM.2019.06.357
Frame JM, Kubaczka C, Long TL et al (2020) Metabolic regulation of inflammasome activity controls embryonic hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell production. Dev Cell 55:133. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DEVCEL.2020.07.015
He X, Gonzalez V, Tsang A et al (2005) Differential gene expression profiling of CD34+ CD133+ umbilical cord blood hematopoietic stem progenitor cells. Stem Cells Dev 14:188–198. https://doi.org/10.1089/SCD.2005.14.188
Huang S, Xu K, Xu S et al (2021) Enumeration of viable CD34+ cells in cord blood using a novel stem cell enumeration kit. J Int Med Res. https://doi.org/10.1177/03000605211055384
Lenkiewicz AM, Adamiak M, Thapa A et al (2019) The Nlrp3 inflammasome orchestrates mobilization of bone marrow-residing stem cells into peripheral blood. Stem Cell Rev Rep 15:391–403. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12015-019-09890-7/FIGURES/5
Li Q, Zhao D, Chen Q et al (2019) Wharton’s jelly mesenchymal stem cell-based or umbilical vein endothelial cell-based serum-free coculture with cytokines supports the ex vivo expansion/maintenance of cord blood hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Stem Cell Res Ther 10:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/S13287-019-1502-8/FIGURES/4
Mousavi SH, Abroun S, Zarrabi M, Ahmadipanah M (2017) The effect of maternal and infant factors on cord blood yield. Pediatr Blood Cancer 64:e26381. https://doi.org/10.1002/PBC.26381
Qu Q, Liu L, Chen G et al (2016) Endothelial progenitor cells promote efficient ex vivo expansion of cord blood–derived hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Cytotherapy 18:452–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCYT.2015.12.005
Ratajczak MZ, Kucia M (2021) The Nlrp3 inflammasome-the evolving story of its positive and negative effects on hematopoiesis. Curr Opin Hematol 28:251–261. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOH.0000000000000658
Ratajczak MZ, Bujko K, Cymer M et al (2020) The Nlrp3 inflammasome as a “rising star” in studies of normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Leukemia 34:1512–1523. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41375-020-0827-8
Shen B, Zhang Y, Dai W et al (2016) Ex-vivo expansion of nonhuman primate CD34+ cells by stem cell factor Sall4B. Stem Cell Res Ther 7:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/S13287-016-0413-1/FIGURES/7
Sica RA, Terzioglu MK, Mahmud D, Mahmud N (2020) Mechanistic basis of ex vivo umbilical cord blood stem progenitor cell expansion. Stem Cell Rev Rep 16:628–638. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12015-020-09981-W/FIGURES/2
Stanevsky A, Shimoni A, Yerushalmi R, Nagler A (2011) Cord blood stem cells for hematopoietic transplantation. Stem Cell Rev Rep 7:425–433. https://doi.org/10.1007/S12015-010-9183-9/TABLES/1
Sutterwala FS, Haasken S, Cassel SL (2014) Mechanism of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1319:82–95. https://doi.org/10.1111/NYAS.12458
Thapa A, Adamiak M, Bujko K et al (2021) Danger-associated molecular pattern molecules take unexpectedly a central stage in Nlrp3 inflammasome–caspase-1-mediated trafficking of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Leukemia 35:2658. https://doi.org/10.1038/S41375-021-01158-9
Wang Z, Zhang S, Xiao Y et al (2020b) NLRP3 inflammasome and inflammatory diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4063562
Wani K, Alharthi H, Alghamdi A et al (2021) Role of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in obesity-mediated metabolic disorders. Int J Environ Res Public Heal 18:511. https://doi.org/10.3390/IJERPH18020511
Wu W, Liu BH, Wan YG et al (2019) [Triptolide inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome activation and ameliorates podocyte epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by high glucose]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 44:5457–5464. https://doi.org/10.19540/J.CNKI.CJCMM.20191114.401
Xie J, Cui Y, Chen X et al (2021) VDAC1 regulates mitophagy in NLRP3 inflammasome activation in retinal capillary endothelial cells under high-glucose conditions. Exp Eye Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.EXER.2021.108640
Yuan Y, Tse KT, Sin FWY et al (2011) Ex vivo amplification of human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in an alginate three-dimensional culture system. Int J Lab Hematol 33:516–525. https://doi.org/10.1111/J.1751-553X.2011.01324.X
Zhang Y, Lv X, Hu Z et al (2017) Protection of Mcc950 against high-glucose-induced human retinal endothelial cell dysfunction. Cell Death Dis. https://doi.org/10.1038/CDDIS.2017.308
Zhou L, Che Z, Zhang X et al (2019) Influence of neonatal gender on cord blood CD34+ cell amplification and gene expression. Exp Ther Med 18:105–118. https://doi.org/10.3892/ETM.2019.7549
Wang J, Shen X, Liu J et al (2020a) High glucose mediates NLRP3 inflammasome activation via upregulation of ELF3 expression. Cell Death Dis. https://doi.org/10.1038/S41419-020-2598-6
Acknowledgements
This study was conducted with the financial support of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences (IRAN) with grant number 3991037.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the local ethics committee of Isfahan University of Medical Sciences (IRAN) and the study has been approved by the appropriate institutional and/or national research ethics committee and have been performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent for publication
All authors have read and approved the final submitted manuscript.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Dadkhah, M., Sharifi, M., Sharifi, M.J. et al. Effects of glucose on the proliferation of human umbilical cord blood hematopoietic stem cells. Cell Tissue Bank 24, 485–494 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-022-10048-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-022-10048-y