Abstract
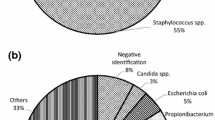
The transmission of microbial infection through tissue allografts is one of the main risks that must be controlled in tissue banks. Therefore, microbiological monitoring controls and validated protocols for the decontamination of tissues during processing have been implemented. This study is based on the evaluation of data from microbiological cultures of arteries (mainly long peripheral arteries) processed in the tissue bank of Valencia (Spain). Donors’ profile, pre- and post-disinfection tissue samples were assessed. The presence of residual antibiotics in disinfected tissues was determined and the antimicrobial potential of these tissues was tested. Our overall contamination rate was 23.69%, with a disinfection rate (after antibiotic incubation) of 87.5%. Most (76.09%) of the microbial contaminants were identified as Gram positive. Arterial allografts collected from body sites affected by prior organ removal showed higher risk of contamination. Only vancomycin was detected as tissue release. The antimicrobial effect on Candida albicans was lower than that for bacterial species. Risk assessment for microbial contamination suggested the donor’s skin and the environment during tissue collection as the main sources for allograft contamination. Antibiotic-disinfected arterial allografts showed antimicrobial potential.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The dataset generated during and/or analyzed during the current study is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bisdas TE, Mattner F, Ott E, Pichlmaier MA, Wilhelmi M, Haverich A, Teebken O (2009) Significance of infection markers and microbiological findings during tissue processing of cryopreserved arterial homografts for the early postoperative course. Vasa 38:365–373. https://doi.org/10.1024/0301-1526.38.4.365
Brubaker S, Lotherington K, Zhao J, Hamilton B, Rockl G, Duong A, Garibaldi A, Simunovic N, Alsop D, Dao D, Bessemer R, Ayeni OR, Bioburden Steering Committee and Tissue Recovery Working Group (2016) Tissue recovery practices and bioburden: a systematic review. Cell Tissue Bank 17:561–571. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-016-9590-5
Buzzi M, Guarino A, Gatto C, Manara S, Dainese L, Polvani G, Tóthová JD (2014) Residual antibiotics in decontaminated human cardiovascular tissues intended for transplantation and risk of falsely negative microbiological analyses. PLOS ONE 9:e112679. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0112679
Camiade C, Goldschmidt P, Koskas F, Ricco JB, Jarraya M, Gerota J, Kieffer E (2001) Optimization of the resistance of arterial allografts to infection: comparative study with synthetic prostheses. Ann Vasc Surg 15:186–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100160010051
de By TMMH, McDonald C, Süßner S, Davies J, Heng WL, Jashari R, Bogers AJJC, Petit P (2017) Validation of microbiological testing in cardiovascular tissue banks: results of a quality round trial. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 52:895–900. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejcts/ezx178
de By TMMH, Parker R, Delmo Walter EM, Hetzer R (2012) Cardiovascular tissue banking in Europe. HSR Proc Intensive Care Cardiovasc Anesth 4:251–260
Díaz Rodríguez R, Van Hoeck B, Mujaj B, Ngakam R, Fan Y, Bogaerts K, Jashari R (2016) Bacteriology testing of cardiovascular tissues: comparison of transport solution versus tissue testing. Cell Tissue Bank 17:211–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-015-9537-2
European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines and HealthCare (EDQM) (2019) Guide to the quality and safety of tissues and cells for human application, 4th edn. Council of Europe, Strasbourg, France
Fan YD, Van Hoeck B, Holovska V, Jashari R (2012) Evaluation of decontamination process of heart valve and artery tissues in European Homograft Bank (EHB): a retrospective study of 1,055 cases. Cell Tissue Bank 13:297–304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-011-9255-3
Furlough CL, Jain AK, Ho KJ, Rodriguez HE, Tomita TM, Eskandari MK (2019) Peripheral artery reconstructions using cryopreserved arterial allografts in infected fields. J Vasc Surg 70:562–568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2018.10.111
Gatto C, Giurgola L, D’Amato Tothova J (2013) A suitable and efficient procedure for the removal of decontaminating antibiotics from tissue allografts. Cell Tissue Bank 14:107–115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-012-9305-5
Germain M, Thibault L, Jacques A, Tremblay J, Bourgeois R (2010) Heart valve allograft decontamination with antibiotics: impact of the temperature of incubation on efficacy. Cell Tissue Bank 11:197–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-009-9155-y
Gross RE, Bill AH Jr, Pierce EC Jr (1949) Methods for preservation and transplantation of arterial grafts; observations on arterial grafts in dogs; report of transplantation of preserved arterial grafts in nine human cases. Surg Gynecol Obstet 88:689–701
Hardy JD (1983) Landmark perspective. Transplantation of blood vessels, organs, and limbs. JAMA 250:954–957
Heng WL, Albrecht H, Chiappini P, Lim YP, Manning L (2013) International heart valve bank survey: a review of processing practices and activity outcomes. J Transplant 2013:163150. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/163150
Heng WL, Madhavan K, Wee P, Seck T, Lim YP, Lim CH (2015) Banking of cryopreserved iliac artery and vein homografts: clinical uses in transplantation. Cell Tissue Bank 16:235–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-014-9469-2
Jashari R, Faucon F, Hoeck BV, Gelas SD, Fan Y, Vandenbulcke S (2011) Determination of residual antibiotics in cryopreserved heart valve allografts. Transfus Med Hemother 38:379–386. https://doi.org/10.1159/000334706
Jashari R, Tabaku M, Van Hoeck B, Cochéz C, Callant M, Vanderkelen A (2007) Decontamination of heart valve and arterial allografts in the European Homograft Bank (EHB): comparison of two different antibiotic cocktails in low temperature conditions. Cell Tissue Bank 8:247–255. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-007-9040-5
Jashari R, Van Hoeck B, Ngakam R, Goffin Y, Fan Y (2013) Banking of cryopreserved arterial allografts in Europe: 20 years of operation in the European Homograft Bank (EHB) in Brussels. Cell Tissue Bank 14:589–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-012-9359-4
Jashari R, Van Hoeck B, Tabaku M, Vanderkelen A (2004) Banking of the human heart valves and the arteries at the European homograft bank (EHB)-overview of a 14-year activity in this International Association in Brussels. Cell Tissue Bank 5:239–251. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-004-1441-0
Kuehnert MJ, Clark E, Lockhart SR, Soll DR, Chia J, Jarvis WR (1998) Candida albicans endocarditis associated with a contaminated aortic valve allograft: implications for regulation of allograft processing. Clin Infect Dis 27:688–691. https://doi.org/10.1086/514944
Leber AL (eds) (2016) Clinical microbiology procedures handbook, 4th edn. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC
Leeming JP, Lovering AM, Hunt CJ (2005) Residual antibiotics in allograft heart valve tissue samples following antibiotic disinfection. J Hosp Infect 60:231–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhin.2004.12.022
Lejay A, Delay C, Girsowicz E, Chenesseau B, Bonnin E, Ghariani MZ, Thaveau F, Georg Y, Geny B, Chakfe N (2017) Cryopreserved cadaveric arterial allograft for arterial reconstruction in patients with prosthetic infection. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 54:636–644. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejvs.2017.07.016
Mallick TK, Mosquera A, Zinderman CE, St Martin L, Wise RP (2012) Reported infections after human tissue transplantation before and after new Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulations, United States, 2001 through June, 2010. Cell Tissue Bank 13:259–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-011-9253-5
Mirabet V, Melero A, Ocete MD, Bompou D, Torrecillas M, Carreras JJ, Valero I, Marqués AI, Medina R, Larrea LR, Arbona C, Garrigues TM, Gimeno C (2018) Effect of freezing and storage temperature on stability and antimicrobial activity of an antibiotic mixture used for decontamination of tissue allografts. Cell Tissue Bank 19:489–497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-018-9693-2
Mirabet V, Salvador C, Valentín A, Escobedo-Lucea C, Navarro L, Gimeno C, Pemán J (2021) Risk assessment of arterial allograft contamination from tissue donors colonized by Candida auris. J Hosp Infect 112:49–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhin.2021.03.003
Paolin A, Romualdi C, Romagnoli L, Trojan D (2017) Analysis of potential factors affecting allografts contamination at retrieval. Cell Tissue Bank 18:539–545. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-017-9667-9
Pirvu A, Alharbi H, Gallet N, Merloz P, Magne JL (2018) Cryopreserved arterial allograft vascular reconstruction for lower limb salvage during sarcoma surgery. ANZ J Surg 88:381–382. https://doi.org/10.1111/ans.13391
Pitt TL, Tidey K, Roy A, Ancliff S, Lomas R, McDonald CP (2014) Activity of four antimicrobial cocktails for tissue allograft decontamination against bacteria and Candida spp. of known susceptibility at different temperatures. Cell Tissue Bank 15:119–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-013-9382-0
Sawa B, Ribeiro VST, Kraft L, Wollmann LC, Pegoraro D, Suss PH, Tuon FF (2019) Risk factors associated with contamination of allograft valves in a tissue bank. Cell Tissue Bank 20:87–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-019-09754-x
Serafini A, Riello E, Trojan D, Cogliati E, Palù G, Manganelli R, Paolin A (2016) Evaluation of new antibiotic cocktails against contaminating bacteria found in allograft tissues. Cell Tissue Bank 17:619–628. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-016-9581-6
Vardanian AJ, Chau A, Quinones-Baldrich W, Lawrence PE (2009) Arterial allograft allows in-line reconstruction of prosthetic graft infection with low recurrence rate and mortality. Am Surg 75:1000–1003
Verscheure D, Gaudric J, Jayet J, Tresson P, Jarraya M, Julia P, Coggia M, Chiche L, Koskas F (2018) Postmortem Retrieval of arterial allografts: preliminary results. Ann Vasc Surg 52:201–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avsg.2018.04.001
Vogt PR, Brunner-LaRocca HP, Lachat M, Ruef C, Turina MI (2002) Technical details with the use of cryopreserved arterial allografts for aortic infection: influence on early and midterm mortality. J Vasc Surg 35:80–86. https://doi.org/10.1067/mva.2002
Zahra S, Galea G, Jashari R, Petit P, de By TMMH (2019) Validation of microbiological testing in cardiovascular tissue banks: results of a second international quality-round trial. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 38:1481–1490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-019-03576-1
Acknowledgements
We want to thank Dr. Andrés Sanz, for his comments on data organization, and Mr. Jack Paton for English language editing.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VM conception and design, manuscript writing, data analysis and interpretation; MA, JB provision of study material, data collection, data analysis and interpretation, manuscript revision; MPB, MDO, AM, LA, AJG, JP material preparation, data analysis and interpretation, manuscript revision; SM, CEL, data analysis and interpretation, statistics, manuscript revision; LL, data analysis and interpretation, manuscript revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The study complied with the policies of the institutional review.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Consent to publication
All the authors reviewed this study and agreed to publish this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirabet, V., Arrébola, M., Briones, J. et al. Microbiological assessment of arterial allografts processed in a tissue bank. Cell Tissue Bank 22, 539–549 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-021-09951-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10561-021-09951-7