Abstract
Background
Patients with mixed dyslipidemia characterized by elevated low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), elevated triglycerides (TG), and reduced high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) often require combination therapy to improve multiple lipid and nonlipid parameters. This phase 3, multicenter, randomized, double-blind study evaluated the efficacy and safety of rosuvastatin 5 mg coadministered with fenofibric acid 135 mg in patients with mixed dyslipidemia.
Methods
A total of 760 patients with TG ≥ 150 mg/dL, HDL-C <40 mg/dL (<50 mg/dL for women), and LDL-C ≥ 130 mg/dL were randomized for a 12-week treatment period to rosuvastatin 5 mg, fenofibric acid 135 mg, or rosuvastatin 5 mg + fenofibric acid 135 mg. The primary efficacy comparisons were mean percentage changes in HDL-C and TG (rosuvastatin + fenofibric acid vs. rosuvastatin monotherapy), and LDL-C (rosuvastatin + fenofibric acid vs. fenofibric acid monotherapy).
Results
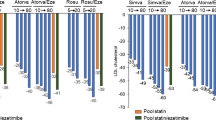
Treatment with rosuvastatin + fenofibric acid resulted in statistically significant greater improvements in HDL-C (23.0% vs. 12.4%; P < 0.001) and TG (–40.3% vs. –17.5%; P < 0.001), compared with rosuvastatin monotherapy; and LDL-C (–28.7% vs. –4.1%; P < 0.001), compared with fenofibric acid monotherapy. All secondary efficacy variables improved with combination therapy. Combination therapy was generally well tolerated with a safety profile consistent with individual monotherapies. No unexpected muscle, hepatic, or renal safety signals were identified with combination therapy versus individual monotherapies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, rosuvastatin 5 mg + fenofibric acid 135 mg resulted in comprehensive improvements in the lipid profile of patients with mixed dyslipidemia without unanticipated adverse events.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hokanson JE, Austin MA. Plasma triglyceride level is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease independent of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level: a meta-analysis of population-based prospective studies. J Cardiovasc Risk. 1996;3:213–9.
Sarwar N, Danesh J, Eiriksdottir G, et al. Triglycerides and the risk of coronary heart disease: 10, 158 incident cases among 262, 525 participants in 29 Western prospective studies. Circulation. 2007;115:450–8.
Assmann G, Schulte H. Relation of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and triglycerides to incidence of atherosclerotic coronary artery disease (the PROCAM experience). Prospective Cardiovascular Munster study. Am J Cardiol. 1992;70:733–7.
Assmann G, Schulte H, Cullen P, et al. Assessing risk of myocardial infarction and stroke: new data from the Prospective Cardiovascular Munster (PROCAM) study. Eur J Clin Invest. 2007;37:925–32.
Third Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP) Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults (Adult Treatment Panel III) final report. Circulation. 2002;106:3143–421.
Jones PH, Davidson MH, Kashyap ML, et al. Efficacy and safety of ABT-335 (fenofibric acid) in combination with rosuvastatin in patients with mixed dyslipidemia: a phase 3 study. Atherosclerosis. 2009;204:208–15.
Jones PH, Bays HE, Davidson MH, et al. Evaluation of a new formulation of fenofibric acid, ABT-335, co-administered with statins: study design and rationale of a phase III clinical programme. Clin Drug Investig. 2008;28:625–34.
Pasternak RC, Smith Jr SC, Bairey-Merz CN, et al. ACC/AHA/NHLBI clinical advisory on the use and safety of statins. Circulation. 2002;106:1024–8.
Goldberg AC, Bays HE, Ballantyne CM, et al. Efficacy and safety of ABT-335 (fenofibric acid) in combination with atorvastatin in patients with mixed dyslipidemia. Am J Cardiol. 2009;103:515–22.
Mohiuddin SM, Pepine CJ, Kelly MT, et al. Efficacy and safety of ABT-335 (fenofibric acid) in combination with simvastatin in patients with mixed dyslipidemia: a phase 3, randomized, controlled study. Am Heart J. 2009;157:195–203.
Roth EM, McKenney JM, Kelly MT, et al. Efficacy and safety of rosuvastatin and fenofibric acid combination therapy versus simvastatin monotherapy in patients with hypercholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia: a randomized, double-blind study. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2010;10:175-86.
Durrington PN, Tuomilehto J, Hamann A, et al. Rosuvastatin and fenofibrate alone and in combination in type 2 diabetes patients with combined hyperlipidaemia. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2004;64:137–51.
Grundy SM, Vega GL, Yuan Z, et al. Effectiveness and tolerability of simvastatin plus fenofibrate for combined hyperlipidemia (the SAFARI trial). Am J Cardiol. 2005;95:462–8.
Koh KK, Quon MJ, Han SH, et al. Additive beneficial effects of fenofibrate combined with atorvastatin in the treatment of combined hyperlipidemia. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;45:1649–53.
Ridker PM, Danielson E, Fonseca FA, et al. Rosuvastatin to prevent vascular events in men and women with elevated C-Reactive protein. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2195–207.
Bays HE, Jones PH, Mohiuddin SM, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of fenofibric acid in combination with statin therapy for the treatment of patients with mixed dyslipidemia. J Clin Lipidol. 2008;2:426–35.
Acknowledgments
We thank all investigators, study coordinators, and patients who participated in the study. Aditya Lele, Chuya Yang, and Hsiaoming Sun, of Abbott provided assistance with statistical analyses; Lura Morris, of Abbott provided assistance with clinical study management; and Geeta Thakker and Darryl Sleep, of Abbott provided assistance with medical writing and manuscript preparation.
Eli Roth has received clinical trial funding from Abbott, AstraZeneca, and Merck; is a consultant for Abbott; and serves on the speaker’s bureau for AstraZeneca, Merck, and Schering-Plough. Robert Rosenson is a consultant for Abbott. Dawn Carlson, Sandra Fukumoto, Carolyn Setze, James Stolzenbach, and Laura Williams are employees and stockholders of Abbott. James Blasetto and Nardev Khurmi are AstraZeneca employees. Abbott and AstraZeneca provided financial support for the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roth, E.M., Rosenson, R.S., Carlson, D.M. et al. Efficacy and Safety of Rosuvastatin 5 mg in Combination with Fenofibric Acid 135 mg in Patients with Mixed Dyslipidemia – A Phase 3 Study. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 24, 421–428 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-010-6266-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-010-6266-4