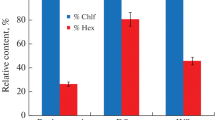
Based on the analytical hierarchic procedure developed by Saati, an evaluation has been made of the methods of detoxification (alternatives) of oil-containing soils (OCS), making a comparison of the weights of criteria in the absence of comprehensive information, to justify the selection of the most efficient and economically suitable method of detoxification of oil-containing soils. It turned out that the most efficient method of detoxification of oil-containing soils is chemical method, provided the hydrocarbons are extracted from them beforehand. Experiments have been conducted to determine the influence of oil hydrocarbons on the degree of extraction: amount of oil products, solvent/OCS ratio, process temperature, etc.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Saati, Adoption of Solutions. Method of Analysis of Hierarchies [Russian translation from English], Radio i Svyaz, Moscow (1993).
R. Sh. Sufiyanov, “Influence of reagents on efficiency of chemical detoxification of oil-containing soils,” Zash. Okruzh. Sredy Neftegaz. Kompl., No. 4, 12–16 (2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Khimicheskoe i Neftegazovoe Mashinostroenie, No. 6, pp. 29–31, June, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sufiyanov, R.S., Katalymov, A.V. & Sinyakov, O.A. Selection of a method of detoxification of oil-containing soils. Chem Petrol Eng 47, 404 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10556-011-9483-1
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10556-011-9483-1