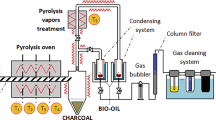
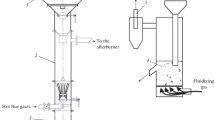
An experimental plant for optimization of production regimes for the pyrolysis of biomass and wastes of organogenic origin with an output of 500 kg/day is proposed. All equipment of the plant is grouped in a single production module. Processes involving catalytic pyrolysis of peat and refined products of used truck tires are tested on the plant for the production of gaseous fuel. The experimental industrial tests demonstrate the plant’s high efficiency, and the expediency of catalytic pyrolysis for utilization of organogenic wastes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. V. Bridgwater and G. V. C. Peacocke, “Fast pyrolysis processes for biomass,” Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, No. 4, 1–73 (2000).
S. Yaman, “Pyrolysis of biomass to produce fuels and chemical feedstocks,” Energy Convers. Manag., No. 45, 651–671 (2004).
B. N. Kuznetsov, “Production of liquid fuels and their components from lignen biomass,” J. Ross. Khim. Obsh. Mendeleeva, 47, No. 6, 83–91 (2003).
W. L. Van de Kamp and J. P. Smart, “Evaluation of the combustion characteristics of pyrolytic oils derived from biomass,” in: Proc. of Energy from Biomass Contractors Meeting, edited by G. Grassi, P. Moncada, and H. Zibetta, CEC DG XII Biomass Unit (F/4) (1991), pp. 317–319.
A. V. Bridgwater and G. V. C. Peacocke, “Engineering developments in fast pyrolysis for bio-oils,” in: Proc. of Biomass Pyrolysis Oil Properties and Combustion Meeting, edited by T. A. Milne, NREL (1994), pp. 110–127.
J. P. Diebold and A. V. Bridgwater, “Overview of fast pyrolysis of biomass for the production of liquid fuels,” in: Developments in Thermochemical Biomass Conversion, edited by A. V. Bridgwater and D. G. B. Boocock, Blackie (1997), pp. 5–26.
Yu. Yu. Kosivtsov et al., “The development of the method of low-temperature peat pyrolysis on the basis of alumosilicate catalytic system,” Chem. Engin. J., 134, No. 1–3, 162–167 (2007).
E. M. Sulman,Yu. Yu. Kosivtsov, et al., “Influence of alumosilicate materials on the peat low-temperature pyrolysis and gas formation,” Chem. Engin. J., 154, No. 1–3, 355–360 (2009).
Yu. Yu. Kosivtsov, Yu. V. Lugovoi, and E. M. Sulman, “Catalytic pyrolysis of the polymeric cord of worn truck tires in the presence of metal chlorides of the iron subgroup,” Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved.: Khimiya Khim. Tekhnol., 51, No. 12, 73–76 (2008).
V. G. Sister, E. M. Sulman,Yu. Yu. Kosivtsov, E. M. Ivannikova, and Yu. V. Lugovoi, “Pyrolysis of polymeric materials in the presence of metal chlorides of the iron subgroup,” Khim. Neftegaz. Mashinostr., No. 6, 36–38 (2010).
A. G. Gayubo, A. T. Aguayo, A. Atutxa, R. Aguado, and J. Bilbao, “Transformation of oxygenate components of biomass pyrolysis oil on a HZSM-5 Zeolite. I. Alcohols and Phenols,” Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 43, No. 11, 2610–2618 (2004).
H. Yang, R. Yan, H. Chen, C. Zheng, D. H. Lee, and D. T. Liang, “In-depth investigation of biomass pyrolysis based on three major components: hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignen,” Energy Fuels, 20, No. 1, 388–393 (2006).
C. J. Gomez, J. J. Manya, E. Velo, and L. Puigjaner, “Further application of a revisited summative model for kinetics of biomass pyrolysis,” Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 43, No. 4, 901–906 (2004).
J. B. Wooten, J. I. Seeman, and M. R. Hajaligol, “Observation and characterization of cellulose pyrolysis intermediates by 13C CPMAS NMR. A new mechanistic model,” Energy Fuels, 18, No. 1, 1–15 (2004).
H. Yang, R. Yan, H. Chen, C. Zheng, D. H. Lee, and D. T. Liang, “In-depth investigation of biomass pyrolysis based on three major components: hemicellulose, cellulose, and lignen,” Energy Fuels, 20, No. 1, 388–393 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Khimicheskoe i Neftegazovoe Mashinistroenie, No. 6, pp. 9–11, June, 2011.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kosivtsov, Y.Y., Sister, V.G., Ivannikova, E.M. et al. Experimental industrial plant for catalytic pyrolysis of biomass. Chem Petrol Eng 47, 378 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10556-011-9477-z
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10556-011-9477-z