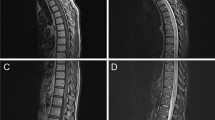
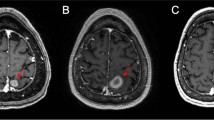
Abstract
Both the onset of various malignancies as well as the treatment of cancer can lead to neurologic symptoms which can be difficult to diagnose. In this review, we highlight the varied ways in which neurologic sequelae of cancer and its treatment manifest in children. Initial neurologic presentation may be secondary to mass effect or to immune-mediated paraneoplastic syndromes. Treatment effects on the nervous system may arise from surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, or bone marrow transplantation. In addition, the rapidly expanding field of immunotherapies for cancer has generated numerous new approaches to eradicating cancer including monoclonal antibodies, checkpoint inhibitors, and chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CAR-T cells), which have neurologic side effects mediated by immune responses that are also being recognized. Here we review common consult questions to the neurologist and our general approach to these scenarios including altered mental status, headaches, seizures, and sensorimotor complaints, considering the multifactorial nature of each.
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
12 February 2020
The authors have noticed a typographical error in the published article.
References
Dobrovoljac, M., Hengartner, H., Boltshauser, E., & Grotzer, M. (2002). Delay in the diagnosis of paediatric brain tumours. Eur J Pediatr, 161(12), 663–667. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-002-1088-4.
Reulecke, B. C., Erker, C. G., Fiedler, B. J., Niederstadt, T.-U., & Kurlemann, G. (2008). Brain tumors in children: Initial symptoms and their influence on the time span between symptom onset and diagnosis. J Child Neurol, 23(2), 178–183. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073807308692.
Ullrich, N. J. (2009). Neurologic sequelae of brain tumors in children. J Child Neurol, 24(11), 1446–1454. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073809342491.
Wells, E. M., & Packer, R. J. (2015). Pediatric brain tumors. CONTINUUM: Lifelong Learning in Neurology, 21(2), 373–396. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.CON.0000464176.96311.d1.
Malbari, F., Gershon, T. R., Garvin, J. H., Allen, J. C., Khakoo, Y., Levy, A. S., & Dunkel, I. J. (2016). Psychiatric manifestations as initial presentation for pediatric CNS germ cell tumors, a case series. Childs Nerv Syst, 32(8), 1359–1362. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-016-3145-8.
Taylor M, Couto-Silva, A-C, Adan L, Trivin C, Sainte-Rose C, Zerah M, … Brauner R (2012). Hypothalamic-pituitary lesions in pediatric patients: endocrine symptoms often precede neuro-ophthalmic presenting symptoms. J Pediatr, 161(5), 855–63. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.05.014.
Pretell-Mazzini, J., Chikwava, K. R., & Dormans, J. P. (2012). Low back pain in a child associated with acute onset cauda equina syndrome: a rare presentation of an aggressive vertebral hemangioma: a case report. J Pediatr Orthop, 32(3), 271–276. https://doi.org/10.1097/BPO.0b013e318247195a.
Mora, J., & Wollner, N. (1999). Primary epidural non-Hodgkin lymphoma: spinal cord compression syndrome as the initial form of presentation in childhood non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Med Pediatr Oncol, 32(2), 102–105. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-911X(199902)32:2<102::AID-MPO6>3.0.CO;2-Y.
Da Silva, A. N., Lopes, M. B., & Schiff, D. (2006). Rare pathological variants and presentations of primary central nervous system lymphomas. Neurosurg Focus, 21(5), E1–E7. https://doi.org/10.3171/foc.2006.21.5.8.
Wilson, R. E., Oleszek, J. L., & Clayton, G. H. (2007). Pediatric spinal cord tumors and masses. J Spinal Cord Med, 30(sup1), S15–S20. https://doi.org/10.1080/10790268.2007.11753963.
Ma, G. M., Chow, J. S., & Taylor, G. A. (2019). Review of paraneoplastic syndromes in children. Pediatr Radiol, 49(4), 534–550. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-019-04371-y.
Nikolic, D. M., Nikolic, A. V., Lavrnic, D. V., Medjo, B. P., & Ivanovski, P. I. (2012). Childhood-onset myasthenia gravis with thymoma. Pediatr Neurol, 46(5), 329–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2012.02.025.
Wells, E. M., & Dalmau, J. (2011). Paraneoplastic neurologic disorders in children. Curr Neurol Neuroscie Rep, 11(2), 187–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-010-0169-4.
Dalmau, J., & Rosenfeld, M. R. (2008). Paraneoplastic syndromes of the CNS. Lancet Neurol, 7(4), 327–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70060-7.
Graus, F., Delattre, J. Y., Antoine, J. C., Dalmau, J., Giometto, B., Grisold, W., Honnorat, J., Smitt, P. S., Vedeler Ch, Verschuuren, J. J., Vincent, A., & Voltz, R. (2004). Recommended diagnostic criteria for paraneoplastic neurological syndromes. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 75(8), 1135–1140. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2003.034447.
Pranzatelli, M. R., Tate, E. D., Swan, J. A., Travelstead, A. L., Colliver, J. A., Verhulst, S. J., Crosley, C. J., Graf, W. D., Joseph, S. A., Kelfer, H. M., & Raju, G. P. (2010). B cell depletion therapy for new-onset opsoclonus-myoclonus. Mov Disord, 25(2), 238–242. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.22941.
Shams’ili, S., de Beukelaar, J., Gratama, J. W., Hooijkaas, H., van den Bent, M., van’t Veer, M., & Sillevis Smitt, P. (2006). An uncontrolled trial of rituximab for antibody associated paraneoplastic neurological syndromes. J Neurol, 253(1), 16–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-005-0882-0.
Honnorat, J., Didelot, A., Karantoni, E., Ville, D., Ducray, F., Lambert, L., Deiva, K., Garcia, M., Pichit, P., Cavillon, G., Rogemond, V., DeLattre, J., & Tardieu, M. (2013). Autoimmune limbic encephalopathy and anti-Hu antibodies in children without cancer. Neurology, 80(24), 2226–2232. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e318296e9c3.
Florance-Ryan, N., & Dalmau, J. (2010). Update on anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis in children and adolescents. Curr Opin Pediatr, 22(6), 739–744. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOP.0b013e3283402d2f.
Lebas, A., Husson, B., Didelot, A., Honnorat, J., & Tardieu, M. (2010). Expanding spectrum of encephalitis with NMDA receptor antibodies in young children. J Child Neurol, 25(6), 742–745. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073809343319.
Haberlandt, E., Bast, T., Ebner, A., Holthausen, H., Kluger, G., Kravljanac, R., Kröll-Seger, J., Kurlemann, G., Makowski, C., Rostasy, K., Tuschen-Hofstätter, E., Weber, G., Vincent, A., & Bien, C. G. (2011). Limbic encephalitis in children and adolescents. Arch Dis Child, 96(2), 186–191. https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.2010.183897.
Nosadini M, Toldo I, Tascini B, Bien CG, Parmeggiani L, De Gaspari P, … Sartori S (2019). LGI1 and CASPR2 autoimmunity in children: systematic literature review and report of a young girl with Morvan syndrome. J Neuroimmunol, 335, 577008. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JNEUROIM.2019.577008.
Nikolaus, M., Jackowski-Dohrmann, S., Prüss, H., Schuelke, M., & Knierim, E. (2018). Morvan syndrome associated with CASPR2 and LGI1 antibodies in a child. Neurology, 90(4), 183–185. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000004861.
Allen, N. M., McKeon, A., O’Rourke, D. J., O’Meara, A., & King, M. D. (2012). Excessive blinking and ataxia in a child with occult neuroblastoma and voltage-gated potassium channel antibodies. Pediatrics, 129(5), e1348–e1352. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2011-2690.
Rosenfeld, M. R. (2018). Paraneoplastic syndromes affecting the spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia. Up To Date, 12, 1–12.
Sharp, L., & Vernino, S. (2012). Paraneoplastic neuromuscular disorders. Muscle Nerve, 46(6), 839–840. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.23502.
Amini, A., Lang, B., Heaney, D., & Irani, S. R. (2016). Multiple sequential antibody-associated syndromes with a recurrent mutated neuroblastoma. Neurology, 87(6), 634–636. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000002945.
Younes-Mhenni S, Janier MF, Cinotti L, Antoine JC, Tronc F, Cottin V, … Honnorat J (2004). FDG-PET improves tumour detection in patients with paraneoplastic neurological syndromes. Brain, 127(10), 2331–2338. doi:https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awh247.
Linke, R., Schroeder, M., Helmberger, T., & Voltz, R. (2004). Antibody-positive paraneoplastic neurologic syndromes: Value of CT and PET for tumor diagnosis. Neurology, 63(2), 282–286. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.WNL.0000129983.06983.4E.
Blaes, F., Pike, M. G., & Lang, B. (2008). Autoantibodies in childhood opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome. J Neuroimmunol, 201, 221–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2008.05.033.
van Vuurden, D. G., Plötz, F. B., de Jong, M., Bokenkamp, A., & van Wijk, J. A. E. (2005). Therapeutic total plasma exchange in a child with neuroblastoma-related anti-Hu syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol, 20(11), 1655–1656. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-2004-8.
Sillevis Smitt, P., Grefkens, J., De Leeuw, B., Van Den Bent, M., Van Putten, W., Hooijkaas, H., & Vecht, C. (2002). Survival and outcome in 73 anti-Hu positive patients with paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis/sensory neuronopathy. J Neurol, 249(6), 745–753. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-002-0706-4.
Chong, C., Soon, D. T. L., & Yeo, L. L. L. (2019). Opsoclonus - myoclonus syndrome. J Clin Neurosci, 61, 254–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2018.10.099.
Tate, E. D., Allison, T. J., Pranzatelli, M. R., & Verhulst, S. J. (2005). Neuroepidemiologic trends in 105 US cases of pediatric opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome. J Pediatr Oncol Nurs, 22(1), 8–19. https://doi.org/10.1177/1043454204272560.
Morales La Madrid, A., Rubin, C. M., Kohrman, M., Pytel, P., & Cohn, S. L. (2012). Opsoclonus-myoclonus and anti-Hu positive limbic encephalitis in a patient with neuroblastoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer, 58(3), 472–474. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.23131.
Fisher, P. G., Wechsler, D. S., & Singer, H. S. (1994). Anti-Hu antibody in a neuroblastoma-associated paraneoplastic syndrome. Pediatr Neurol, 10(4), 309–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/0887-8994(94)90127-9.
Wilfong, A. A., Parke, J. T., & McCrary, J. A. (1992). Opsoclonus-myoclonus with Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome and hepatoblastoma. Pediatr Neurol, 8(1), 77–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/0887-8994(92)90060-c.
Swart, J. F., De Kraker, J., & Van der Lely, N. (2002). Metaiodobenzylguanidine total-body scintigraphy required for revealing occult neuroblastoma in opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome. Eur J Pediatr, 161(5), 255–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-002-0934-8.
McGarvey, C. K., Applegate, K., Lee, N. D., & Sokol, D. K. (2006). False-positive metaiodobenzylguanidine scan for neuroblastoma in a child with opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome treated with adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). J Child Neurol, 21(7), 606–610. https://doi.org/10.1177/08830738060210070801.
Brunklaus, A., Pohl, K., Zuberi, S. M., & De Sousa, C. (2012). Investigating neuroblastoma in childhood opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome. Arch Dis Child. https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.2010.204792.
Baizabal-Carvallo, J. F., Stocco, A., Muscal, E., & Jankovic, J. (2013). The spectrum of movement disorders in children with anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis. Mov Disord, 28(4), 543–547. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25354.
Mohammad, S. S., Fung, V. S. C., Grattan-Smith, P., Gill, D., Pillai, S., Ramanathan, S., et al. (2014). Movement disorders in children with anti-NMDAR encephalitis and other autoimmune encephalopathies. Mov Disord, 29(12), 1539–1542. https://doi.org/10.1002/mds.25999.
Yeshokumar, A. K., Sun, L. R., Klein, J. L., Baranano, K. W., & Pardo, C. A. (2016). Gait disturbance as the presenting symptom in young children with anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis. Pediatrics, 138(3), e20160901. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2016-0901.
Darnell, R. B. (2007). NMDA receptor as a target in paraneoplastic encephalitis. Ann Neurol, 61(1), 3–4. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.21074.
Dalmau, J., Tüzün, E., Wu, H., & Masjuan, J. (2007). Paraneoplastic anti–N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis associated with ovarian teratoma. Ann Neurol, 61(1), 25–36.
Dalmau, J., Gleichman, A. J., Hughes, E. G., Rossi, J. E., Peng, X., Lai, M., Dessain, S. K., Rosenfeld, M. R., Balice-Gordon, R., & Lynch, D. R. (2008). Anti-NMDA-receptor encephalitis: case series and analysis of the effects of antibodies. Lancet Neurol, 7(12), 1091–1098. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(08)70224-2.
Kunstreich, M., Kreth, J. H., Oommen, P. T., Schaper, J., Karenfort, M., Aktas, O., Tibussek, D., Distelmaier, F., Borkhardt, A., & Kuhlen, M. (2017). Paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis with SOX1 and PCA2 antibodies and relapsing neurological symptoms in an adolescent with Hodgkin lymphoma. Eur J Paediatr Neurol, 21(4), 661–665. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpn.2017.03.005.
Chan, D. W. S., Thomas, T., Lim, M., Ling, S., Woodhall, M., & Vincent, A. (2017). Focal status epilepticus and progressive dyskinesia: a novel phenotype for glycine receptor antibody-mediated neurological disease in children. Eur J Paediatr Neurol, 21(2), 414–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpn.2016.08.013.
Spatola, M., Sabater, L., Planagumà, J., Martínez-Hernandez, E., Armangué, T., Prüss, H., Iizuka, T., Caparó Oblitas, R. L., Antoine, J. C., Li, R., Heaney, N., Tubridy, N., Munteis Olivas, E., Rosenfeld, M. R., Graus, F., & Dalmau, J. (2018). Encephalitis with mGluR5 antibodies: symptoms and antibody effects. Neurology, 90(22), e1964–e1972. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000005614.
Rudock R, Helis J, & Mar SS (2017). Anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase limbic encephalitis. In Pediatric demyelinating diseases of the central nervous system and their mimics (pp. 67–73). Springer International Publishing. doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-61407-6_9.
Gresa-Arribas, N., Titulaer, M. J., Torrents, A., Aguilar, E., McCracken, L., Leypoldt, F., Gleichman, A. J., Balice-Gordon, R., Rosenfeld, M. R., Lynch, D., Graus, F., & Dalmau, J. (2014). Antibody titres at diagnosis and during follow-up of anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis: a retrospective study. Lancet Neurol, 13(2), 167–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70282-5.
Rosenfeld, M. R., & Dalmau, J. (2011). Anti-NMDA-receptor encephalitis and other synaptic autoimmune disorders. Curr Treat Options Neurol, 13(3), 324–332. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-011-0116-y.
Gungor, S., Kilic, B., Arslan, M., Ozgen, U., & Dalmau, J. (2017). Hodgkin’s lymphoma associated with paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration in children: a case report and review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst, 33(3), 509–512. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-016-3284-y.
Nakamura, T., Morimoto, N., Goto, F., Shioda, Y., Hoshino, H., Kubota, M., & Taiji, H. (2012). Langerhans cell histiocytosis with disequilibrium. Auris Nasus Larynx, 39(6), 627–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anl.2012.01.003.
Emir, S., Tezer Kutluk, M., Göğüş, S., & Büyükpamukçu, M. (2000). Paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration and horner syndrome: association of two uncommon findings in a child with hodgkin disease. Am J Pediatr Hematol/Oncol, 22(2), 158–161. https://doi.org/10.1097/00043426-200003000-00015.
Greenlee, J. E. (2013). Treatment of paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration. Curr Treat Options Neurol, 15(2), 185–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-012-0215-4.
Ojeda, V. J., & Ojeda, V. J. (1984). Necrotizing myelopathy associated with malignancy. a clinicopathologic study of two cases and literature review. Cancer, 53(5), 1115–1123. https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(19840301)53:5<1115::aid-cncr2820530517>3.0.co;2-w.
Pittock, S. J., & Lennon, V. A. (2008). Aquaporin-4 autoantibodies in a paraneoplastic context. Arch Neurol, 65(5), 629–632. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.65.5.629.
de Buys Roessingh, A. S., Loriot, M. H., Wiesenauer, C., & Lallier, M. (2009). Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome revealing an abdominal neuroblastoma. J Pediatr Surg, 44(8), E5–E7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2009.04.023.
Sun, L. R., & Cooper, S. (2018). Neurological complications of the treatment of pediatric neoplastic disorders. Pediatr Neurol, 85, 33–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2018.05.011.
Küper, M., & Timmann, D. (2013). Cerebellar mutism. Brain Lang, 127(3), 327–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BANDL.2013.01.001.
Neil, E. C., Hanmantgad, S., & Khakoo, Y. (2016). Neurological complications of pediatric cancer. J Child Neurol, 31(12), 1412–1420. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073815620673.
Newton HB (2012). Neurological complications of chemotherapy to the central nervous system. In Handbook of clinical neurology (Vol. 105, pp. 903–916). Elsevier B.V. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-53502-3.00031-8.
Staff, N. P, Grisold, A., Grisold, W., & Windebank, A. J. (2017). Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a current review. Ann Neurol, 81(6), 772–781. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.24951.
Schiff, D., Wen, P. Y., & van den Bent, M. J. (2009). Neurological adverse effects caused by cytotoxic and targeted therapies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol, 6(10), 596–603. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2009.128.
Wick, W., Hertenstein, A., & Platten, M. (2016). Neurological sequelae of cancer immunotherapies and targeted therapies. Lancet Oncol, 17(12), e529–e541. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30571-X.
Cordelli, D. M., Masetti, R., Zama, D., Toni, F., Castelli, I., Ricci, E., Franzoni, E., & Pession, A. (2017). Central nervous system complications in children receiving chemotherapy or hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Front Pediatr, 5, 105. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2017.00105.
Carson KR, Newsome SD, Kim EJ, Wagner-Johnston ND, Von Geldern G, Moskowitz CH, … Bennett CL (2014). Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy associated with brentuximab vedotin therapy: a report of 5 cases from the Southern Network on Adverse Reactions (SONAR) project. Cancer, 120(16), 2464–2471. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.28712.
Toxicology and Environmental Health Information Program (TEHIP). (2019). TOXNET. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved November 26, 2019, from https://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/index.html Accessed 12/2/2019.
Aspesberro, F., Milewski, L. S., & Brogan, T. V. (2014). Acute central nervous system complications in pediatric hematopoietic stem cell patients. J Pediatr Intensive Care, 3, 169–181. https://doi.org/10.3233/PIC-14100.
Tibussek D, Natesirinilkul R, Sun LR, Wasserman, B. A., Brandao LR, deVeber G, … deVeber G (2016). Severe cerebral vasospasm and childhood arterial ischemic stroke after intrathecal cytarabine. Pediatrics, 137(2), e20152143–e20152143. doi:https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2015-2143.
Sait, S., & Modak, S. (2017). Anti-GD2 immunotherapy for neuroblastoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther, 17(10), 889–904. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737140.2017.1364995.
Han, R., Yang, Y. M., Dietrich, J., Luebke, A., Mayer-Pröschel, M., & Noble, M. (2008). Systemic 5-fluorouracil treatment causes a syndrome of delayed myelin destruction in the central nervous system. J Biol, 7(4), 12. https://doi.org/10.1186/jbiol69.
Ewins, K., Malone, A., Phelan, E., Webb, D., McHugh, J. C., & Smith, O. (2017). Nelarabine-induced peripheral and central neurotoxicity: can sequential MRI brain imaging help to define its natural history? Br J Haematol, 179(2), 294–297. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.14921.
Judge, C., Moheb, N., & Melinosky, C. (2019). Nilotinib-associated demyelinating disease. Neurology, 92(Suppl 15), P2.2–P093.
Dombi E, Baldwin A, Marcus LJ, Fisher MJ, Weiss B, Kim A, … Widemann BC (2016). Activity of selumetinib in neurofibromatosis type 1-related plexiform neurofibromas. N Eng J Med, 375(26), 2550–2560. doi:https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1605943.
Grace, R. F., Dahlberg, S. E., Neuberg, D., Sallan, S. E., Connors, J. M., Neufeld, E. J., Deangelo, D. J., & Silverman, L. B. (2011). The frequency and management of asparaginase-related thrombosis in paediatric and adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia treated on Dana-Farber Cancer Institute consortium protocols. Br J Haematol, 152(4), 452–459. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2010.08524.x.
Mitchell LG, Andrew M, Abshire T, Halton J, Anderson R, Cherrick I, … Way C (2003). A prospective cohort study determining the prevalence of thrombotic events in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and a central venous line who are treated with l-asparaginase: results of the Prophylactic antithrombin Replacement in Kids with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Treated with Asparaginase (PARKAA) study. Cancer, 97(2), 508–516. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.11042.
Caruso, V., Iacoviello, L., Di Castelnuovo, A., Storti, S., Mariani, G., De Gaetano, G., & Donati, M. B. (2006). Thrombotic complications in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a meta-analysis of 17 prospective studies comprising 1752 pediatric patients. Blood. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2006-04-015511.
Greiner J, Schrappe M, Claviez A, Zimmermann M, Niemeyer C, Kolb R, … Möricke A (2019). THROMBOTECT – a randomized study comparing low molecular weight heparin, antithrombin and unfractionated heparin for thromboprophylaxis during induction therapy of acute lymphoblastic leukemia in children and adolescents. Haematologica, 104(4), 756–765. doi:https://doi.org/10.3324/haematol.2018.194175.
Malhotra, P., Jain, S., & Kapoor, G. (2018). Symptomatic cerebral sinovenous thrombosis associated with l-asparaginase in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a single institution experience over 17 years. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol, 40(7), e450–e453. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPH.0000000000001127.
Nicolao, P., & Giometto, B. (2003). Neurological toxicity of ifosfamide. Oncology, 65(Suppl 2), 11–16. https://doi.org/10.1159/000073352.
Taupin, D., Racela, R., & Friedman, D. (2014). Ifosfamide chemotherapy and nonconvulsive status epilepticus: case report and review of the literature. Clin EEG Neurosci, 45(3), 222–225. https://doi.org/10.1177/1550059413500777.
Bhojwani, D., Sabin, N. D., Pei, D., Yang, J. J., Khan, R. B., Panetta, J. C., Krull, K. R., Inaba, H., Rubnitz, J. E., Metzger, M. L., Howard, S. C., Ribeiro, R. C., Cheng, C., Reddick, W. E., Jeha, S., Sandlund, J. T., Evans, W. E., Pui, C. H., & Relling, M. V. (2014). Methotrexate-induced neurotoxicity and leukoencephalopathy in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol, 32(9), 949–959. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2013.53.0808.
Inaba, H., Khan, R. B., Laningham, F. H., Crews, K. R., Pui, C. H., & Daw, N. C. (2008). Clinical and radiological characteristics of methotrexate-induced acute encephalopathy in pediatric patients with cancer. Ann Oncol, 19(1), 178–184. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdm466.
Cheung, Y. T., Sabin, N. D., Reddick, W. E., Bhojwani, D., Liu, W., Brinkman, T. M., Glass, J. O., Hwang, S. N., Srivastava, D., Pui, C. H., Robison, L. L., Hudson, M. M., & Krull, K. R. (2016). Leukoencephalopathy and long-term neurobehavioural, neurocognitive, and brain imaging outcomes in survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia treated with chemotherapy: a longitudinal analysis. Lancet Haematol, 3(10), 456–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2352-3026(16)30110-7.
Koh, S., Nelson, M. D., Kovanlikaya, A., & Chen, L. S. (1999). Anterior lumbosacral radiculopathy after intrathecal methotrexate treatment. Pediatr Neurol, 21(2), 576–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0887-8994(99)00040-5.
Junna, M. R., & Rabinstein, A. A. (2007). Tacrolimus induced leukoencephalopathy presenting with status epilepticus and prolonged coma. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 78(12), 1410–1411. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp.2007.121806.
Antoine, J. C., & Camdessanché, J. P. (2007). Peripheral nervous system involvement in patients with cancer. Lancet Neurol, 6(1), 75–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(06)70679-2.
Tang, J.-H., Tian, J.-M., Sheng, M., Hu, S.-Y., Li, Y., Zhang, L.-Y., Gu, Q., & Wang, Q. (2016). Study of posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia after induction chemotherapy. J Child Neurol, 31(3), 279–284. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073815589758.
Landi, D. B., Thompson, E. M., & Ashley, D. M. (2018). Immunotherapy for pediatric brain tumors. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm, 5, 29. https://doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2018.35.
Kabir, T. F., Chauhan, A., Anthony, L., & Hildebrandt, G. C. (2018). Immune checkpoint inhibitors in pediatric solid tumors: status in 2018. Ochsner J, 18(4), 370–376. https://doi.org/10.31486/toj.18.0055.
AlHarbi M, Mobark NA, AlMubarak L, Aljelaify R, AlSaeed M, Almutairi A, … Abedalthagafi M (2018). Durable response to nivolumab in a pediatric patient with refractory glioblastoma and constitutional biallelic mismatch repair deficiency Saudi human genome project View project medulloblastoma View project, 23(12), 1401–1406. doi:https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0163.
Gorsi H, Malicki DM, Barsan, V, Tumblin M, Yeh-Nayre L, Milburn M, … Crawford JR (2019). Nivolumab in the treatment of recurrent or refractory pediatric brain tumors: a single institutional experience. J Pediatr Hematol/Oncol, 41(4), e235–241. doi:https://doi.org/10.1097/MPH.0000000000001339.
Wang, S. S., Bandopadhayay, P., & Jenkins, M. R. (2019). Towards immunotherapy for pediatric brain tumors. Trends Immunol, 40(8), 748–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2019.05.009.
Williams TJ, Benavides DR, Patrice, K A, Dalmau JO, De Ávila AL R, Le DT, … Mowry EM (2016). Association of autoimmune encephalitis with combined immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment for metastatic cancer. JAMA Neurol, 73(8), 928–933. doi:https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.1399.
Zekeridou, A., & Lennon, V. A. (2019). Neurologic autoimmunity in the era of checkpoint inhibitor cancer immunotherapy. Mayo Clin Proc, 94(9), 1865–1878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2019.02.003.
Dalakas, M. C. (2018). Neurological complications of immune checkpoint inhibitors: what happens when you ‘take the brakes off’ the immune system. Ther Adv Neurol Disord, 11, 1756286418799864. https://doi.org/10.1177/1756286418799864.
Brudno, J. N., & Kochenderfer, J. N. (2019). Recent advances in CAR T-cell toxicity: mechanisms, manifestations and management. Blood Rev, 34, 45–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.blre.2018.11.002.
Gust, J., Hay KA, Hanafi L A, Li D, Myerson D, Gonzalez-Cuyar LF, … Turtle CJ (2017). Endothelial activation and blood–brain barrier disruption in neurotoxicity after adoptive immunotherapy with CD19 CAR-T cells. Cancer Discov doi:https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0698.
Hay, K. A. (2018). Cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity after CD19 chimeric antigen receptor-modified (CAR-) T cell therapy. Br J Haematol. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjh.15644.
Santomasso BD, Park JH, Salloum D, Riviere, I., Flynn J, Mead E, … Brentjens RJ (2018). Clinical and biological correlates of neurotoxicity associated with car t-cell therapy in patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Discov. doi:https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-1319.
Willis, M. D., & Robertson, N. P. (2019). Neurotoxicity of novel cancer immunotherapies. J Neurol, 266, 2087–2089. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-019-09444-4.
Gust, J., Taraseviciute, A., & Turtle, C. J. (2018). Neurotoxicity associated with CD19-targeted CAR-T cell therapies. CNS Drugs, 32(12), 1091–1101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-018-0582-9.
Le RQ, Li L, Yuan W, Shord SS, Nie L, Habtemariam BA, … Pazdur R (2018). FDA approval summary: tocilizumab for treatment of chimeric antigen receptor T cell-induced severe or life-threatening cytokine release syndrome. The Oncologist, 23(8), 943–947. doi:https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0028.
Reynolds, M. R., Haydon, D. H., Caird, J., & Leonard, J. R. (2016). Radiation-induced moyamoya syndrome after proton beam therapy in the pediatric patient: a case series. Pediatr Neurosurg, 51(6), 297–301. https://doi.org/10.1159/000446075.
Meadows, A. T., Massari, D. J., Fergusson, J., Gordon, J., Littman, P., & Moss, K. (1981). Declines in IQ scores and cognitive dysfunctions in children with acute lymphocytic leukaemia treated with cranial irradiation. Lancet, 2(8254), 1015–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(81)91216-2.
Amirjamshidi, A., & Abbassioun, K. (2000). Radiation-induced tumors of the central nervous system occurring in childhood and adolescence. Childs Nerv Syst, 16(7), 390–397. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003819900125.
Gastelum, E., Sear, K., Hills, N., Roddy, E., Randazzo, D., Chettout, N., Hess, C., Cotter, J., Haas-Kogan, D. A., Fullerton, H., & Mueller, S. (2015). Rates and characteristics of radiographically detected intracerebral cavernous malformations after cranial radiation therapy in pediatric cancer patients. J Child Neurol, 30(7), 842–849. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073814544364.
Strenger, V., Sovinz, P., Lackner, H., Dornbusch, H. J., Lingitz, H., Eder, H. G., Moser, A., & Urban, C. (2008). Intracerebral cavernous hemangioma after cranial irradiation in childhood: incidence and risk factors. Strahlenther Onkol, 184(5), 276–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-008-1817-3.
Lew, S. M., Morgan, J. N., Psaty, E., Lefton, D. R., Allen, J. C., & Abbott, R. (2006). Cumulative incidence of radiation-induced cavernomas in long-term survivors of medulloblastoma. J Neurosurg, 104(Suppl 2), 103–107. https://doi.org/10.3171/ped.2006.104.2.6.
Sciubba, D. M., Gallia, G. L., Recinos, P., Garonzik, I. M., & Clatterbuck, R. E. (2006). Intracranial aneurysm following radiation therapy during childhood for a brain tumor: case report and review of the literature. J Neurosurg, 105(2), 134–139. https://doi.org/10.3171/ped.2006.105.2.134.
Fan, E. P., Heiber, G., Gerard, E. E., & Schuele, S. (2018). Stroke-like migraine attacks after radiation therapy: a misnomer? Epilepsia, 59(1), 259–268. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.13963.
Wai, K., Balabanski, A., Chia, N., & Kleinig, T. (2017). Reversible hemispheric hypoperfusion in two cases of SMART syndrome. J Clin Neurosci, 43, 146–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2017.05.013.
Stubblefield, M. D. (2017). Neuromuscular complications of radiation therapy. Muscle Nerve, 56(6), 1031–1040. https://doi.org/10.1002/mus.25778.
Neglia, J. P., Robison, L. L., Stovall, M., Liu, Y., Packer, R. J., Hammond, S., Yasui, Y., Kasper, C. E., Mertens, A. C., Donaldson, S. S., Meadows, A. T., & Inskip, P. D. (2006). New primary neoplasms of the central nervous system in survivors of childhood cancer: a report from the childhood cancer survivor study. J Natl Cancer Inst, 98(21), 1528–1537. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djj411.
Schmidt-Hieber, M., Silling, G., Schalk, E., Heinz, W., Panse, J., Penack, O., Christopeit, M., Buchheidt, D., Meyding-Lamadé, U., Hähnel, S., Wolf, H. H., Ruhnke, M., Schwartz, S., & Maschmeyer, G. (2016). CNS infections in patients with hematological disorders (including allogeneic stem-cell transplantation)-guidelines of the infectious DiseasesWorking party (AGIHO) of the German Society of Hematology and Medical Oncology (DGHO). Ann Oncol, 27(7), 1207–1225. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdw155.
Schoettler, M., Duncan, C., & Lehmann, L. (2019). Severe, persistent neurotoxicity after transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy in a pediatric patient despite treatment with eculizumab. Pediatr Transplant, 23(3), e13381. https://doi.org/10.1111/petr.13381.
Callahan, M. J., MacDougall, R. D., Bixby, S. D., Voss, S. D., Robertson, R. L., & Cravero, J. P. (2018). Ionizing radiation from computed tomography versus anesthesia for magnetic resonance imaging in infants and children: patient safety considerations. Pediatr Radiol, 48(1), 21–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-017-4023-6.
Tekes, A., Senglaub, S. S., Ahn, E. S., Huisman, T. A. G. M., & Jackson, E. M. (2018). Ultrafast brain MRI can be used for indications beyond shunted hydrocephalus in pediatric patients. Am J Neuroradiol, 39(8), 1515–1518. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A5724.
Tuma, R., & DeAngelis, L. M. (2000). Altered mental status in patients with cancer. Arch Neurol, 57(12), 1727–1731. https://doi.org/10.1001/archneur.57.12.1727.
Khan, R. B., Hunt, D. L., Boop, F. A., Sanford, R. A., Merchant, T. E., Gajjar, A., & Kun, L. E. (2005). Seizures in children with primary brain tumors: Incidence and long-term outcome. Epilepsy Res, 64(3), 85–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2005.03.007.
Ibrahim, K., & Appleton, R. E. (2004). Seizures as the presenting symptom of brain tumours in children. Seizure, 13(2), 108–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1059-1311(03)00083-9.
Glantz MJ, Cole BF, Forsyth PA, Recht LD, Wen PY, Chamberlain MC, … Cairncross JG (2000). Practice parameter: anticonvulsant prophylaxis in patients with newly diagnosed brain tumors: report of the quality standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of neurology. Neurology, 54(10), 1886–1893. doi:https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.54.10.1886.
Hardesty, D. A., Sanborn, M. R., Parker, W. E., & Storm, P. B. (2011). Perioperative seizure incidence and risk factors in 223 pediatric brain tumor patients without prior seizures: clinical article. J Neurosurg Pediatr. https://doi.org/10.3171/2011.3.PEDS1120.
Patsalos, P. N., & St. Louis, E. K. (2018). The epilepsy prescriber’s guide to antiepileptic drugs (3rd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. https://doi.org/10.1017/9781108669399.
The Childhood Brain Tumor Consortium. (1991). The epidemiology of headache among children with brain tumor. Headache in children with brain tumors. J Neuro-Oncol, 10(1), 31–46. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00151245.
Kirby, S., & Purdy, R. A. (2007). Headache and brain tumors. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep, 7(2), 110–116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11910-007-0005-7.
Demaree, C. J., Soliz, J. M., & Gebhardt, R. (2016). Cancer seeding risk from an epidural blood patch in patients with leukemia or lymphoma. Pain Med, 18(4), 218. https://doi.org/10.1093/pm/pnw218.
Rusch, R., Schulta, C., Hughes, L., & Withycombe, J. S. (2014). Evidence-based practice recommendations to prevent/manage post-lumbar puncture headaches in pediatric patients receiving intrathecal chemotherapy. J Pediatr Oncol Nurs, 31(4), 230–238. https://doi.org/10.1177/1043454214532026.
Lee, L. C.-Y., Sennett, M., & Erickson, J. M. (2007). Prevention and management of post–lumbar puncture headache in pediatric oncology patients. J Pediatr Oncol Nurs, 24(4), 200–207. https://doi.org/10.1177/1043454207303884.
Kranick, S. M., Campen, C. J., Kasner, S. E., Kessler, S. K., Zimmerman, R. A., Lustig, R. A., Phillips, P. C., Beslow, L. A., Ichord, R., & Fisher, M. J. (2013). Headache as a risk factor for neurovascular events in pediatric brain tumor patients. Neurology, 80(16), 1452–1456. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e31828cf81e.
Black, D., Bartleson, J., Bell, M., & Lachance, D. (2006). SMART: stroke-like migraine attacks after radiation therapy. Cephalalgia, 26(9), 1137–1142. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-2982.2006.01184.x.
Sporns PB, Sträter R, Minnerup, J, Wiendl H, Hanning U, Chapot R, … Kemmling A (2019). Feasibility, safety, and outcome of endovascular recanalization in childhood stroke: the Save ChildS Study. JAMA Neurol. doi:https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaneurol.2019.3403.
Bigi, S., Dulcey, A., Gralla, J., Bernasconi, C., Melliger, A., Datta, A. N., Arnold, M., Kaesmacher, J., Fluss, J., Hackenberg, A., Maier, O., Weber, J., Poloni, C., Fischer, U., & Steinlin, M. (2018). Feasibility, safety, and outcome of recanalization treatment in childhood stroke. Ann Neurol, 83(6), 1125–1132. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.25242.
Amlie-Lefond, C., & Wainwright, M. S. (2019). Organizing for acute arterial ischemic stroke in children. Stroke, 50(12), 3662–3668. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.119.025497.
Furuhata, M., Aihara, Y., Eguchi, S., Horiba, A., Tanaka, M., Komori, T., & Okada, Y. (2014). Pediatric medulloblastoma presenting as cerebellar hemorrhage: a case report. No shinkei geka. Neurol Surg, 42(6), 545–551.
Wilson, M. P., Johnson, E. S., Hawkins, C., Atkins, K., Alshaya, W., & Pugh, J. A. (2016). Hemorrhagic presentations of cerebellar pilocytic astrocytomas in children resulting in death: report of 2 cases. J Neurosurg Pediatr, 17(4), 446–452. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.10.PEDS1580.
Packer, R. J., Rorke, L. B., Lange, B. J., Siegel, K. R., & Evans, A. E. (1985). Cerebrovascular accidents in children with cancer. Pediatrics, 76(2), 194–201.
Bajzar, L., Chan, A. K., Massicotte, M. P., & Mitchell, L. G. (2006). Thrombosis in children with malignancy. Curr Opin Pediatr, 18(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mop.0000193270.09001.ea.
Herrlinger, U., Schabet, M., Bitzer, M., Petersen, D., & Krauseneck, P. (1999). Primary central nervous system lymphoma: from clinical presentation to diagnosis. J Neuro-Oncol, 43(3), 219–226. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006298201101.
Bühring, U., Herrlinger, U., Krings, T., Thiex, R., Weller, M., & Küker, W. (2001). MRI features of primary central nervous system lymphomas at presentation. Neurology, 57(3), 393–396. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.57.3.393.
Bjornard, K. L., Leventaki, V., Nichols, K. E., Sandlund, J. T., Prockop, S., & Ehrhardt, M. J. (2018). Two-year-old female with EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and subsequent CNS involvement with neurolymphomatosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer, 65(12), e27415. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.27415.
Grisariu S, Avni B, Batchelor T T, Bent MJ van den, Bokstein F, Schiff, D, … Siegal T (2010). Neurolymphomatosis: an international primary CNS lymphoma collaborative group report. Blood, 115(24), 5005–5011. doi:https://doi.org/10.1182/BLOOD-2009-12-258210.
Grisold, W., Cavaletti, G., & Windebank, A. J. (2012). Peripheral neuropathies from chemotherapeutics and targeted agents: diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Neuro-Oncology, 14(suppl 4), v45–v54. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nos203.
Ness, K. K., Hudson, M. M., Pui, C. H., Green, D. M., Krull, K. R., Huang, T. T., Robison, L. L., & Morris, E. B. (2012). Neuromuscular impairments in adult survivors of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: associations with physical performance and chemotherapy doses. Cancer, 118(3), 828–838. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.26337.
Chu, S. H., Lee, Y. J., Lee, E. S., Geng, Y., Wang, X. S., & Cleeland, C. S. (2015). Current use of drugs affecting the central nervous system for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in cancer patients: A systematic review. Support Care Cancer, 23(2), 513–524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-014-2408-8.
Hou, S., Huh, B., Kim, H. K., Kim, K. H., & Abdi, S. (2018). Treatment of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: systematic review and recommendations. Pain Physician, 21(6), 571–592.
Acknowledgments
We thank Stacy Cooper for her assistance with the chemotherapy section of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C.A. and L.S. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Armstrong, C., Sun, L.R. Neurological complications of pediatric cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 39, 3–23 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-020-09847-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-020-09847-0