Abstract
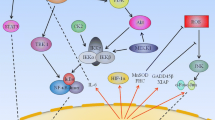
Nuclear Factor-kappa B (NF-κ B) is an inducible transcription factor that regulates the expression of many genes involved in the immune response. Recently, NF-κ B activity has been shown to be upregulated in many cancers, including melanoma. Data indicate that the enhanced activation of NF-κ B may be due to deregulations in upstream signaling pathways such as Ras/Raf, PI3K/Akt, and NIK. Multiple studies have shown that NF-κ B is involved in the regulation of apoptosis, angiogenesis, and tumor cell invasion, all of which indicate the important role of NF-κ B in tumorigenesis. Thus, understanding the molecular mechanism of melanoma progression will aid in designing new therapeutic approaches for melanoma. In this review, the association between NF-κ B and melanoma tumorigenesis are discussed. Additionally, the potential of emerging selective NF-κ B inhibitors for the treatment of melanoma is reviewed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Murray T, Samuels A, Ghafoor A, Ward E, Thun MJ: Cancer statistics, 2003. CA Cancer J Clin 53: 5–26, 2003
Oliveria S, Dusza S, Berwick M: Issues in the epidemiology of melanoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 1: 453–459, 2001
Clark WH: Tumour progression and the nature of cancer. Br J Cancer 64: 631–644, 1991
Sun W, Schuchter LM: Metastatic melanoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol 2: 193–202, 2001
Balch CM, Buzaid AC, Soong SJ, Atkins MB, Cascinelli N, Coit DG, Fleming ID, Gershenwald JE, Houghton A, Jr., Kirkwood JM, McMasters KM, Mihm MF, Morton DL, Reintgen DS, Ross MI, Sober A, Thompson JA, Thompson JF: Final version of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system for cutaneous melanoma. J Clin Oncol 19: 3635–3648, 2001
Punt CJ, Eggermont AM: Adjuvant interferon-alpha for melanoma revisited: News from old and new studies. Ann Oncol 12: 1663–1666, 2001
Ivanov VN, Bhoumik A, Ronai Z: Death receptors and melanoma resistance to apoptosis. Oncogene 22: 3152–3161, 2003
Nyormoi O, Bar-Eli M: Transcriptional regulation of metastasis-related genes in human melanoma. Clin Exp Metastasis 20: 251–263, 2003
Wang W, Abbruzzese JL, Evans DB, Larry L, Cleary KR, Chiao PJ: The nuclear factor-kappa B RelA transcription factor is constitutively activated in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells. Clin Cancer Res 5: 119–127, 1999
Bours V, Dejardin E, Goujon-Letawe F, Merville MP, Castronovo V: The NF-kappa B transcription factor and cancer: High expression of NF-kappa B- and I kappa B-related proteins in tumor cell lines. Biochem Pharmacol 47: 145–149, 1994
Sovak MA, Bellas RE, Kim DW, Zanieski GJ, Rogers AE, Traish AM, Sonenshein GE: Aberrant nuclear factor-kappaB/Rel expression and the pathogenesis of breast cancer. J Clin Invest 100: 2952–2960, 1997
Dejardin E, Bonizzi G, Bellahcene A, Castronovo V, Merville MP, Bours V: Highly-expressed p100/p52 (NFKB2) sequesters other NF-kappa B-related proteins in the cytoplasm of human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 11: 1835–1841, 1995
Duffey DC, Chen Z, Dong G, Ondrey FG, Wolf JS, Brown K, Siebenlist U, Van Waes C: Expression of a dominant-negative mutant inhibitor-kappaBalpha of nuclear factor-kappaB in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma inhibits survival, proinflammatory cytokine expression, and tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Res 59: 3468–3474, 1999
Nakshatri H, Bhat-Nakshatri P, Martin DA, Goulet RJ, Jr., Sledge GW, Jr.: Constitutive activation of NF-kappaB during progression of breast cancer to hormone-independent growth. Mol Cell Biol 17: 3629–3639, 1997
Abraham E: NF-kappaB activation. Crit Care Med 28: N100–104, 2000
Beg AA, Ruben SM, Scheinman RI, Haskill S, Rosen CA, Baldwin AS, Jr.: I kappa B interacts with the nuclear localization sequences of the subunits of NF-kappa B: A mechanism for cytoplasmic retention. Genes Dev 6: 1899–1913, 1992
Makarov SS: NF-kappaB as a therapeutic target in chronic inflammation: Recent advances. Mol Med Today 6: 441–448, 2000
Chen FE, Ghosh G: Regulation of DNA binding by Rel/NF-kappaB transcription factors: Structural views. Oncogene 18: 6845–6852, 1999
Baldwin AS: Control of oncogenesis and cancer therapy resistance by the transcription factor NF-kappaB. J Clin Invest 107: 241–246, 2001
McNulty SE, Tohidian NB, Meyskens FL, Jr.: RelA, p50 and inhibitor of kappa B alpha are elevated in human metastatic melanoma cells and respond aberrantly to ultraviolet light B. Pigment Cell Res 14: 456–465, 2001
Dhawan P, Richmond A: A novel NF-kappa B-inducing kinase-MAPK signaling pathway up-regulates NF-kappa B activity in melanoma cells. J Biol Chem 277: 7920–7928, 2002
McNulty SE, del Rosario R, Cen D, Meyskens FL, Jr., Yang S: Comparative expression of NF-kappaB proteins in melanocytes of normal skin vs. benign intradermal naevus and human metastatic melanoma biopsies. Pigment Cell Res 17: 173–180, 2004
Deveraux QL, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Van Arsdale T, Zhou Q, Srinivasula SM, Alnemri ES, Salvesen GS, Reed JC: IAPs block apoptotic events induced by caspase-8 and cytochrome c by direct inhibition of distinct caspases. Embo J 17: 2215–2223, 1998
Wang CY, Mayo MW, Korneluk RG, Goeddel DV, Baldwin AS, Jr.: NF-kappaB antiapoptosis: Induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation. Science 281: 1680–1683, 1998
Baldwin AS, Jr.: The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: New discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol 14: 649–683, 1996
Micheau O, Lens S, Gaide O, Alevizopoulos K, Tschopp J: NF-kappaB signals induce the expression of c-FLIP. Mol Cell Biol 21: 5299–5305, 2001
Ravi R, Bedi GC, Engstrom LW, Zeng Q, Mookerjee B, Gelinas C, Fuchs EJ, Bedi A: Regulation of death receptor expression and TRAIL/Apo2L-induced apoptosis by NF-kappaB. Nat Cell Biol 3: 409–416, 2001
Catz SD, Johnson JL: Transcriptional regulation of bcl-2 by nuclear factor kappa B and its significance in prostate cancer. Oncogene 20: 7342–7351, 2001
Grossman D, McNiff JM, Li F, Altieri DC: Expression and targeting of the apoptosis inhibitor, survivin, in human melanoma. J Invest Dermatol 113: 1076–1081, 1999
Vucic D, Stennicke HR, Pisabarro MT, Salvesen GS, Dixit VM: ML-IAP, a novel inhibitor of apoptosis that is preferentially expressed in human melanomas. Curr Biol 10: 1359–1366, 2000
Alonso SR, Ortiz P, Pollan M, Perez-Gomez B, Sanchez L, Acuna MJ, Pajares R, Martinez-Tello FJ, Hortelano CM, Piris MA, Rodriguez-Peralto JL: Progression in cutaneous malignant melanoma is associated with distinct expression profiles: A tissue microarray-based study. Am J Pathol 164: 193–203, 2004
Franco AV, Zhang XD, Van Berkel E, Sanders JE, Zhang XY, Thomas WD, Nguyen T, Hersey P: The role of NF-kappa B in TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced apoptosis of melanoma cells. J Immunol 166: 5337–5345, 2001
Ivanov VN, Fodstad O, Ronai Z: Expression of ring finger-deleted TRAF2 sensitizes metastatic melanoma cells to apoptosis via up-regulation of p38, TNFalpha and suppression of NF-kappaB activities. Oncogene 20: 2243–2253, 2001
Bakker TR, Reed D, Renno T, Jongeneel CV: Efficient adenoviral transfer of NF-kappaB inhibitor sensitizes melanoma to tumor necrosis factor-mediated apoptosis. Int J Cancer 80: 320–323, 1999
Wang D, Yang W, Du J, Devalaraja MN, Liang P, Matsumoto K, Tsubakimoto K, Endo T, Richmond A: MGSA/GRO-mediated melanocyte transformation involves induction of Ras expression. Oncogene 19: 4647–4659, 2000
Guttridge DC, Albanese C, Reuther JY, Pestell RG, Baldwin AS, Jr.: NF-kappaB controls cell growth and differentiation through transcriptional regulation of cyclin D1. Mol Cell Biol 19: 5785–5799, 1999
Hinz M, Krappmann D, Eichten A, Heder A, Scheidereit C, Strauss M: NF-kappaB function in growth control: Regulation of cyclin D1 expression and G0/G1-to-S-phase transition. Mol Cell Biol 19: 2690–2698, 1999
Bash J, Zong WX, Gelinas C: c-Rel arrests the proliferation of HeLa cells and affects critical regulators of the G1/S-phase transition. Mol Cell Biol 17: 6526–6536, 1997
Yang J, Richmond A: Constitutive IkappaB kinase activity correlates with nuclear factor-kappaB activation in human melanoma cells. Cancer Res 61: 4901–4909, 2001
Kunz M, Hartmann A, Flory E, Toksoy A, Koczan D, Thiesen HJ, Mukaida N, Neumann M, Rapp UR, Brocker EB, Gillitzer R: Anoxia-induced up-regulation of interleukin-8 in human malignant melanoma. A potential mechanism for high tumor aggressiveness. Am J Pathol 155: 753–763, 1999
Luca M, Huang S, Gershenwald JE, Singh RK, Reich R, Bar-Eli M: Expression of interleukin-8 by human melanoma cells up-regulates MMP-2 activity and increases tumor growth and metastasis. Am J Pathol 151: 1105–1113, 1997
Rofstad EK, Halsor EF: Vascular endothelial growth factor, interleukin 8, platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor, and basic fibroblast growth factor promote angiogenesis and metastasis in human melanoma xenografts. Cancer Res 60: 4932–4938, 2000
Kashani-Sabet M, Shaikh L, Miller JR, 3rd, Nosrati M, Ferreira CM, Debs RJ, Sagebiel RW: NF-kappa B in the vascular progression of melanoma. J Clin Oncol 22: 617–623, 2004
Denkert C, Kobel M, Berger S, Siegert A, Leclere A, Trefzer U, Hauptmann S: Expression of cyclooxygenase 2 in human malignant melanoma. Cancer Res 61: 303–308, 2001
Goulet AC, Einsphar JG, Alberts DS, Beas A, Burk C, Bhattacharyya A, Bangert J, Harmon JM, Fujiwara H, Koki A, Nelson MA: Analysis of cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) expression during malignant melanoma progression. Cancer Biol Ther 2: 713–718, 2003
van de Stolpe A, Caldenhoven E, Stade BG, Koenderman L, Raaijmakers JA, Johnson JP, van der Saag PT: 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate- and tumor necrosis factor alpha-mediated induction of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 is inhibited by dexamethasone. Functional analysis of the human intercellular adhesion molecular-1 promoter. J Biol Chem 269: 6185–6192, 1994
Iademarco MF, McQuillan JJ, Rosen GD, Dean DC: Characterization of the promoter for vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1). J Biol Chem 267: 16323–16329, 1992
Whelan J, Ghersa P, Hooft van Huijsduijnen R, Gray J, Chandra G, Talabot F, DeLamarter JF: An NF kappa B-like factor is essential but not sufficient for cytokine induction of endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule 1 (ELAM-1) gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res 19: 2645–2653, 1991
Borghaei RC, Rawlings PL, Jr., Javadi M, Woloshin J: NF-kappaB binds to a polymorphic repressor element in the MMP-3 promoter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 316: 182–188, 2004
Bond M, Fabunmi RP, Baker AH, Newby AC: Synergistic upregulation of metalloproteinase-9 by growth factors and inflammatory cytokines: An absolute requirement for transcription factor NF-kappa B. FEBS Lett 435: 29–34, 1998
Johnson JP, Stade BG, Holzmann B, Schwable W, Riethmuller G: De novo expression of intercellular-adhesion molecule-1 in melanoma correlates with increased risk of metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 641–644, 1989
Boyano MD, Garcia-Vazquez MD, Lopez-Michelena T, Gardeazabal J, Bilbao J, Canavate ML, Galdeano AG, Izu R, Diaz-Ramon L, Raton JA, Diaz-Perez JL: Soluble interleukin-2 receptor, intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and interleukin-10 serum levels in patients with melanoma. Br J Cancer 83: 847–852, 2000
Hirai S, Kageshita T, Kimura T, Tsujisaki M, Imai K, Wakamatsu K, Ito S, Ono T: Serum levels of sICAM-1 and 5-S-cysteinyldopa as markers of melanoma progression. Melanoma Res 7: 58–62, 1997
Langley RR, Carlisle R, Ma L, Specian RD, Gerritsen ME, Granger DN: Endothelial expression of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 correlates with metastatic pattern in spontaneous melanoma. Microcirculation 8: 335–345, 2001
Biancone L, Araki M, Araki K, Vassalli P, Stamenkovic I: Redirection of tumor metastasis by expression of E-selectin in vivo. J Exp Med 183: 581–587, 1996
van den Oord JJ, Paemen L, Opdenakker G, de Wolf-Peeters C: Expression of gelatinase B and the extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer EMMPRIN in benign and malignant pigment cell lesions of the skin. Am J Pathol 151: 665–670, 1997
Wang CY, Cusack JC, Jr., Liu R, Baldwin AS, Jr.: Control of inducible chemoresistance: Enhanced anti-tumor therapy through increased apoptosis by inhibition of NF-kappaB. Nat Med 5: 412–417, 1999
Kuo MT, Liu Z, Wei Y, Lin-Lee YC, Tatebe S, Mills GB, Unate H: Induction of human MDR1 gene expression by 2-acetylaminofluorene is mediated by effectors of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase pathway that activate NF-kappaB signaling. Oncogene 21: 1945–1954, 2002
Deng L, Lin-Lee YC, Claret FX, Kuo MT: 2-acetylaminofluorene up-regulates rat mdr1b expression through generating reactive oxygen species that activate NF-kappa B pathway. J Biol Chem 276: 413–420, 2001
Zhou G, Kuo MT: NF-kappaB-mediated induction of mdr1b expression by insulin in rat hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem 272: 15174–15183, 1997
Um JH, Kang CD, Lee BG, Kim DW, Chung BS, Kim SH: Increased and correlated nuclear factor-kappa B and Ku autoantigen activities are associated with development of multidrug resistance. Oncogene 20: 6048–6056, 2001
Tamatani T, Azuma M, Aota K, Yamashita T, Bando T, Sato M: Enhanced IkappaB kinase activity is responsible for the augmented activity of NF-kappaB in human head and neck carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett 171: 165–172, 2001
Mukhopadhyay T, Roth JA, Maxwell SA: Altered expression of the p50 subunit of the NF-kappa B transcription factor complex in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Oncogene 11: 999–1003, 1995
Shattuck-Brandt RL, Richmond A: Enhanced degradation of I-kappaB alpha contributes to endogenous activation of NF-kappaB in Hs294T melanoma cells. Cancer Res 57: 3032–3039, 1997
Shattuck RL, Wood LD, Jaffe GJ, Richmond A: MGSA/GRO transcription is differentially regulated in normal retinal pigment epithelial and melanoma cells. Mol Cell Biol 14: 791–802, 1994
Wood LD, Farmer AA, Richmond A: HMGI(Y) and Sp1 in addition to NF-kappa B regulate transcription of the MGSA/GRO alpha gene. Nucleic Acids Res 23: 4210–4219, 1995
Wood LD, Richmond A: Constitutive and cytokine-induced expression of the melanoma growth stimulatory activity/GRO alpha gene requires both NF-kappa B and novel constitutive factors. J Biol Chem 270: 30619–30626, 1995
Kondo S, Kono T, Sauder DN, McKenzie RC: IL-8 gene expression and production in human keratinocytes and their modulation by UVB. J Invest Dermatol 101: 690–694, 1993
Wang Y, Becker D: Antisense targeting of basic fibroblast growth factor and fibroblast growth factor receptor-1 in human melanomas blocks intratumoral angiogenesis and tumor growth. Nat Med 3: 887–893, 1997
Shih IM, Herlyn M: Autocrine and paracrine roles for growth factors in melanoma. In Vivo 8: 113–123, 1994
Gilmore TD, Koedood M, Piffat KA, White DW: Rel/NF-kappaB/IkappaB proteins and cancer. Oncogene 13: 1367–1378, 1996
Karin M, Lin A: NF-kappaB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol 3: 221–227, 2002
Pando MP, Verma IM: Signal-dependent and -independent degradation of free and NF-kappa B-bound IkappaBalpha. J Biol Chem 275: 21278–21286, 2000
Devalaraja MN, Wang DZ, Ballard DW, Richmond A: Elevated constitutive IkappaB kinase activity and IkappaB-alpha phosphorylation in Hs294T melanoma cells lead to increased basal MGSA/GRO-alpha transcription. Cancer Res 59: 1372–1377, 1999
Sizemore N, Lerner N, Dombrowski N, Sakurai H, Stark GR: Distinct roles of the Ikappa B kinase alpha and beta subunits in liberating nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B) from Ikappa B and in phosphorylating the p65 subunit of NF-kappa B. J Biol Chem 277: 3863–3869, 2002
Ling L, Cao Z, Goeddel DV: NF-kappaB-inducing kinase activates IKK-alpha by phosphorylation of Ser-176. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 3792–3797, 1998
Nakano H, Shindo M, Sakon S, Nishinaka S, Mihara M, Yagita H, Okumura K: Differential regulation of IkappaB kinase alpha and beta by two upstream kinases, NF-kappaB-inducing kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase/ERK kinase kinase-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 3537–3542, 1998
Smith C, Andreakos E, Crawley JB, Brennan FM, Feldmann M, Foxwell BM: NF-kappaB-inducing kinase is dispensable for activation of NF-kappaB in inflammatory settings but essential for lymphotoxin beta receptor activation of NF-kappaB in primary human fibroblasts. J Immunol 167: 5895–5903, 2001
Malinin NL, Boldin MP, Kovalenko AV, Wallach D: MAP3K-related kinase involved in NF-kappaB induction by TNF, CD95 and IL-1. Nature 385: 540–544, 1997
Xiao G, Harhaj EW, Sun SC: NF-kappaB-inducing kinase regulates the processing of NF-kappaB2 p100. Mol Cell 7: 401–409, 2001
Cogswell PC, Guttridge DC, Funkhouser WK, Baldwin AS, Jr.: Selective activation of NF-kappa B subunits in human breast cancer: Potential roles for NF-kappa B2/p52 and for Bcl-3. Oncogene 19: 1123–1131, 2000
Li X, Stark GR: NF-kappaB-dependent signaling pathways. Exp Hematol 30: 285–296, 2002
Delhase M, Li N, Karin M: Kinase regulation in inflammatory response. Nature 406: 367–368, 2000
Koul D, Yao Y, Abbruzzese JL, Yung WK,Reddy SA: Tumor suppressor MMAC/PTEN inhibits cytokine-induced NF-kappaB activation without interfering with the IkappaB degradation pathway. J Biol Chem 276: 11402–11408, 2001
Madrid LV, Mayo MW, Reuther JY, Baldwin AS, Jr.: Akt stimulates the transactivation potential of the RelA/p65 Subunit of NF-kappa B through utilization of the Ikappa B kinase and activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase p38. J Biol Chem 276: 18934–18940, 2001
Dhawan P, Singh AB, Ellis DL, Richmond A: Constitutive activation of Akt/protein kinase B in melanoma leads to up-regulation of nuclear factor-kappaB and tumor progression. Cancer Res 62: 7335–7342, 2002
Celebi JT, Shendrik I, Silvers DN, Peacocke M: Identification of PTEN mutations in metastatic melanoma specimens. J Med Genet 37: 653–657, 2000
Zhou XP, Gimm O, Hampel H, Niemann T, Walker MJ, Eng C: Epigenetic PTEN silencing in malignant melanomas without PTEN mutation. Am J Pathol 157: 1123–1128, 2000
Tsao H, Mihm MC, Jr., Sheehan C: PTEN expression in normal skin, acquired melanocytic nevi, and cutaneous melanoma. J Am Acad Dermatol 49: 865–872, 2003
Mayo MW, Wang CY, Cogswell PC, Rogers-Graham KS, Lowe SW, Der CJ, Baldwin AS, Jr.: Requirement of NF-kappaB activation to suppress p53-independent apoptosis induced by oncogenic Ras. Science 278: 1812–1815, 1997
Finco TS, Westwick JK, Norris JL, Beg AA, Der CJ, Baldwin AS, Jr.: Oncogenic Ha-Ras-induced signaling activates NF-kappaB transcriptional activity, which is required for cellular transformation. J Biol Chem 272: 24113–24116, 1997
Norris JL, Baldwin AS, Jr.: Oncogenic Ras enhances NF-kappaB transcriptional activity through Raf-dependent and Raf-independent mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 274: 13841–13846, 1999
Millan O, Ballester A, Castrillo A, Oliva JL, Traves PG, Rojas JM, Bosca L: H-Ras-specific activation of NF-kappaB protects NIH 3T3 cells against stimulus-dependent apoptosis. Oncogene 22: 477–483, 2003
Herlyn M, Satyamoorthy K: Activated ras. Yet another player in melanoma? Am J Pathol 149: 739–744, 1996
Castellano M, Parmiani G: Genes involved in melanoma: An overview of INK4a and other loci. Melanoma Res 9: 421–432, 1999
Pollock PM, Harper UL, Hansen KS, Yudt LM, Stark M, Robbins CM, Moses TY, Hostetter G, Wagner U, Kakareka J, Salem G, Pohida T, Heenan P, Duray P, Kallioniemi O, Hayward NK, Trent JM, Meltzer PS: High frequency of BRAF mutations in nevi. Nat Genet 33: 19–20, 2003
Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P, Edkins S, Clegg S, Teague J, Woffendin H, Garnett MJ, Bottomley W, Davis N, Dicks E, Ewing R, Floyd Y, Gray K, Hall S, Hawes R, Hughes J, Kosmidou V, Menzies A, Mould C, Parker A, Stevens C, Watt S, Hooper S, Wilson R, Jayatilake H, Gusterson BA, Cooper C, Shipley J, Hargrave D, Pritchard-Jones K, Maitland N, Chenevix-Trench G, Riggins GJ, Bigner DD, Palmieri G, Cossu A, Flanagan A, Nicholson A, Ho JW, Leung SY, Yuen ST, Weber BL, Seigler HF, Darrow TL, Paterson H, Marais R, Marshall CJ, Wooster R, Stratton MR, Futreal PA: Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature 417: 949–954, 2002
Troppmair J, Hartkamp J, Rapp UR: Activation of NF-kappa B by oncogenic Raf in HEK 293 cells occurs through autocrine recruitment of the stress kinase cascade. Oncogene 17: 685–690, 1998
Yin MJ, Christerson LB, Yamamoto Y, Kwak YT, Xu S, Mercurio F, Barbosa M, Cobb MH, Gaynor RB: HTLV-I Tax protein binds to MEKK1 to stimulate IkappaB kinase activity and NF-kappaB activation. Cell 93: 875–884, 1998
Chu ZL, DiDonato JA, Hawiger J, Ballard DW: The tax oncoprotein of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 associates with and persistently activates IkappaB kinases containing IKKalpha and IKKbeta. J Biol Chem 273: 15891–15894, 1998
Geleziunas R, Ferrell S, Lin X, Mu Y, Cunningham ET, Jr., Grant M, Connelly MA, Hambor JE, Marcu KB, Greene WC: Human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 Tax induction of NF-kappaB involves activation of the IkappaB kinase alpha (IKKalpha) and IKKbeta cellular kinases. Mol Cell Biol 18: 5157–5165, 1998
Mosialos G: The role of Rel/NF-kappa B proteins in viral oncogenesis and the regulation of viral transcription. Semin Cancer Biol 8: 121–129, 1997
La Porta CA, Comolli R: PKC-dependent modulation of IkB alpha-NFkB pathway in low metastatic B16F1 murine melanoma cells and in highly metastatic BL6 cells. Anticancer Res 18: 2591–2597, 1998
Biswas DK, Dai SC, Cruz A, Weiser B, Graner E, Pardee AB: The nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B): A potential therapeutic target for estrogen receptor negative breast cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98: 10386–10391, 2001
Wilson L, Szabo C, Salzman AL: Protein kinase C-dependent activation of NF-kappaB in enterocytes is independent of IkappaB degradation. Gastroenterology 117: 106–114, 1999
Han Y, Meng T, Murray NR, Fields AP, Brasier AR: Interleukin-1-induced nuclear factor-kappaB-IkappaBalpha autoregulatory feedback loop in hepatocytes. A role for protein kinase calpha in post-transcriptional regulation of ikappabalpha resynthesis. J Biol Chem 274: 939–947, 1999
Anrather J, Csizmadia V, Soares MP, Winkler H: Regulation of NF-kappaB RelA phosphorylation and transcriptional activity by p21(ras) and protein kinase Czeta in primary endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 274: 13594–13603, 1999
Wang D, Baldwin AS, Jr.: Activation of nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent transcription by tumor necrosis factor-alpha is mediated through phosphorylation of RelA/p65 on serine 529. J Biol Chem 273: 29411–29416, 1998
Wang D, Westerheide SD, Hanson JL, Baldwin AS, Jr.: Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced phosphorylation of RelA/p65 on Ser529 is controlled by casein kinase II. J Biol Chem 275: 32592–32597, 2000
Sakurai H, Chiba H, Miyoshi H, Sugita T, Toriumi W: IkappaB kinases phosphorylate NF-kappaB p65 subunit on serine 536 in the transactivation domain. J Biol Chem 274: 30353–30356, 1999
Zhong H, SuYang H, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Ghosh S: The transcriptional activity of NF-kappaB is regulated by the IkappaB-associated PKAc subunit through a cyclic AMP-independent mechanism. Cell 89: 413–424, 1997
Zhong H, Voll RE, Ghosh S: Phosphorylation of NF-kappa B p65 by PKA stimulates transcriptional activity by promoting a novel bivalent interaction with the coactivator CBP/p300. Mol Cell 1: 661–671, 1998
Vermeulen L, De Wilde G, Van Damme P, Vanden Berghe W, Haegeman G: Transcriptional activation of the NF-kappaB p65 subunit by mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase-1 (MSK1). Embo J 22: 1313–1324, 2003
Berman KS, Verma UN, Harburg G, Minna JD, Cobb MH, Gaynor RB: Sulindac enhances tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated apoptosis of lung cancer cell lines by inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB. Clin Cancer Res 8: 354–360, 2002
May MJ, D’Acquisto F, Madge LA, Glockner J, Pober JS, Ghosh S: Selective inhibition of NF-kappaB activation by a peptide that blocks the interaction of NEMO with the IkappaB kinase complex. Science 289: 1550–1554, 2000
Yamamoto Y, Gaynor RB: Therapeutic potential of inhibition of the NF-kappaB pathway in the treatment of inflammation and cancer. J Clin Invest 107: 135–142, 2001
Hideshima T, Chauhan D, Richardson P, Mitsiades C, Mitsiades N, Hayashi T, Munshi N, Dang L, Castro A, Palombella V, Adams J, Anderson KC: NF-kappa B as a therapeutic target in multiple myeloma. J Biol Chem 277: 16639–16647, 2002
Tan C, Waldmann TA: Proteasome inhibitor PS-341, a potential therapeutic agent for adult T-cell leukemia. Cancer Res 62: 1083–1086, 2002
Adams J: Proteasome inhibition: A novel approach to cancer therapy. Trends Mol Med 8: S49–54, 2002
Amiri KI, Horton LW, LaFleur BJ, Sosman JA, Richmond A: Augmenting chemosensitivity of malignant melanoma tumors via proteasome inhibition: Implication for bortezomib (VELCADE, PS-341) as a therapeutic agent for malignant melanoma. Cancer Res 64: 4912–4918, 2004
Banerji A, Chakrabarti J, Mitra A, Chatterjee A: Effect of curcumin on gelatinase A (MMP-2) activity in B16F10 melanoma cells. Cancer Lett 211: 235–242, 2004
Odot J, Albert P, Carlier A, Tarpin M, Devy J, Madoulet C: In vitro and in vivo anti-tumoral effect of curcumin against melanoma cells. Int J Cancer 111: 381–387, 2004
Chawla-Sarkar M, Bauer JA, Lupica JA, Morrison BH, Tang Z, Oates RK, Almasan A, DiDonato JA, Borden EC, Lindner DJ: Suppression of NF-kappa B survival signaling by nitrosylcobalamin sensitizes neoplasms to the anti-tumor effects of Apo2L/TRAIL. J Biol Chem 278: 39461–39469, 2003
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amiri, K.I., Richmond, A. Role of nuclear factor-κ B in melanoma. Cancer Metastasis Rev 24, 301–313 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-005-1579-7
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-005-1579-7