Abstract
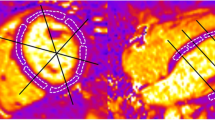
T2 star mapping can be applied for in vivo cardiac iron quantification. Current recommendations of imaging acquisition, post-processing and interpretation of normal values are based on old scanner types and in house software packages. A standardized comparison of short (SAX) and long axis (LAX) segments using commercially available software packages and modern scanners is lacking. To provide a standardized comparison of T2 star time values in SAX and LAX and to investigate intersegmental, interregional and inter-level comparison and the interscanner reproducibility. 84 cardiac MRIs in 28 healthy volunteers were performed with three structurally identical 1.5 T MRI scanners. A commercially available software package for T2 star mapping with automatic in-line motion correction was used for analysis. Regions of interest were manually placed in each of the 16 myocardial segments according to the AHA model in three SAX and three LAX. A total of 2856 ROIs were drawn and 102 segments per volunteer were analysed. Interscanner reproducibility was high (91%) and the mean myocardial T2 star time value for all evaluated segments was 34 ± 5.7 ms. No significant difference was found between all measurements in SAX (35 ± 5.5 ms) and LAX (34 ± 5.8 ms). T2 star time values varied significantly between heart segments in the same axis and in 44% between corresponding SAX and LAX segments. T2 star time values in SAX and LAX have a high interscanner reproducibility but can vary significantly between heart segments in the same axis. Comparability between corresponding SAX and LAX segments is limited. To get representative results T2 star time values should be obtained in more than one heart segment and for follow-up studies identical segments should be used to avoid a systematic bias.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AHA:
-
American Heart Association
- bpm:
-
Beats per minute
- cMRI:
-
Cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging
- ECG:
-
Electrocardiography
- FOV:
-
Field of view
- ICC:
-
Intraclass correlation coefficient
- LAX:
-
Long axis view
- LE:
-
Late enhancement
- MHz:
-
Megahertz
- MOLLI:
-
Modified look-locker inversion recovery sequence
- ms:
-
Milliseconds
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
- RR:
-
RR-interval
- SAX:
-
Short axis view
- T:
-
Tesla
- TE:
-
Echo time
- TI:
-
Inversion time
- TR:
-
Repetition time
References
Messroghli DR, Moon JC, Ferreira VM, Grosse-Wortmann L, He T, Kellman P, Mascherbauer J, Nezafat R, Salerno M, Schelbert EB, Taylor AJ, Thompson R, Ugander M, van Heeswijk RB, Friedrich MG (2017) Clinical recommendations for cardiovascular magnetic resonance mapping of T1, T2, T2* and extracellular volume: A consensus statement by the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (SCMR) endorsed by the European Association for Cardiovascular Imaging (EACVI). J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 19(1):75. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12968-017-0389-8
Brittenham GM (2011) Iron-chelating therapy for transfusional iron overload. N Engl J Med 364(2):146–156. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMct1004810
Messroghli DR, Niendorf T, Schulz-Menger J, Dietz R, Friedrich MG (2003) T1 mapping in patients with acute myocardial infarction. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 5(2):353–359
Messroghli DR, Radjenovic A, Kozerke S, Higgins DM, Sivananthan MU, Ridgway JP (2004) Modified Look-Locker inversion recovery (MOLLI) for high-resolution T1 mapping of the heart. Magn Reson Med 52(1):141–146. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.20110
Pennell DJ, Udelson JE, Arai AE, Bozkurt B, Cohen AR, Galanello R, Hoffman TM, Kiernan MS, Lerakis S, Piga A, Porter JB, Walker JM, Wood J (2013) Cardiovascular function and treatment in beta-thalassemia major: a consensus statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 128(3):281–308. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0b013e31829b2be6
Zia MI, Ghugre NR, Connelly KA, Strauss BH, Sparkes JD, Dick AJ, Wright GA (2012) Characterizing myocardial edema and hemorrhage using quantitative T2 and T2* mapping at multiple time intervals post ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 5(5):566–572. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCIMAGING.112.973222
Westwood MA, Anderson LJ, Firmin DN, Gatehouse PD, Lorenz CH, Wonke B, Pennell DJ (2003) Interscanner reproducibility of cardiovascular magnetic resonance T2* measurements of tissue iron in thalassemia. J Magn Reson Imaging 18(5):616–620. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.10396
Ghugre NR, Enriquez CM, Gonzalez I, Nelson MD, Coates TD, Wood JC (2006) MRI detects myocardial iron in the human heart. Magn Reson Med 56(3):681–686. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.20981
House MJ, Fleming AJ, de Jonge MD, Paterson D, Howard DL, Carpenter JP, Pennell DJ, St Pierre TG (2014) Mapping iron in human heart tissue with synchrotron X-ray fluorescence microscopy and cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 16:80. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12968-014-0080-2
Positano V, Pepe A, Santarelli MF, Ramazzotti A, Meloni A, De Marchi D, Favilli B, Cracolici E, Midiri M, Spasiano A, Lombardi M, Landini L (2009) Multislice multiecho T2* cardiac magnetic resonance for the detection of heterogeneous myocardial iron distribution in thalassaemia patients. NMR Biomed 22(7):707–715. https://doi.org/10.1002/nbm.1382
Carpenter JP, He T, Kirk P, Roughton M, Anderson LJ, de Noronha SV, Sheppard MN, Porter JB, Walker JM, Wood JC, Galanello R, Forni G, Catani G, Matta G, Fucharoen S, Fleming A, House MJ, Black G, Firmin DN, St Pierre TG, Pennell DJ (2011) On T2* magnetic resonance and cardiac iron. Circulation 123(14):1519–1528. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.007641
Ramazzotti A, Pepe A, Positano V, Rossi G, De Marchi D, Brizi MG, Luciani A, Midiri M, Sallustio G, Valeri G, Caruso V, Centra M, Cianciulli P, De Sanctis V, Maggio A, Lombardi M (2009) Multicenter Validation of the Magnetic Resonance T2*Technique for Segmental and Global Quantification of Myocardial Iron. J Magn Reson Imaging 30(1):62–68. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.21781
Pepe A, Positano V, Santarelli MF, Meloni A, Favilli B, De Marchi D, Keilberg P, Caruso V, Landini L, Lombardi M (2009) Multislice multiecho T2*cardiac magnetic resonance can detect heterogeneous myocardial iron distribution in thalassemia patients. Eur Heart J 30:487–487
Moon JC, Messroghli DR, Kellman P, Piechnik SK, Robson MD, Ugander M, Gatehouse PD, Arai AE, Friedrich MG, Neubauer S, Schulz-Menger J, Schelbert EB (2013) Myocardial T1 mapping and extracellular volume quantification: a Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (SCMR) and CMR Working Group of the European Society of Cardiology consensus statement. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 15:92. https://doi.org/10.1186/1532-429X-15-92
Cerqueira MD, Weissman NJ, Dilsizian V, Jacobs AK, Kaul S, Laskey WK, Pennell DJ, Rumberger JA, Ryan T, Verani MS (2002) Standardized myocardial segmentation and nomenclature for tomographic imaging of the heart. A statement for healthcare professionals from the Cardiac Imaging Committee of the Council on Clinical Cardiology of the American Heart Association. Circulation 105(4):539–542
Messroghli DR, Plein S, Higgins DM, Walters K, Jones TR, Ridgway JP, Sivananthan MU (2006) Human myocardium: single-breath-hold MR T1 mapping with high spatial resolution–reproducibility study. Radiology 238(3):1004–1012. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2382041903
Lota AS, Gatehouse PD, Mohiaddin RH (2017) T2 mapping and T2*imaging in heart failure. Heart Fail Rev 22(4):431–440. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10741-017-9616-5
Modell B, Khan M, Darlison M, Westwood MA, Ingram D, Pennell DJ (2008) Improved survival of thalassaemia major in the UK and relation to T2* cardiovascular magnetic resonance. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 10:42. https://doi.org/10.1186/1532-429X-10-42
Abdel-Gadir A, Vorasettakarnkij Y, Ngamkasem H, Nordin S, Ako EA, Tumkosit M, Sucharitchan P, Uaprasert N, Kellman P, Piechnik SK, Fontana M, Fernandes JL, Manisty C, Westwood M, Porter JB, Walker JM, Moon JC (2016) Ultrafast magnetic resonance imaging for iron quantification in thalassemia participants in the developing world: The TIC-TOC Study (Thailand and UK International Collaboration in Thalassaemia Optimising Ultrafast CMR). Circulation 134(5):432–434. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.022803
Rogers T, Dabir D, Mahmoud I, Voigt T, Schaeffter T, Nagel E, Puntmann VO (2013) Standardization of T1 measurements with MOLLI in differentiation between health and disease—the ConSept study. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 15:78. https://doi.org/10.1186/1532-429X-15-78
Rogers T, Puntmann VO (2014) T1 mapping—beware regional variations. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 15(11):1302. https://doi.org/10.1093/ehjci/jeu082
Kawel N, Nacif M, Zavodni A, Jones J, Liu S, Sibley CT, Bluemke DA (2012) T1 mapping of the myocardium: intra-individual assessment of the effect of field strength, cardiac cycle and variation by myocardial region. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 14:27. https://doi.org/10.1186/1532-429X-14-27
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Institutional review board approval was obtained and all volunteers gave written informed consent.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heiss, R., Wiesmueller, M., Treutlein, C. et al. Cardiac T2 star mapping: standardized inline analysis of long and short axis at three identical 1.5 T MRI scanners. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 35, 695–702 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-018-1503-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-018-1503-1