Abstract
The present study aimed to present a workflow algorithm for automatic processing of 2D echocardiography images. The workflow was based on several sequential steps. For each step, we compared different approaches. Epicardial 2D echocardiography datasets were acquired during various open-chest beating-heart surgical procedures in three porcine hearts. We proposed a metric called the global index that is a weighted average of several accuracy coefficients, indices and the mean processing time. This metric allows the estimation of the speed and accuracy for processing each image. The global index ranges from 0 to 1, which facilitates comparison between different approaches. The second step involved comparison among filtering, sharpening and segmentation techniques. During the noise reduction step, we compared the median filter, total variation filter, bilateral filter, curvature flow filter, non-local means filter and mean shift filter. To clarify the endocardium borders of the right heart, we used the linear sharpen. Lastly, we applied watershed segmentation, clusterisation, region-growing, morphological segmentation, image foresting segmentation and isoline delineation. We assessed all the techniques and identified the most appropriate workflow for echocardiography image segmentation of the right heart. For successful processing and segmentation of echocardiography images with minimal error, we found that the workflow should include the total variation filter/bilateral filter, linear sharpen technique, isoline delineation/region-growing segmentation and morphological post-processing. We presented an efficient and accurate workflow for the precise diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases. We introduced the global index metric for image pre-processing and segmentation estimation.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avendi M, Kheradvar A, Jafarkhani H (2016) Fully automatic segmentation of heart chambers in cardiac MRI using deep learning. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 18:P351. https://doi.org/10.1186/1532-429X-18-S1-P351
Kang HC, Lee J, Shin J (2016) Automatic four-chamber segmentation using level-set method and split energy function. Healthc Inform Res 22:285. https://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2016.22.4.285
Ecabert O, Peters J, Walker MJ, Ivanc T, Lorenz C, von Berg J, Lessick J, Vembar M, Weese J (2011) Segmentation of the heart and great vessels in CT images using a model-based adaptation framework. Med Image Anal 15:863–876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2011.06.004
Awan R, Rajpoot K (2015) Spatial and spatio-temporal feature extraction from 4D echocardiography images. Comput Biol Med 64:138–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2015.06.017
Danilov VV, Skirnevskiy IP, Gerget OM (2017) Segmentation of anatomical structures of the heart based on echocardiography. J Phys Conf Ser 803:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/803/1/012031
Filippov AA, Del Nido PJ, Vasilyev NV (2016) Management of systemic right ventricular failure in patients with congenitally corrected transposition of the great arteries. Circulation 134:1293–1302. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.022106
Horvath MA, Wamala I, Rytkin E, Doyle E, Payne CJ, Thalhofer T, Berra I, Solovyeva A, Saeed M, Hendren S, Roche ET, del Nido PJ, Walsh CJ, Vasilyev NV (2017) An intracardiac soft robotic device for augmentation of blood ejection from the failing right ventricle. Ann Biomed Eng 45:2222–2233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-017-1855-z
Payne CJ, Wamala I, Bautista-Salinas D, Saeed M, Van Story D, Thalhofer T, Horvath MA, Abah C, del Nido PJ, Walsh CJ, Vasilyev NV (2017) Soft robotic ventricular assist device with septal bracing for therapy of heart failure. Sci Robot 2:eaan6736. https://doi.org/10.1126/scirobotics.aan6736
Bersvendsen J, Orderud F, Massey RJ, Fossa K, Gerard O, Urheim S, Samset E (2016) Automated segmentation of the right ventricle in 3D echocardiography: a Kalman filter state estimation approach. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35:42–51. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2015.2453551
Brunklaus A, Parish E, Muntoni F, Scuplak S, Tucker SK, Fenton M, Hughes ML, Manzur AY (2015) The value of cardiac MRI versus echocardiography in the pre-operative assessment of patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 19:395–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpn.2015.03.008
Zhu Y, Huang C (2012) An improved median filtering algorithm for image noise reduction. Phys Procedia 25:609–616. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2012.03.133
Zeng H, Liu Y-Z, Fan Y-M, Tang X (2012) An improved algorithm for impulse noise by median filter. AASRI Procedia 1:68–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aasri.2012.06.014
Rudin LI, Osher S, Fatemi E (1992) Nonlinear total variation noise removal algorithm. Phys D Nonlinear Phenom 60:259–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/0167-2789(92)90242-F
Kwon K, Kim M-S, Shin B-S (2016) A fast 3D adaptive bilateral filter for ultrasound volume visualization. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 133:25–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2016.05.008
Tomasi C, Manduchi R (1998) Bilateral filtering for gray and color images. Int Conf Comput Vis. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.1998.710815
Malladi R, Sethian J (1995) Image processing via level set curvature flow. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:7046–7050. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.92.15.7046
Buades A, Coll B, Morel J-M (2011) Non-local means denoising. Image Process Line 1:490–530. https://doi.org/10.5201/ipol.2011.bcm_nlm
Comaniciu D, Meer P (2002) Mean shift: a robust approach toward feature space analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 24:603–619. https://doi.org/10.1109/34.1000236
Ahi K, Anwar M (2016) Developing terahertz imaging equation and enhancement of the resolution of terahertz images using deconvolution. SPIE Commer Sci Sens Imaging 9856:98560N–98560N. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2228680
Bertero M, Boccacci P (2005) Image deconvolution. Springer, New York, pp 349–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/1-4020-3616-7_17
Arbelaez P, Maire M, Fowlkes C, Malik J, Arbeláez P, Maire M, Fowlkes C, Malik J (2011) Contour detection and hierarchical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 33:898–916. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2010.161
Kanungo T, Mount DM, Netanyahu NS, Piatko CD, Silverman R, Wu AY (2002) An efficient k-means clustering algorithm: analysis and implementation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 24:881–892. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2002.1017616
Pratt WK (2001) Digital image processing, 3rd edn. Wiley, Rochester, NY. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0146-664X(78)80023-9
Haralick RM, Sternberg SR, Zhuang X (1987) Image analysis using mathematical morphology. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell PAMI -9:532–550. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.1987.4767941
Falcão AX, Stolfi J, de Alencar Lotufo R (2004) The image foresting transform: theory, algorithms, and applications. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 26:19–29. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2004.10012
Popowicz A, Smolka B (2014) Isoline based image colorization. 2014 UKSim-AMSS 16th Int. Conf. Comput. Model. Simul. IEEE, pp 280–285
Serra J (1982) Image analysis and mathematical morphology. Academic Press, Inc, Orlando. https://doi.org/10.2307/2531038
Wang Z, Bovik AC, Sheikh HR, Simoncelli EP (2004) Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans Image Process 13:600–612. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2003.819861
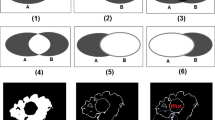
Dice LR (1945) Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 26:297–302. https://doi.org/10.2307/1932409
Sørensen T (1948) A method of establishing groups of equal amplitude in plant sociology based on similarity of species and its application to analyses of the vegetation on Danish commons. K Danske Vidensk Selsk Biol Skr 5:1–34
Jaccard P (1901) Étude comparative de la distribution florale dans une portion des Alpes et des Jura. Bull del la Société. Vaudoise des Sci Nat 37:547–579. https://doi.org/10.5169/seals-266450
Shapiro MD, Blaschko MB (2004) On Hausdorff distance measures. Comput Vis Lab Univ Mass Amherst MA 1003:1–21
Dubuisson M-P, Jain AK (1994) A modified Hausdorff distance for object matching. Proc 12th Int Conf Pattern Recognit 1:566–568. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICPR.1994.576361
Funding
This study was supported by the Russian Federation Governmental Program ‘Nauka’ № 12.8205.2017/БЧ (Addition Number: 4.1769.ГЗБ.2017) and the Tomsk Polytechnic University Competitiveness Enhancement Programme Grant (TPU CEP-RIO-52/2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and animals
The animal experimental protocols were approved by the Boston Children’s Hospital Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. All animals received humane care in accordance with the 1996 Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals recommended by the US National Institutes of Health. This paper does not contain any studies using human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Danilov, V.V., Skirnevskiy, I.P., Gerget, O.M. et al. Efficient workflow for automatic segmentation of the right heart based on 2D echocardiography. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 34, 1041–1055 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-018-1314-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-018-1314-4