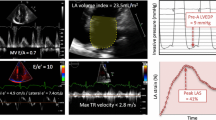
Abstract
Purpose: There exists no consensus on the site of E/e′ measurement. This study aimed to evaluate the predictive value of septal and lateral E/e′ along with the importance of their intra-individual difference. Methods: In 1775 persons from the general population, peak early diastolic velocity (e′) was obtained by color tissue Doppler at the septal and lateral mitral annular sites. The endpoint was combined of cardiovascular death or admission due to heart failure or acute myocardial infarction. Results: During a median follow-up of 10.9 years, the endpoint occurred in 227 participants. E/e′septal and E/e′lateral were equally strong predictors of cardiac events; in age- and sex-adjusted models they did not differ in AUC (septal: 0.8385, lateral: 0.8389; p = 0.94) or in continuous NRI (p = 0.84). Models using E/e′average did not improve AUC or NRI, and the intra-individual difference between sites had no predictive value (p = 0.79). E/e′septal was generally higher than E/e′lateral, thus age- and sex-specific normal values were reported for both sites for a population free of cardiac events during 10 years of follow-up. Conclusions: Septal and lateral E/e′ are equally useful in predicting cardiac events in the general population. Measuring both sites provides no further predictive value than measuring a single site.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nagueh SF, Smiseth OA, Appleton CP, Byrd BF, Dokainish H, Edvardsen T, et al (2016) Recommendations for the evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function by echocardiography: an update from the american society of echocardiography and the european association of cardiovascular imaging. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 29(4):277–314
Ommen SR, Nishimura RA, Appleton CP, Miller FA, Oh JK, Redfield MM, et al (2000) Clinical utility of Doppler echocardiography and tissue Doppler imaging in the estimation of left ventricular filling pressures: a comparative simultaneous Doppler-catheterization study. Circulation 102(15):1788–1794
Kasner M, Westermann D, Steendijk P, Gaub R, Wilkenshoff U, Weitmann K, et al (2007) Utility of doppler echocardiography and tissue doppler imaging in the estimation of diastolic function in heart failure with normal ejection fraction: a comparative doppler-conductance catheterization study. Circulation 116(6):637–47
Sharp ASP, Tapp RJ, Thom SAM, Francis DP, Hughes AD, Stanton AV, et al (2010) Tissue Doppler E/E′ ratio is a powerful predictor of primary cardiac events in a hypertensive population: an ASCOT substudy. Eur Heart J 31(6):747–752
Hillis GS, Møller JE, Pellikka PA, Gersh BJ, Wright RS, Ommen SR, et al (2004) Noninvasive estimation of left ventricular filling pressure by e/e′ is a powerful predictor of survival after acute myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol 43(3):360–7
Buck T, Breithardt O-A, Faber L, Fehske W, Flachskampf F, Franke A, et al (2009) Manual zur Indikation und Durchführung der Echokardiographie. Clin Res Cardiol Suppl 4(1):3–51
Picard MH, Adams D, Bierig SM, Dent JM, Douglas PS, Gillam LD et al (2011) American Society of Echocardiography Recommendations for Quality Echocardiography Laboratory Operations. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 24(1):1–10
Mortensen U, Jensen HS, Iversen K, Munk K, Ihlemann N, Gill S, et al Anbefalinger til udførelse og rapportering af transthorakal ekkokardiografi hos voksne [Internet]. 2014. Available from: http://cardio.dk/rapporter/holdningspapir-menu/496-anbefalinger-til-udforelse-og-rapportering-af-transthorakal-ekkokardiografi-hos-voksne
Wharton G, Steeds R, Allen J, Brewerton H, Jones R, Kanagala P, et al A Minimum Dataset for a Standard Transthoracic Echocardiogram From the British Society of Echocardiography Education Committee [Internet]. 2012. Available from: http://www.bsecho.org/tte-minimum-dataset/
Chahal NS, Lim TK, Jain P, Chambers JC, Kooner JS, Senior R (2010) Normative reference values for the tissue Doppler imaging parameters of left ventricular function: a population-based study. Eur Heart J 11(1): 466–471
Bach DS, Armstrong WF, Donovan CL, Muller DW (1996) Quantitative Doppler tissue imaging for assessment of regional myocardial velocities during transient ischemia and reperfusion. Am Heart J 132(4):721–725
Appleyard M, Hansen A, Schnohr P, Jensen G, Nyboe J (1989) The Copenhagen City Heart Study. Osterbroundersogelsen. a book of tables with data from the first examination (1976–78) and a five year follow-up (1981–83). Scand J Soc Med 170(suppl 41):1–160
Mogelvang R, Sogaard P, Pedersen SA, Olsen NT, Schnohr P, Jensen JS (2009) Tissue Doppler echocardiography in persons with hypertension, diabetes, or ischaemic heart disease: the Copenhagen City Heart Study. Eur Heart J Mar 1;30(6):731–9
Knegt MC de, Biering-Sorensen T, Sogaard P, Sivertsen J, Jensen JS, Mogelvang R (2014) Concordance and reproducibility between M-mode, tissue Doppler imaging, and two-dimensional strain imaging in the assessment of mitral annular displacement and velocity in patients with various heart conditions. Eur Heart J 15(1):62–69
Hummel YM, Klip IJT, Jong RM de, Pieper PG, Veldhuisen DJ van, Voors AA (2010) Diastolic function measurements and diagnostic consequences: a comparison of pulsed wave- and color-coded tissue Doppler imaging. Clin Res Cardiol 99(7):453–458
R Core Team (2015) R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing [Internet]. Vienna, Austria. Available from: https://www.R-project.org/
Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Merz CNB, Brewer HB, Clark LT, Hunninghake DB, et al (2004) Implications of Recent Clinical Trials for the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III Guidelines. Circulation. 110(2):227–239
Troughton RW, Prior DL, Frampton CM, Nash PJ, Pereira JJ, Martin M, et al (2005) Usefulness of tissue doppler and color m-mode indexes of left ventricular diastolic function in predicting outcomes in systolic left ventricular heart failure (from the ADEPT Study). Am J Cardiol 96(2):257–262
Hadano Y, Murata K, Tanaka N, Muro A, Akagawa E, Tanaka T et al (2007) Ratio of early transmitral velocity to lateral mitral annular early diastolic velocity has the best correlation with wedge pressure following cardiac surgery. Circ J 71(8):1274–1278
Rivas-Gotz C, Manolios M, Thohan V, Nagueh SF (2003) Impact of left ventricular ejection fraction on estimation of left ventricular filling pressures using tissue Doppler and flow propagation velocity. Am J Cardiol 91(6):780–784
Gellen B, Canoui-Poitrine F, Lesault P-F, Le Thuaut A, Lim P, Gueret P, et al (2013) Usefulness of tissue Doppler imaging for assessing left ventricular filling pressure in patients with stable severe systolic heart failure. Am J Cardiol 112(10):1619–1624
Nagueh SF, Rao L, Soto J, Middleton KJ, Khoury DS (2004) Haemodynamic insights into the effects of ischaemia and cycle length on tissue Doppler-derived mitral annulus diastolic velocities. Clin Sci. 106(2):147
Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, Afilalo J, Armstrong A, Ernande L, et al (2015) Recommendations for cardiac chamber quantification by echocardiography in adults: an update from the american society of echocardiography and the european association of cardiovascular imaging. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 16(3):233–271
Munagala VK, Jacobsen SJ, Mahoney DW, Rodeheffer RJ, Bailey KR, Redfield MM (2003) Association of newer diastolic function parameters with age in healthy subjects: a population-based study. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 16(10):1049–1056
De Sutter J, De Backer J, Van de Veire N, Velghe A, De Buyzere M, Gillebert TC (2005) Effects of age, gender, and left ventricular mass on septal mitral annulus velocity (E′) and the ratio of transmitral early peak velocity to E′ (E/E′). Am J Cardiol 95(8):1020–3
Caballero L, Kou S, Dulgheru R, Gonjilashvili N, Athanassopoulos GD, Barone D, et al (2015) Echocardiographic reference ranges for normal cardiac Doppler data: results from the NORRE Study. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 16(9):1031–1041
Dalen H, Thorstensen A, Vatten LJ, Aase SA, Stoylen A (2010) Reference values and distribution of conventional echocardiographic Doppler measures and longitudinal tissue Doppler velocities in a population free from cardiovascular disease. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 3(5):614–622
Wierzbowska-Drabik K, Krzemińska-Pakuła M, Chrzanowski Ł, Plewka M, Waszyrowski T, Drożdż J, et al (2008) Age-Dependency of classic and new parameters of diastolic function. Echocardiography 25(2):149–155
Okura H, Takada Y, Yamabe A, Kubo T, Asawa K, Ozaki T et al (2009) Age- and gender-specific changes in the left ventricular relaxation: a Doppler echocardiographic study in healthy individuals. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging 2(1):41–46
Innelli P, Sanchez R, Marra F, Esposito R, Galderisi M (2008) The impact of aging on left ventricular longitudinal function in healthy subjects: a pulsed tissue Doppler study. Eur Heart J 9(2):241–249
McCulloch M, Zoghbi WA, Davis R, Thomas C, Dokainish H (2006) Color tissue Doppler myocardial velocities consistently underestimate spectral tissue doppler velocities: impact on calculation peak transmitral pulsed doppler velocity/early diastolic tissue doppler velocity (E/Ea). J Am Soc Echocardiogr 19(6):744–748
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Danish Council for Independent Research (DFF-4183-00499).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest
Additional information
Investigations were carried out at the Copenhagen City Heart Study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J.N., Biering-Sørensen, T., Jørgensen, P.G. et al. Left ventricular filling pressure by septal and lateral E/e′ equally predict cardiovascular events in the general population. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 33, 653–661 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-016-1052-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-016-1052-4