Abstract
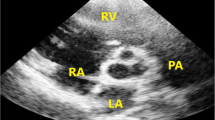
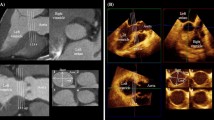
This report sought to compare live/real-time three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography (3D-TEE) with two-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography (2D-TEE) and to determine whether there are advantages to using 3D-TEE on patients with pulmonary stenosis (PS). Sixteen consecutive adult patients (50 % male and 50 % female; mean age 33 ± 13.4 years) with PS and indications of TEE were prospectively enrolled in this study. Following this, initial 2D-TEE and 3D-TEE examinations were performed, and 3D-TEE images were analyzed using an off-line Q-lab software system. Finally, the 2D-TEE and 3D-TEE findings were compared. In the present study, 3D-TEE allowed us to obtain the en face views of pulmonary valves (PVs) in all but one patient. While this patient was without a PV due to a previous tetralogy of Fallot operation, we could detect the type of PV in the other 15 (93.7 %) patients by using 3D-TEE. Due to poor image quality, the most stenotic area was not measurable in only one (6.2 %) of the patients. In eight (50 %) of the patients, severity and localization of stenosis were more precisely determined with 3DTEE than with 2D-TEE. The PVs’ maximal annulus dimensions were found to be significantly larger when they were measured using 3D modalities. This study provides evidence of the incremental value of using 3D-TEE rather than 2D-TEE during assessments of PS, specifically in cases where special conditions (pregnancy, pulmonary regurgitation, and concomitant atrial septal defects) cause recordings of the transvalvular peak gradient to be inaccurate. Therefore, 3D-TEE should be used as a complementary imaging tool to 2D-TEE during routine echocardiographic examinations.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goss CM, Gray H (1973) Valves of the heart. Gray’s anatomy of the human body, 29th edn. Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia, pp 543–544
Gross L, Kugel MA (1931) Topographic anatomy and histology of the valves in the human heart. Am J Pathol 7:445
Barry A, Patten BM (1968) The structure of the adult heart. In: Gould SE (ed) Pathology of the heart and blood vessels, 5th edn. Charles C. Thomas, Springfield, p 91
Misfeld M, Sievers HH (2007) Heart valve macro- and microstructure. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 362:1421–1436
Dominik J, Zacek P (2010) Heart valve surgery; an illustrated guide, 1st edn. Springer, Berlin, pp 40–41
Camm AJ, Lüsher TF, Serruys WP (2009) The ESC textbook of cardiovascular medicine, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, New York, p 347
Waller BF, Howard J, Fess S (1995) Pathology of pulmonic valve stenosis and pure regurgitation. Clin Cardiol 18:45–50
Popelová J, Oechslin E, Kaemmerer H, Sutton MGJ, Žácek P (2008) Congenital heart disease in adults, 1st edn. Informa Healthcare, London, pp 87–89
Armstrong WF, Ryan T (2010) Feigenbaum’s echocardiography, 7th edn. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 337–359
Baumgartner H, Hung J, Bermejo J, Chambers JB, Evangelista A, Griffin BP et al (2009) Echocardiographic assessment of valve stenosis: EAE/ASE recommendations for clinical practice. Eur J Echocardiogr 10:1–25
Baumgartner H, Bonhoeffer P, De Groot NMS, Haan F, Deanfield JE, Galie N et al (2010) ESC guidelines for the management of grown-up congenital heart disease. Eur Heart J 31:2915–2957
Hahn RT, Abraham T, Adams MS, Bruce CJ, Glas KE, Lang RM et al (2013) Guidelines for performing a comprehensive transesophageal echocardiographic examination: recommendations from the American Society of Echocardiography and the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 26:921–964
Lang RM, Badano LP, Tsang W, Adams DH, Agricola E, Buck T et al (2012) American Society of Echocardiography; European Association of Echocardiography. EAE/ASE recommendations for image acquisition and display using three-dimensional echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 25(1):3–46
Anwar AM, Soliman O, Van Den Bosch AE, McGhie JS, Geleijnse ML, Cate FL (2007) Assessment of pulmonary valve and right ventricular outflow tract with real-time three-dimensional echocardiography. Int J Cardiavasc Imaging 23:167–175
Kelly NF, Platts DG, Burstow DJ (2010) Feasibility of pulmonary valve imaging using three-dimensional transthoracic echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 23:1076–1080
Anwar AM, Nosir YF, Zainal-Abidin SK, Ajam A, Chamsi-Pasha H (2012) Real-time three dimensional transthoracic echocardiography in daily practice: initial experience. Cardiovasc Ultrasound 10:14
Ahmed MI, Escañuela MG, Crosland WA, McMahon WS, Alli OO, Nanda NC (2014) Utility of live/real time three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography in the assessment and percutaneous intervention of bioprosthetic pulmonary valve stenosis. Echocardiography 31:531–533
Waller AH, Chatzizisis YS, Moslehi JJ, Chen FY, Mangion JR (2014) Real-time three-dimensional transoesophageal echocardiography enables preoperative pulmonary valvulopathy assessment. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging 15:713
Bhattacharyya S, Burke M, Caplin ME, Davar J (2011) Utility of 3D transesophageal echocardiography for the assessment of tricuspid and pulmonary valves in carcinoid heart disease. Eur J Echocardiogr 12:E4
Cho SW, Kim BG, Kim DH, Kim BO, Goh CW, Rhee KJ et al (2014) Three-dimensional echocardiographic views of bicuspid pulmonic valve. J Cardiovasc Ultrasound 22:162–163
Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Zipes DP (2008) Braunwald’s heart disease, 8th edn. Sounders Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 1577–1580 and 1967–1968
Cuypers JA, Witsenburg M, van der Linde D, Roos-Hesselink JW (2013) Pulmonary stenosis: update on diagnosis and therapeutic options. Heart 99:339–347
Rajiah P, Nazarian J, Vogelius E, Gilkeson RC (2014) CT and MRI of pulmonary valvular abnormalities. Clin Radiol 69:630–638
Kivelitz DE, Dohmen PM, Lembcke A, Kroencke TJ, Klingebiel R, Hamm B et al (2003) Visualization of the pulmonary valve using cine MR imaging. Acta Radiol 44:172–176
Saremi F, Gera A, Ho SY, Hijazi ZM, Sánchez-Quintana D (2014) CT and MR imaging of the pulmonary valve. Radiographics 34:51–71
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (AVI 356 kb)
Supplementary material 2 (AVI 620 kb)
Supplementary material 3 (AVI 204 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kemaloğlu Öz, T., Özpamuk Karadeniz, F., Akyüz, Ş. et al. The advantages of live/real time three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography during assessments of pulmonary stenosis. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 32, 573–582 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-015-0811-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-015-0811-y